Chapters 18 & 19 Guided Reading
advertisement

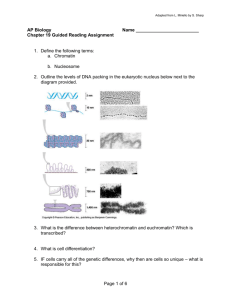
Adapted from L. Miriello by S. Sharp AP Biology Chapter 18 Guided Reading Assignment Name _________________________ 1. What kind of nucleic acids are the viral genomes made of? 2. What is the name for a protein shell enclosing the viral genome? 3. What are viral envelopes and what is their function? 4. List the full steps of the simplified viral reproductive cycle. 5. What kind of phage only reproduces by a lytic cycle? 6. How do bacteria defend themselves against phages? 7. What is the phage reproductive cycle that replicates the phage genome without destroying the host? 8. What are phages called that care capable of using both modes of reproduction? 9. What is a prophage? 10. What are retroviruses and how do they use reverse transcriptase? 11. Describe the reproductive cycle of HIV, a retrovirus. Page 1 of 4 Adapted from L. Miriello by S. Sharp 12. What are viroids? 13. Define prions. 14. What is a plasmid? 15. What is the process of alteration of a bacterial cell’s genotype by the uptake of naked, foreign DNA from the surrounding environment? 16. Define transduction. . 17. What is conjugation? 18. What is special about the F plasmid? 19. What is an episome? 20. What are R plasmids and why are these a problem to humans? 21. How does this relate to natural selection? 22. Define transposable elements. 23. What is an example of the benefit to bacteria of these transposable elements? 24. What are the two ways that metabolic control can occur within bacteria? 25. What is the key advantage of grouping genes of related function in to one transcription unit? 26. What is this “switch” called? Page 2 of 4 Adapted from L. Miriello by S. Sharp 27. Where is an operator positioned? 28. What does the operator control? 29. What is the name for the operator, promoter, and the genes they control? 30. What can happen if the trp operan is turned “on”? 31. What turns the “switch” off? 32. How does a repressor work? 33. What gene controls the making of the trp repressor protein? 34. What are the two states that the operator vacillates (switches between)? 35. How is the trp repressor protein and allosteric protein? 36. Define corepressor. 37. What are the two methods of negative gene regulation? 38. Why is the trp operan considered repressible? 39. What is the definition of an inducible operan? 40. What does the inducer do? 41. Why are repressible enzymes generally associated with anabolic pathways and how is this an advantage to the organism? 42. How does positive gene regulation work? Page 3 of 4 Adapted from L. Miriello by S. Sharp AP Biology Chapter 18 Guided Reading Assignment Name _________________________ 1. What is the difference between heterochromatin and euchromatin? Which is transcribed? 2. What is cell differentiation? 3. IF cells carry all of the genetic differences, why then are cells so unique – what is responsible for this? 4. What effect do the following have on gene expression? a. Histone acetylation b. Histone deacteylation c. DNA methylation 5. How does methylation relate to genomic imprinting? 6. Define epigenetic inheritance. 7. How do the following control elements assist in regulation? a. Transcription factors b. Enhancers c. Activators d. Repressors Page 4 of 4