Terms to know - King William County Public Schools
advertisement

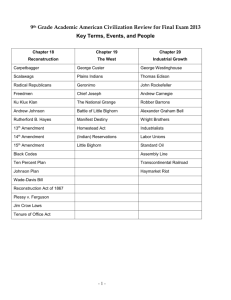
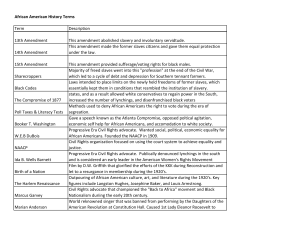
Terms to know Reconstruction a period of reuniting and rebuilding the South following the end of the Civil War Ten Percent Plan Lincoln’s Reconstruction plan, which required that 10 percent of voters in a state pledge loyalty to the United States before that state could rejoin the Union Thirteenth Amendment the amendment that made slavery illegal throughout the United States Freedmen’s Bureau an organization established by Congress to provide relief for all the South’s poor people Andrew Johnson vice president who became president upon Lincoln’s death Black Codes southern laws that greatly limited the freedom of African Americans Radical Republicans Republicans who wanted more federal control in Reconstruction Civil Rights Act of 1866 act giving African Americans the same legal rights as whites Fourteenth Amendment amendment guaranteeing citizens equal protection of laws Reconstruction Acts laws passed to protect African American rights impeachment process of bringing charges of wrongdoing against a public official Fifteenth Amendment amendment guaranteeing suffrage to African American men Hiram Revels first African American senator Ku Klux Klan secret society that used violence to oppress African Americans Compromise of 1877 agreement in which Democrats accepted Hayes’s election to the presidency in exchange for removing federal troops form the South poll tax special tax people had to pay before they could vote segregation forced separation of whites and African Americans in public places Jim Crow laws laws that enforced segregation Plessy v. Ferguson Supreme Court ruling that upheld segregation sharecropping system in which farm laborers kept some of the crop frontier an area that is undeveloped Chisholm Trail a popular route for cattle drives from San Antonio to Abilene, Kansas transcontinental railroad railroad across United States, connecting East and West Treaty of Fort Laramie first major agreement signed with northern Plains nations reservations areas of federal land set aside for Native Americans Crazy Horse Sioux leader who violently protested reservations buffalo soldiers nickname given by Indians to African American cavalry George Armstrong Custer army commander who lost to the Sioux at Little Bighorn Sitting Bull Sioux leader who defeated Custer at Little Bighorn Battle of the Little Bighorn last great victory for Sioux, in which they defeated Custer Massacre at Wounded Knee battle in which U.S. troops killed about 150 Sioux Geronimo Apache leader who continued to fight against the U.S. Army until 1886 Ghost Dance religious movement predicting a coming paradise for Native Americans Dawes General Allotment Act act that took back almost 70 percent of reservation land Homestead Act an 1862 act that gave government-owned land to farmers Exodusters African Americans who left the South for Kansas in 1879 sodbusters nickname given Great Plains farmers because of the toughness of the soil dry farming farming using hardy crops that need less water than others deflation a decrease in the money supply and overall lower prices William Jennings Bryan Democratic candidate for president in the 1888 election Populist Party new national party formed by the country’s farmers Second Industrial Revolution a period of rapid growth in U.S. manufacturing in the late 1800s Bessemer process Henry Bessemer’s invention that made steel production faster and cheaper Thomas Edison inventor who created the electric lightbulb patent an exclusive right to make or sell an invention Alexander Graham Bell inventor of the telephone Henry Ford inventor of the first affordable car and the moving assembly line Wilbur and Orville Wright brothers who made the first piloted flight in a gas-powered airplane implement to put in place corporations businesses owned by stockholders Andrew Carnegie business leader who concentrated his efforts on steel production vertical integration owning the businesses involved in each step of manufacturing John D. Rockefeller business leader who concentrated on oil refining horizontal integration owning all of the businesses in a certain field trust a legal arrangement grouping together a number of companies under a single board of directors social Darwinism belief that Charles Darwin’s theory of natural selection and “survival of the fittest” holds true for humans monopoly total ownership of a product or service Sherman Antitrust Act law that made it illegal to monopolize a business Knights of Labor large labor union that included both skilled and unskilled workers Samuel Gompers leader of the American Federation of Labor American Federation of Labor group that organized individual national unions of skilled workers collective bargaining workers acting together for better wages or working conditions Mary Harris Jones union supporter who organized strikes and educated workers Haymarket Riot a union protest in Chicago where strikers fought with police Homestead strike violent 1892 strike of Carnegie steelworkers ended by state militia Pullman strike strike of Pullman railroad workers that ended in 1894 when federal troops were sent to stop it old immigrants people who arrived from northern Europe in the mid-1800s new immigrants people who arrived from southern and eastern Europe in the late 1800s steerage an area below a ship’s deck where immigrants often traveled benevolent societies organizations that offered help to immigrant families tenements poorly built, overcrowded apartment buildings sweatshops workplaces in small shops with poor working conditions and low pay Chinese Exclusion Act law in 1880 banning immigration by Chinese people for ten years suburbs residential neighborhoods outside of downtown areas mass culture leisure and cultural activities shared by many people Joseph Pulitzer publisher of New York World newspaper William Randolph Hearst publisher of New York Journal newspaper Frederick Law Olmsted landscape architect who designed Central Park in New York Jacob Riis journalist and photographer who exposed the horrible conditions in New York City tenements settlement houses neighborhood centers in poor areas that offered education, recreation, and social activities Jane Addams founder of Hull House Hull House Chicago’s most famous settlement house political machines powerful organizations that influenced local governments Progressives reformers who wanted to solve the problems of a fast-growing society muckrakers journalists who exposed the corruption, scandal, and filth of society Seventeenth Amendment a law letting Americans vote directly for U.S. senators recall a vote to remove an official before the end of his or her term initiative procedure allowing voters to propose a new law referendum procedure permitting voters to approve or reject a law Triangle Shirtwaist Fire tragic fire that killed 146 workers capitalism system in which private businesses run most industries and competition determines how much goods cost socialism system in which government owns and operates a country’s industry Eighteenth Amendment amendment banning production and sale of alcoholic drinks National American Woman Suffrage Association group that worked for women’s voting rights, founded by Elizabeth Cady Stanton and Susan B. Anthony Nineteenth Amendment a constitutional amendment giving women the right to vote Booker T. Washington African American educator who encouraged other African Americans to improve their own lives rather than fight discrimination Ida B. Wells African American journalist who publicized lynchings in her newspaper W. E. B. Du Bois African American reformer who publicized cases of racial prejudice National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP)organization that brought attention to racial inequality Spanish American War-last less than 4 months called, “A splendid little war” –US acquired Guam, Philippines, and Puerto Rico from the Spanish- Cuba gained its independence Theodore (Teddy)Roosevelt –Rough Rider in Spanish American War vice president who became president upon McKinley’s death Pure Food and Drug Act law stopping the manufacture, sale, or transportation of mislabeled or contaminated food and drugs conservation protection of nature and its resources Progressive Party nicknamed the Bull Moose Party; formed so Roosevelt could run for President in 1912 Woodrow Wilson Democratic president who worked to regulate tariffs, banking, and Business-WWI-League of Nations -14 Points Sixteenth Amendment amendment that allows the federal government to impose direct taxes on people’s incomes imperialism the practice of building an empire by founding colonies or conquering other nations isolationism a policy of avoiding involvement in the affairs of other countries William H. Seward Secretary of State who arranged for the purchase of Alaska in 1867 spheres of influence areas where foreign nations control trade and natural resources Open Door Policy policy stating that all nations should have equal access to trade in China yellow journalism technique that exaggerates and sensationalizes news stories Teller Amendment war resolution amendment stating that the United States had no interest in taking control of Cuba *Anti-Imperialist League organization that accused the United States of building a colonial empire *Platt Amendment amendment to Cuba’s constitution that limited Cuba’s rights and kept the United States involved in Cuban affairs Panama Canal canal built in Panama that shortened the Atlantic-to-Pacific voyage Roosevelt Corollary President Theodore Roosevelt’s warning that nations in the Western Hemisphere should pay their debts and “behave” ”Big Stick” Diplomacy dollar diplomacy President William Howard Taft’s policy of influencing governments through economic intervention John J. Pershing United States general who pursued Pancho Villa through Mexico but never caught him militarism an aggressive strengthening of armed forces Archduke Francis Ferdinand the heir to the throne of Austria-Hungary who was assassinated in 1914 mobilize to prepare for military war Central Powers an alliance of Austria-Hungary and Germany at the start of the war Allied Powers an alliance among France, Russia, and Britain at the start of the war trench warfare defending a position by fighting from deep ditches stalemate a situation in which neither side can win a decisive victory U-boats submarines used by the German navy in World War I Lusitania a British passenger ship sunk by a German U-boat in 1915 Zimmerman Note a secret telegram from the German foreign minister Zimmerman to Mexico proposing an alliance against the United States Selective Service Act a law that required men between ages of 21 and 30 to register to be drafted into military service Liberty bonds bonds issued to raise billions of dollars for the Allies’ war efforts American Expeditionary Force U. S. troops sent to Europe during World War I Communists people who favor the equal distribution of wealth and the end of all forms of private property armistice a truce between opponents that ends hostilities League of Nations an international assembly of nations to settle disputes between countries and encourage democracy reparations payments for war damages Treaty of Versailles a final peace settlement of World War I Teapot Dome scandal the acceptance of bribes by Secretary of the Interior Albert Fall in exchange for control of government oil reserves Kellogg-Briand Pact an unenforceable agreement among 62 nations to outlaw war Model T a low-cost automobile invented by Ford moving assembly line a production system that moves parts between groups of workers Herbert Hoover a president elected in 1928 with promises for more prosperity flappers young women in the 1920s who challenged traditional women’s roles Red Scare a period of fear of Communists and radicals in the United States Twenty-first Amendment a Constitutional Amendment that repealed prohibition Scopes trial the trial of John Scopes for teaching evolution in school Great Migration the movement of African Americans to northern cities Marcus Garvey a black leader who encouraged an independent black economy talkie motion picture with sound Jazz Age name given to the 1920s due to the popularity of jazz music Harlem Renaissance period of African American artistic accomplishment in New York City Langston Hughes poet and writer who wrote about African American life Lost Generation writers in the 1920s who criticized American society expatriates people who live outside their home country Georgia O’Keeffe innovative artist famous for her detailed drawings of flowers buying on margin purchasing stocks with borrowed money Black Tuesday Tuesday, October 29, 1929, the day of the stock market crash business cycle up-and-down pattern of business production and unemployment Great Depression severe, economic depression that followed the stock crash of 1929 Bonus Army unemployed World War I veterans who camped in Washington D.C. to demand early payment of military bonuses Franklin D. Roosevelt New York governor elected president in the 1932 election New Deal programs developed by Roosevelt and Congress to aid economic recovery fireside chats radio addresses in which Roosevelt spoke directly to the public Tennessee Valley Authority New Deal program to build dams to provide electricity in the Tennessee River valley Frances Perkins Roosevelt’s Secretary of Labor, the first female cabinet member Eleanor Roosevelt First Lady in Roosevelt administration who supported New Deal Social Security Act federal law that started programs to ensure economic well-being of citizens who could not provide for themselves sit-down strike strategy in which striking workers remained inside the workplace Dust Bowl region of the Great Plains affected by extreme drought and dust storms Mary McLeod Bethune African American educator appointed as an adviser by President Roosevelt John Steinbeck novelist who wrote about the hardships of the Great Depression Woody Guthrie Depression-era folksinger from Oklahoma totalitarianism political system in which the government controls every aspect of citizens’ lives. Benito Mussolini fascist Italian dictator who ruled from 1922 to 1944 fascism political system headed by a strong leader in which the state is more important than the individual Adolf Hitler politician and World War I veteran who took advantage of public anger to become chancellor of Germany in 1933 Nazis National Socialist Party members who controlled Germany from 1933 to 1945 Joseph Stalin Communist dictator of the Soviet Union who gained control in 1928 Axis Powers World War II alliance of Germany, Italy, and Japan appeasement policy of avoiding war by giving in to demands Winston Churchill British prime minister during World War II Allied Powers alliance between Great Britain and France in 1939, and later, the Soviet Union and the United States Lend-Lease Act law allowing the president to aid any nation vital to U. S. defense Pearl Harbor American naval base in Hawaii attacked by Japan on December 7, 1941 War Production Board board created to oversee the conversion of factories to war production A. Philip Randolph African American labor leader who protested unfair treatment in factories Tuskegee Airmen African American pilots who trained in Tuskegee, Alabama Benjamin O. Davis group leader of Tuskegee Airmen and later the first African American general in the U. S. Air Force zoot-suit riots Los Angeles riots in which white mobs attacked Mexican Americans internment forced relocation and imprisonment of Japanese Americans during WWII Battle of El Alamein battle in which Montgomery’s British troops stopped Rommel’s Afrika Korps in North Africa in November 1942 Dwight D. Eisenhower American general who commanded Allied forces in Europe; later elected U.S. president Battle of Stalingrad key battle in which Soviets stopped German advance in winter of 1942–1943 D-Day date of Allied sea invasion of occupied France—June 6, 1944 Douglas MacArthur general who commanded U.S. ground troops in the Pacific Battle of Midway key Pacific battle in which Japanese navy was severely weakened island hopping strategy of attacking only key Pacific islands kamikaze tactic of purposely crashing piloted planes into enemy ships Battle of the Bulge key battle at the Ardennes forest; Allies were victorious after an initially successful German attack Harry S. Truman vice president who became president when Roosevelt died in 1945 Holocaust Nazi program of mass murder against the Jewish people genocide extermination of an entire group of people Manhattan Project secret American research program to develop the atomic bomb atomic bomb weapon that produces tremendous power by splitting atoms Yalta Conference meeting of Roosevelt, Churchill, and Stalin to agree on postwar strategies Nuremberg trials postwar trial of Nazi leaders for war crimes United Nations organization of nations dedicated to finding peaceful solutions to international conflicts Cold War long struggle between the United States and Soviet Union for global power containment policy of preventing the Soviet Union from expanding its influence Truman Doctrine policy of providing aid to help countries fight communism Marshall Plan U.S. grants and loans to fund European recovery from World War II North Atlantic Treaty Organization mutual defense alliance of United States, Canada, Iceland, and nine Western European nations GI Bill of Rights laws to help returning veterans readjust after the war Fair Deal domestic programs and civil rights protections proposed by Truman Mao Zedong Communist leader who established the People’s Republic of China 38th parallel line that marked the division between North Korea and South Korea Joseph McCarthy Wisconsin senator who made charges of communism in the government and the military hydrogen bomb nuclear weapon far more powerful than the atomic bomb arms race rush by the United States and the Soviet Union to build more weapons Sputnik world’s first artificial satellite, launched by the Soviet Union in 1957 brinkmanship willingness to go to the brink of war to stop communism baby boom a significant increase in the number of babies born urban renewal programs to improve services and housing in deteriorating cities Thurgood Marshall attorney and first African American Supreme Court justice Brown v. Board of Education lawsuit challenging the segregation of public schools Little Rock Nine first black students to attend a school forced to integrate in Little Rock, Arkansas Rosa Parks African American woman who refused to give up her seat on a public bus to a white passenger Montgomery bus boycott nonviolent protest of segregation in public transportation Martin Luther King Jr. civil rights leader who inspired nonviolent protests against discrimination sit-in demonstration in which protestors sit down and refuse to leave Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee student activists who organized nonviolent civil rights protests and voter registration drives John F. Kennedy U.S. president elected in 1960 Freedom Rides a series of protests in which black and white passengers tried to integrate Southern bus stations March on Washington massive civil rights demonstration in Washington, D.C. in 1963 Lyndon B. Johnson U.S. president after Kennedy was assassinated Civil Rights Act of 1964 law banning segregation in public places and workplace discrimination Voting Rights Act of 1965 law protecting African Americans’ voting rights Great Society Johnson’s program to end poverty and racial injustice Black Power movement that called for African American power and independence Malcolm X leader who combined ideas about independence with teachings of Islam National Organization for Women organization to fight for opportunities for women Shirley Chisholm first African American woman elected to U.S. Congress Equal Rights Amendment constitutional amendment to outlaw all discrimination based on gender American Indian Movement group formed in 1968 to fight for Native American rights Disabled in Action activist organization for rights of disabled people Peace Corps program that sent volunteers to developing countries to help with projects such as digging wells and building schools Fidel Castro Cuban rebel leader who led a revolution and established a Communist government Berlin Wall Cold War barrier that separated the city of Berlin, Germany into two parts Cuban missile crisis attempt by Soviet Union to send nuclear missiles to Cuba followed by American blockade Neil Armstrong American astronaut; the first man to walk on the moon Edwin “Buzz” Aldrin crewmate of Neil Armstrong; second man to walk on the moon Ho Chi Minh leader of Communist revolution against the French in Vietnam domino theory concern that if one nation became Communist, nearby nations would follow Vietcong guerrilla fighters opposed to the South Vietnamese government Tonkin Gulf Resolution Congressional action that gave military authority to President Johnson Ho Chi Minh Trail paths and tunnels used as a supply route by the North Vietnamese Tet Offensive series of coordinated surprise attacks launched by the Vietcong and North Vietnamese on the Vietnamese New Year (Tet)—January 30, 1968 doves opponents of the war who felt money would be better spent on domestic programs hawks supporters of the war who felt that winning the Cold War was the top priority Students for a Democratic Society student group active in protesting the Vietnam War hippies people who “dropped out” of mainstream society and built a counterculture during the 1960s Richard M. Nixon Republican president elected in 1968 Henry Kissinger national security adviser to President Nixon Vietnamization strategy of having the South Vietnamese army take over the fighting Twenty-sixth Amendment constitutional amendment lowering the voting age to 18 Vietnam Veterans Memorial granite wall in Washington, D.C. listing names of soldiers killed and missing in Vietnam Strategic Arms Limitation Talks agreements between the United States and the Soviet Union limiting nuclear weapons détente period of less hostile relations between United States and Soviet Union Watergate scandal involving the planning and coverup of a burglary by the Nixon Administration Gerald Ford vice president who became president when Nixon resigned in 1974 pardon order granting freedom from punishment affirmative action practice of giving special consideration to nonwhites or women to make up for past discrimination human rights basic rights and freedoms of all people deficit amount by which a government’s spending exceeds its income Iran-Contra affair controversial plan for the United States to sell missiles to Iran and give the profits to Nicaraguan rebels known as Contras Mikhail Gorbachev Soviet leader who initiated changes in government policies and new freedoms for Soviet people Saddam Hussein Iraqi dictator Operation Desert Storm U.S.-led coalition offensive to drive Iraqi troops from Kuwait Colin Powell former chairman of the joint chiefs of staff and highest ranking African American to serve in the U.S. military; later served as Secretary of State North American Free Trade Agreement treaty to end trade barriers between the United States, Canada, and Mexico terrorism use of violence by individuals or small groups to advance political goals Al Gore Bill Clinton’s vice president; Democratic presidential nominee in 2000 George W. Bush U.S. president elected in 2000 World Trade Center important business center in New York City Pentagon headquarters of the U.S. Department of Defense, near Washington, D.C. al Qaeda fundamentalist Islamic terrorist group Osama bin Laden wealthy Saudi exile who led al Qaeda weapons of mass destruction chemical, biological, and nuclear weapons capable of killing thousands of people service economy most workers have jobs providing services rather than producing goods globalization growing connections between economies and cultures worldwide Internet global system of computer networks Information Revolution changes that made it easier and faster for people to access and share information AIDS acquired immune deficiency syndrome; disease that causes the body’s immune system to shut down ozone layer thin layer of gas in the upper atmosphere that blocks harmful rays from the sun global warming increase in Earth’s temperature End-of-Year Test 1. d 12. b 2. d 13. b 3. b 14. c 4. b 15. d 5. d 16. d 6. a 17. d 7. a 18. b 8. b 19. b 9. b 20. a 10. a 21. a 11. d 22. a