The Seasons on Earth
advertisement

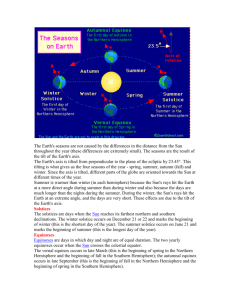
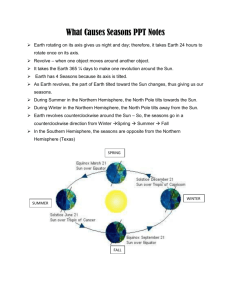
The Seasons on Earth Most places on Earth have 4 distinct seasons: ____________, _____________, ___________, __________ I. How Sunlight Hits Earth a. Sunlight hits Earth surface most directly at the _________, and at a steep angle near the _______ i. That is why it is warmer near the _______________ b. Earth has seasons because its axis is ___________ (23.5˚) as it revolves around the __________ i. Summer and winter are caused by Earth’s ________ as it revolves around the sun ii. The change in __________ is not caused by __________ in Earth’s distance from the sun iii. Earth is farthest from the sun when it is summer in the _________________ Hemisphere II. The Seasons (diagram) a. June Solstice i. The ___________ end of Earth’s axis is tilted toward the sun ii. It is summer in the _____________ Hemisphere and winter in the _____________ Hemisphere b. December Solstice i. The ___________ end of Earth’s axis is tilted toward the sun ii. It is summer in the ___________ Hemisphere and winter in the ___________ Hemisphere c. March & September Equinox i. Neither end of Earth’s axis is ___________ toward the sun ii. Both ________________ receive the same amount of ______________ III. The Earth In a. June - the northern end of Earth is tilted toward the sun i. Northern Hemisphere has more hours of ________________ than _________________ ii. Summer in the Northern Hemisphere iii. Opposite for Southern Hemisphere b. December – the southern end of earth is tilted toward the sun i. Northern Hemisphere has fewer hours of ______________ ii. Winter in the Northern Hemisphere OVER IV. Solstices and Equinoxes a. June 21 – summer solstice for Northern Hemisphere b. December 21 – winter solstice for Northern Hemisphere c. March 21 – spring (vernal) equinox for Northern Hemisphere; ______ hours of day & night everywhere d. September 22 – autumnal equinox for Northern Hemisphere; ______ hours of day & night everywhere i. The word “equinox” means __________ ____________