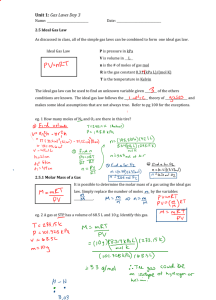
ENTHALPY
advertisement

SCH 3U1 Unit 4: Assignment 2 – Problems on Gases and Moles ( not at STP) PV = nRT (finding V with n) PV = (m/mm)RT (finding V with m ) PVmm = mRT (finding any of the variables) 1 psi=6.89 kPa , 1 tonne = 1000 kg 1. Calculate the volume @ 150 kPa & 60 °C of (a) 0.15 mol F2 (g) & (b) 0.15 mol CO2 (g). 2. Calculate the volume @ 80 kPa & -54 °C of (a) 6.4 g O2 (g) & (b) 6.4 g of SO2 (g) 3. Acetylene , C2H2 , is stored in a 45 L cylinder at 20°C and 1500 psi pressure. Calculate the mass of acetylene in the cylinder. 4. Two ten gallon containers stand beside each other on a truck . Each contains gas at a pressure of 50 psi. The first container is filled with hydrogen ; the fifty zillion molecules have a mass of 10 oz. The other container contains carbon dioxide. a) How many carbon dioxide molecules are in the container ? b) What is the mass of the carbon dioxide in the second container ? .......................................... .......................................... 5. Oxygen is stored in a 6500 L cylinder outside a hospital at 15 °C . The mass of oxygen in the tank is 1.44 t. Calculate the pressure inside the cylinder 6. Calculate (a) the # of moles (b) the mass and (c) the volume at RTP of 1.20 x 1023 molecules of (i) hydrogen gas and (ii) sulfur hexafluoride gas . 7. A sample of NO2 gas has a mass of 2.3 g at 23°C , and 101.9 kPa . Calculate: a) # of moles of gas present (b) the volume this gas will occupy and c) the number of molecules of gas 8. Do questions 21 & 24 on pg 500 in your text 9. Hydrogen is stored in a 0.50 L cylinder at 27°C and 3000 kPa . All the hydrogen is pumped into a balloon at 120 kPa. Calculate the volume of this balloon at 15°C. 10. The density of a substance is defined as the ratio of its mass to its volume or Den = mass / volume. On an earlier assignment you found the density of CO2 at STP where the volume of the gas was known to be 22.4 L or 22400 mL a) Now calculate the density of CO2 in a gas cylinder with a pressure @ 12 000 kPa & 22°C. (see pg 492) HINT: find the volume 1 mole of this gas would occupy at this temp & pressure b) the density of acetylene gas in a welding torch (C2H2 ) @ 26500 kPa & 18°C c) the density of chlorine gas at -50 °C and 800 kPa 11. The molar mass of a gas may be found by finding the mass of a known volume of it at a measured temperature and pressure. At 99.1 kPa , 21°C , a 450 mL flask of an unknown gas was taken to the balance. The following results were obtained mass of evacuated flask = 102.052 g mass of flask containing unknown gas = 102.855 g Calculate the molar mass of the gas and identify it. 12. The molar mass of a volatile liquid can be found by boiling the liquid in a flask until all has been converted into vapour. To minimize the amount of air entering the flask and displacing the vapour , the flask is usually capped with aluminum foil, with a small hole in it to allow the liquid's vapour to escape until the pressure inside is the same as the atmospheric pressure. The flask is then cooled, and the mass found. The following results were obtained in such an experiment: mass of flask and foil cap = 77.62 g temperature = 100 °C mass of flask, cap and condensed liquid= 78.15 g atmospheric pressure = 101.6 kPa volume of flask = 143.2 mL Calculate the molar mass of the volatile liquid. This liquid is a chlorinated hydrocarbon molecule with 3 carbons. Draw an appropriate structural diagram for this molecule.