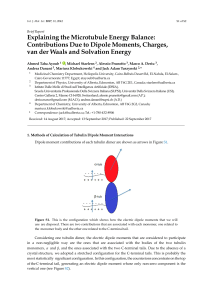
Microtubules (MTs) are key players in neuronal function, involved in
advertisement

Tubulin tyrosination: a regulator of +TIPs and of microtubule stability Microtubules (MTs) are key players in various cellular functions including mitosis, morphogenesis and differentiation. Tubulin, the basic block of MTs, is subject to specific post-translational modifications that principally affect the C-terminus of the -subunit. One of these modifications known as the tyrosination cycle involves the cyclic removal of the C-terminal tyrosine residue of the tubulin chain by a tubulin carboxypeptidase (TCP) and the addition of a tyrosine residue at the same site by the tubulin-tyrosine-ligase (TTL). The tyrosination cycle is highly conserved among eukaryotes and generates two pools of tubulin: Tyr-Tubulin and deTyr-Tubulin. Initially we showed that TTL behaves as a potential tumor suppressor, being frequently suppressed during tumor progression1. Using the yeast system Saccharomyces cerevisiae we found that the Tyr-tubulin is required for the interaction of Bik1p (ortholog of CLIP170) with microtubule + ends and thus for correct nuclear oscillations2. In mammalian cells, we demonstrated that the C-terminal Tyrosine residue of alpha tubulin is crucial for microtubules interaction with two classes of molecules: the + end binding proteins of the CLIP family and the depolymerising motors of the Kin 13 family3. In the absence of TyrTubulin, the interaction between MTs and these two classes of effectors is impaired and results both in 1/an abnormal cross talk between microtubules + ends and the cell cortex 2/an abnormal MT stability. The cellular phenotypes associated with the removal of TTL include anomalies in the control of spindle positioning which may promote tumour progression and in aberrant neuronal morphogenesis4. Complete comprehension of the cellular significance of tubulin tyrosination/detyrosination cycle will rely on the identification and the characterisation of the tubulin carboxypeptidase (TCP). 1 2 3 4 A. Mialhe, L. Lafanechere, I. Treilleux et al., Cancer research 61 (13), 5024 (2001); L. Lafanechere, C. CourtayCahen, T. Kawakami et al., Journal of cell science 111 ( Pt 2), 171 (1998). A. C. Badin-Larcon, C. Boscheron, J. M. Soleilhac et al., Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 101 (15), 5577 (2004). L. Peris, M. Wagenbach, L. Lafanechere et al., The Journal of cell biology 185 (7), 1159 (2009); L. Peris, M. Thery, J. Faure et al., The Journal of cell biology 174 (6), 839 (2006). C. Erck, L. Peris, A. Andrieux et al., Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (2005).




![Anti-beta I Tubulin antibody [SAP.4G5] ab11312 Product datasheet 5 References 1 Image](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/012748402_1-47f3955b9ea53d18884c656b66c9a770-300x300.png)