Ch2__notes_2
advertisement

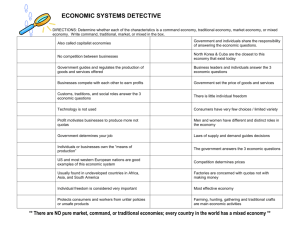
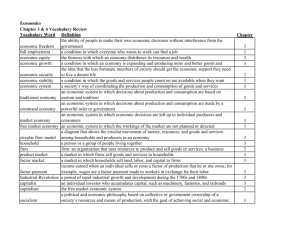
Economic Systems The method used by a society to produce and distribute goods and services! Because resources are so scarce societies and nations have to answer some hard questions. 3 main Questions What goods and services should be produced? How do we decide? How they should be produced? Who consumes these goods and services? Who is it for? How is it divided up? Answer these three questions General Economic Goals Economic systems try to Address Economic Efficiency Try to maximize what they get for the resources they have to work with Create a CD instead of making records Product that will reach consumers Economic Freedom Freedom from the government in production and distribution of goods and services Economic Security and Predictability Goods and services will be available (Milk at the store) o Taken care of in times of need Government plays as a safety net taking care of people (lost jobs, injured, and disasters.) Economic Equity Equal payment for equal work (People make different amounts for different jobs) Economies and Values ☻Traditional Economies Traditional economy -rely on customs, rituals to decide what to produce. No changing Usually small and tight knit Don’t deal well with change ☻Market Economies Decisions are made by individuals Based on exchange or trade Free markets/capitalism ☻Command Economies Centrally planned economy Gov’t decides what to produce and how much Command economies ☻Mixed Economies Combination of both Limited gov’t involvement What is self-interest? ☻it motivates the market Why do the markets exist? ☻Specialization ☻Buying and selling Free Market Economy -voluntary exchanges in markets -money and products Individuals and Markets ☺Households –People living in the same residence --controls/ownes the 3 factors of productions ☺Firm—Organization that uses resources to build and sell goods. Factor Market ☺firms buy factors of production from households and then in turn produces goods. Product Market Self Regulating nature of the Market Self-interest Own personal gain What are our motivating forces? Incentives Hope of reward or fear of punishment that encourages a person to act a certain way Competition The struggle between producers for consumer dollars The Invisible Hand Self-interest and competition work together to regulate the marketplace. Adam Smith explained the market place using this theory. Advantages of the Free Market 1. Economic Efficiency a. Producers make only what consumers want b. When and at a price that they will pay 2. Economic Freedom a. Workers work where they want b. Producer what they want c. Consume what they want 3. 4. Economic Growth/New Ideas Additional Goals a. Wide variety of goods/services b. Consumer sovereignty c. Consumers decide what is produced The Free Market Why do markets exist? What is self-interest? It motivates the market Free market Economy Voluntary exchanges in markets Exchange money and products In the market there are: Specialization Buying and selling Who is involved? Individuals and Markets o Households- People living in the same residence Control/owns the 3 factors of production o Firms- Organization that uses resources to build and sell goods Flow of the market: -Firms buy from households and then in turn produce goods. The market self regulates itself by: Self-interest o Own personal gain o What are our motivating forces? Incentives o Hope of rewards or fear of punishment Competition o The struggle between producers for consumer dollars Advantages of the free market 1. Economic Efficiency a. Producers make only what consumers want 2. Economic Freedom a. Workers work where they want b. Producers produce how they want c. Consumers buy what they want