F.3 Exercise on Heat Capacity & Specific Heat Capacity
advertisement
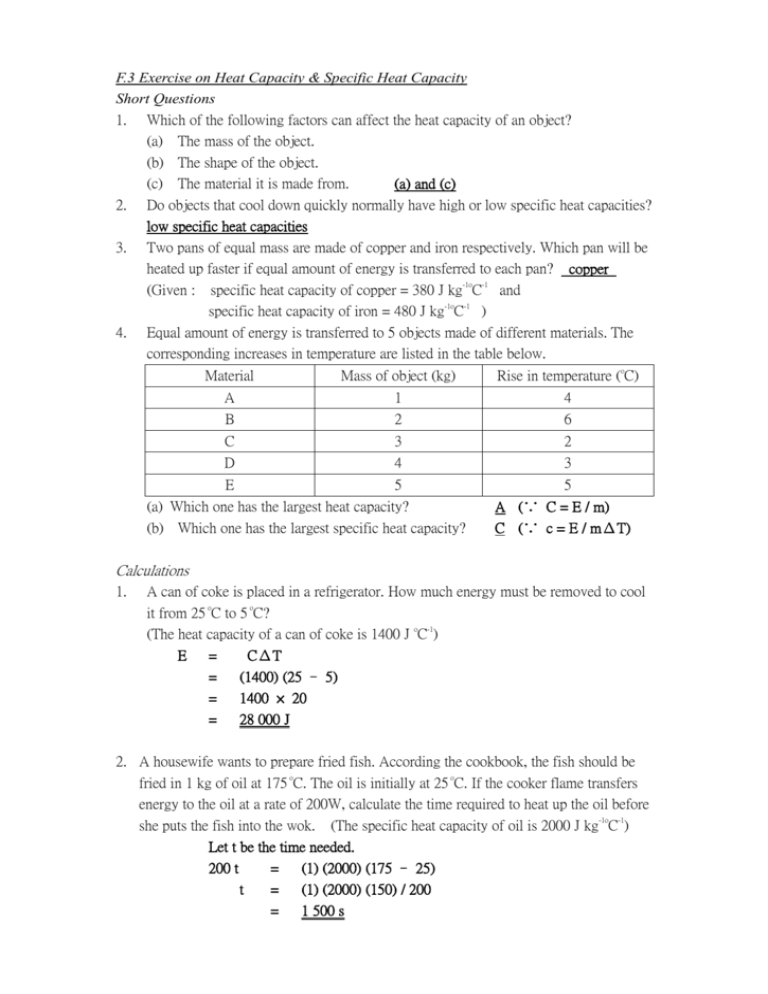
F.3 Exercise on Heat Capacity & Specific Heat Capacity Short Questions 1. Which of the following factors can affect the heat capacity of an object? (a) The mass of the object. (b) The shape of the object. (c) The material it is made from. (a) and (c) 2. Do objects that cool down quickly normally have high or low specific heat capacities? low specific heat capacities 3. Two pans of equal mass are made of copper and iron respectively. Which pan will be heated up faster if equal amount of energy is transferred to each pan? copper (Given : specific heat capacity of copper = 380 J kg-1oC-1 and specific heat capacity of iron = 480 J kg-1oC-1 ) 4. Equal amount of energy is transferred to 5 objects made of different materials. The corresponding increases in temperature are listed in the table below. Material Mass of object (kg) Rise in temperature (oC) A 1 4 B 2 6 C 3 2 D 4 3 E 5 5 (a) Which one has the largest heat capacity? A (∵ C = E / m) (b) Which one has the largest specific heat capacity? C (∵ c = E / mΔT) Calculations 1. A can of coke is placed in a refrigerator. How much energy must be removed to cool it from 25 oC to 5 oC? (The heat capacity of a can of coke is 1400 J oC-1) E = CΔT = (1400) (25 – 5) = 1400 × 20 = 28 000 J 2. A housewife wants to prepare fried fish. According the cookbook, the fish should be fried in 1 kg of oil at 175 oC. The oil is initially at 25 oC. If the cooker flame transfers energy to the oil at a rate of 200W, calculate the time required to heat up the oil before she puts the fish into the wok. (The specific heat capacity of oil is 2000 J kg-1oC-1) Let t be the time needed. 200 t = (1) (2000) (175 – 25) t = (1) (2000) (150) / 200 = 1 500 s











