Course Outline
advertisement

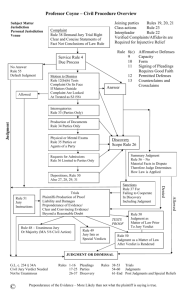
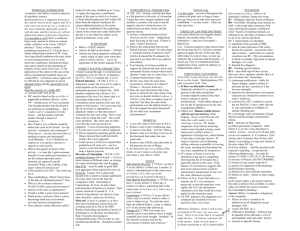
Chap. 2: Jurisdiction, Venue and Conflict of Laws A. Subject Matter Jurisdiction Jurisdictional Classifications Reclassification B. Jurisdiction Over Persons Service of Process 1. Individuals 2. Corporations 3. General and Special Appearances C. Venue 1. P’s options 2. D’s options D. Conflict of Laws Torts Contracts Chap. 3: Pleadings and Joinder A. Complaint 1. Special Filing Requirements 2. Categories of Complaint (a) Terminology (b) Form Pleadings (c) Subscription and Verification 3. Notice v. Fact Pleading 4. Demand for Judgment (a) Statement of Damages (b) Pleading Punitive Damages 5. Economic Litigation Procedure B. Responses 1. General Demurrer 2. Special Demurrer 3. Motion to Strike 4. Judgment on the Pleadings 5. Motion Practice C. Answer 1. General and Specific 2. Affirmative Defenses D. Amendments 1. General Practice 2. Relation Back 1 E. Truth In Pleading 1. Frivolous Pleadings 2. Anti-SLAPP Motions (a) Basic Rule (b) Pub Int & Comm Speech Exceptions (c) Conflict with Federal Law? G. Special Joinder Devices Class Action: (1) governing law at cert. hrg (2) aggregation permitted (3) fed 1367 SMJ Chap. 4: Discovery A. Discovery Philosophy 1. Fed: Initial Core Disclosures Cal: Limited Case Questionnaire 2. Fed: Restore status quo + deterrence (punishment) orientation Cal: Restore status quo B. Scope of Discovery 1. Informal Discovery 2. Relevance and Admissibility 3. Protection From Discovery (a) Privacy (b) Privilege (c) Work Product 4. Waiver C. Discovery Devices (PRIDE & all responses verified) 1. Interrogatory Practice 2. Deposition Practice Designated deponent (corp) 3. Physical and Mental Examinations Elements: In Contro + Good cause (exam circumstances) 4. Production of Documents and Things 5. Requests for Admission Other devices: cast wide net; RFA’s take matters out of issue Unanswered/untimely answer—Fed: Deemed admitted Cal: Motion required 6. Continuing Discovery—Fed: yes (core disc); Cal: No (may re-ask pre-trial) 7. Electronic Discovery—ordinary circumstances: Cal & Fed = responding party —costly translations: Cal = cost shift to demanding party D. Experts Exchange Requirements in both systems (eg, substance of testimony) Fed = core disc & Cal = 2034 exchange 2 E. Systemic Oversight 1. Meet and Confer Requirement 2. Discovery Sanctions 3. Protective Orders 4. Discovery Completion 5. Punitive Damages Chap. 5: Disposition Without Trial A. Arbitration 1. Contractual Arbitration (a) no general public policy exception (i) past: arb error facts/law no basis for review (ii) Fall ’08: if parties expressly agree to judicial reviewability on this ground Fed: contrary & FAA may ultimately pre-empt (b) waiver generally unlikely 2. Judicial Arbitration (not binding, full discovery, 998 consequences if nix award) B. Mediation 1. Statutory Regime 2. Confidentiality C. Case Management 1. Delay Reduction (60 day floor for srvc all Ds) 2. Sanctions (don’t visit sins of atty on client) D. Dismissal 1. Voluntary Dismissal (“until trial commences” v. inevitable disposition) 2. Involuntary Dismissal (a) Failure to Prosecute (whiteboard chart) (b) Other Involuntary Dismissals E. Default Judgment (two types of default & when need Statement of Damages) F. Settlement 1. General Procedure (664.6 motion retain jurisdiction) 2. Settlement Planning (a) Good Faith Settlement Hearing (avoids Suit #2 re dismissed D for contribute (b) Insolvent Defendants (econ v. non-econ effect Prop 51 when insolvent D) 3. Offer of Judgment (a) Statutory Regime (differs from ordinary cost & expert wit fee result) (b) Judicial Applications -- token offer & refused Jud Arb award consequence -- CA both parties; Fed only D 3 G. Summary Judgment 1. Statutory Regime (same as fed) 2. Required Burden (CA requires actually showing of lack evid in record) H. Reconsideration (party = not unless new facts/law; judge = yes + notice/opportunity) Chap. 6: Trial A. Obtaining Trial by Jury 1. Right to Trial by Jury (unlike arbitration, can’t agree in advance to waive) 2. Jury Venire Bergner/Duran/Wheeler: (1) cognizable group; (2) underrepresented; (3) systematic exclu. 3. Petit Jury: cause = unlimited peremptory = 6 per side & strikes not suspect categories (race + gender + sex orientation in CA) B. Advising the Jury Instructions on the Law: properly stated law (form instructions normally ok) C. Verdicts (3/4ths in CA) D. Judicial Control of the Jury 1. Nonsuit (delayed demurrer) 2. Directed Verdict (pre-submit to jury & required for fed 50b motion for jmt) 3. Judgment Notwithstanding Verdict (post-verdict) 4. Motion for a New Trial (miscarriage of justice CA standard) Punitive Damage Awards (bifurcated trial + double–digit flag) E. Relief From Judgment Relief on Grounds of Mistake Mandatory & discretionary 473 motions Chap. 7: Securing and Enforcing Judgments A. Provisional Remedies 1. Attachment for Security (as opposed to jurisdictional attachment) 2. Temporary Restraining Orders and Preliminary Injunctions (timing & elements) B. Enforcement of Judgments and Orders 1. Levy & Execution 2. Contempt of Court C. Costs and Attorney’s Fees 1. Costs (prevailing party) 2. Attorney's Fees (not shift, unless agreement or statute) \ \ \ 4 Chap. 8: Appellate Review A. Right to Appeal (904.1 shopping list) B. Writ (usually discretionary) C. Other Requirements for Appellate Review Timely Notice of Appeal (60 days from entry—max 180) D. Prejudicial v. Harmless Error F. Appellate Sanctions (~ trial level for frivolous appeal/response) Chap. 9: Prior Adjudication A. Stare Decisis 1. Binding v. Persuasive Precedent 2. Retroactivity 3. Law of the Case Doctrine (intra-suit res jud, b/c Appeal I binds where Appeal II) B. Res Judicata 1. Claim Preclusion (CA = “primary rights” jurisdiction, chocked full of holes) 2. Issue Preclusion (same as fed course) 5