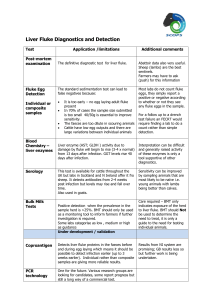
Fluke Corporation BBUS 340C – WTR 2011 I. Executive Summary
advertisement

Fluke Corporation BBUS 340C – WTR 2011 I. Executive Summary WRITE ME! II. Table of Contents I. Executive Summary II. Table of Contents III. Company Overview a. Products and Customers b. Mission and Vision c. Competitors d. Business Statistics IV. Operations Strategy V. Key Area of Focus: Lean Manufacturing a. Pull System b. Cell Manufacturing c. Just-In-Time d. Kaizen e. Quality f. 5S g. Product Process i. Process Structure in Services ii. Process Structure in Manufacturing VI. Recommendations VII. Conclusions VIII. Appendix IX. References 1 III. Company Overview The Fluke Corporation, a manufacturer of industrial testing equipment, was founded in 1948 by John Fluke, Sr. ___________________________________ The company is headquartered in Everett, WA, and __________________. It boasts manufacturing centers on three continents with sales and service subsidiaries in Europe, North America, South America, Asia and Australia. Fluke Corporation has authorized distributor and manufacturer representative channels in more than 100 countries and employs approximately 2,400 people. A. Products and Customers Fluke Corporation consists of three divisions: Fluke Calibration, Fluke Networks, and Fluke Biomedical. Fluke Calibration offers a broad array of electrical, temperature, pressure and flow, rf and power calibrators and standards. It produces waveform generators, calibration software products, and support equipment – provide exacting standards for companies and government organizations who rely on tightly calibrated instruments for their quality and standards programs. Industrial/electronic service installation and maintenance, electrical and temperature, indoor air quality… Fluke Networks “offers network professionals solutions that span network deployment, network performance management and troubleshooting, as well as security and performance monitoring.” Fluke Networks provides innovative solutions for the installation and certification, testing, monitoring and analysis of copper, fiber, and wireless networks used by enterprises and telecommunications carriers. The company’s award-winning solutions provide network installers, owners, and maintainers with supervision, combining speed, accuracy, and ease of use to optimize network performance. (600emps, 50 counties, used by 98 of the Fortune 100 companies) Fluke Biomedical leads the world in the manufacture of biomedical test and simulation products, including electrical safety testers, patient simulators, performance analyzers, and fully-integrated and automated performance testing and documentation systems – asdasdasdasdsd. Fluke Biomedical also provides some of the most trusted and accurate diagnostic imaging, radiation safety, and oncology quality-assurance solutions for regulatory compliance. Fluke Biomedical customers include medical device manufacturers, 2 biomedical professionals, physicists, field service, and other medical personnel who must meet increasing regulatory guidelines, higher quality standards, and rapid technological growth while performing their work faster and more efficiently than ever. Typical customers and users include technicians, engineers, metrologists, medical-device manufacturers, and computer network professionals — people who stake their reputations on their tools, and use tools to help extend their personal power and abilities. B. Mission and Vision The company’s mission is “to delight and empower customers with robust, intuitive tools to help them quickly solve their toughest problems”. Its vision is to be “the world leader in the manufacture, distribution and service of electronic test tools and software”. C. Competition The company has maintained the largest market share in the industry, and considers itself to be “the industry standard”, though it does have some competition. First, there is Agilent Technologies, Inc., based out of Santa Clara, CA… Diehl Stiftung & Co. KG, based out of Germany, is a diverse industrial company that focuses on defense, aerospace, metal, and controls…. AMETEK, Inc. (PA); Itron, Inc. (WA); Hexagon AB (Sweden) D. Business Statistics Though Fluke Corporation does face competition in its industry, is has undoubtedly become the forerunner and market leader for industrial testing equipment. Fluke Corporation is a world well known electronic test and measurement manufacturer and a subsidiary of Danaher Corporation. Its main manufacturing plants sited in the USA, the UK, Asia and The Netherlands. Fluke has about 2,400 employees and more than 100 countries have its distributor channels worldwide (Fluke, 2011). Its major markets are United States, Europe, and Asia. Fluke total sales in 2010 are 54% from North America, 20% from Europe, 20% from Asia/Australia, and 6% from other regions (Danaher, 2011). In 2010, its parent company Danaher’s sales are $13,202,602; it increases $2,017,664, or 18% compare to 2009. See Fig 1 in appendix. E. Strategy 3 The success of the company, many argue, can be credited to its parent company, the Danaher Company, who acquired Fluke Corporation in 1998. This management company is driven by a ___________ called the Danaher Business System, or DBS. The DBS ________, promotes ______, and emphasizes ________. The DBS is fueled by a simple philosophy rooted in four customer-oriented priorities: quality, delivery, cost, and innovation. In line with these priorities, the company seeks kaizen, or continuous improvement, __________________________. (DBS) “The Fluke brand has a reputation for portability, ruggedness, safety, ease of use and rigid standards of quality.” Team-oriented, non-political; Strategic plan is based on the voice-of-the-customer; Never-ending cycle of change and improvement; Customer-facing priorities: quality, delivery, cost, innovation. II. Operations Strategy To fulfill its corporate mission and implement its corporate strategy, Fluke employs its parent company’s Danaher Business System (DBS) into its operation strategies. DBS focus on lean manufacturing that maximize throughput with smallest amount of inventory. The main concept of DBS is “continuous improvement (kaizen)” and to “eliminate waste in every facet of business processes” (Danaher, 2011). With the usage of lean concepts and techniques, Fluke is able to increase its productivity dramatically from 9% to about 40% after the acquisition by Danaher in 1998. Just-In-Time system (JIT) is one of the lean methods Fluke exploits in its production. By using JIT system, Fluke can maintain its production process efficiently while eliminate unnecessary wastes such as waiting time during the production process, unsuitable processing, overproduce inventory, etc. Fluke also implement pull strategy in its work flows, in which it manufactures products according to customers’ demand. This method allows Fluke to “fulfill customers’ request for a particular combination of the components” (Krajewski, Ritzman, Malhotra, 2011). In recent years, Fluke introduce in a single-piece flow concept, which it helps advance its JIT system to much leaner processes. This concept allows Fluke to manage its operation processes without work-in-process (WIP) between steps. Fluke also change its 4 previous layout to cellular layout that with all necessary equipments in the cell area (Dolcemascolo, 2011). By using single-piece flow, Fluke is able to faster it lead time and delivery best products to its customers. The success of DBS enables Fluke to backup its two key competitive priorities. Top quality is one of matters Fluke is greatly proud of. Fluke always think of customers’ needs as its precedence and delight its customers beyond their expectations. The company’s products are famous for its accuracy, safe, reliable, and user friendly. According to Mr. Pfeifer, customer like Fluke’s product is because the products have right feature for the right job and easy to use. For example, a competitor’s product may need 45second to finish a job while Fluke’s product only needs 9 seconds. In addition, each Fluke product packs with an instruction DVD for user and most of them have demo video on Fluke’s website. This really helps user save time on figuring the product feature and functions and demonstrate user to perform the product correctly and safely. Another key competitive priority of Fluke is on-time delivery, which it makes every effort to delivery its products on schedule. Fluke uses a term called Available Time Promise (ATP) for its delivery system. For example, if ATP is for five days, Fluke will ship the ordered products to its customers within five days as promise. By providing ATP, Fluke is able to reduce the lead time and stay competitive in its industry. V. Key Area of Focus: Lean Manufacturing Fluke Corporation is a company that is well-known for its lean manufacturing practices. In the words of Fluke’s employees, the company is as lean as it can be. At the same time, it always works on process improvement. The lean philosophy came from their parent company, Danaher Corporation, which is a world leader in lean manufacturing. Danaher usually acquires a new company and implements more efficient business practices that are known as Danaher Business System (DBS). After Danaher acquired Fluke Corporation in 1998, they completely changed the manufacturing process. Changes included decreasing inventory on hand to one and a half months, applying cell manufacturing approach and implementing Just-In-Time 5 production scheduling concept. All those practices doubled Fluke’s profits and freed cash flow for Danaher to acquire more manufacturing companies. A. Pull System Fluke Corporation created a concept of delighting a customer and always thinking about the value provided. Fluke always aims to give its customer more than they paid for. In order to accomplish this goal, Fluke implements a pull manufacturing system. It is a manufacturing planning system based on communication of actual real time needs from downstream operations. Fluke starts production when customer orders a product. They use a special in-house term, ATP-available to promise to customer. ATP for most of the products is five days. This means that a product will be shipped to a customer within five days after the order was placed. Fluke also uses a Kanban system, cards that coordinate the pull production system. Fluke employs three components of the Kanban system: each operation only performed as required by a downstream operation; a special cardboard card is used to authorize production process; the quality per individual Kanban is usually one. B. Cell Manufacturing Cell manufacturing at Fluke means that each product has a designated, mostly a U shape, cell. This cell is operated by one worker, and has everything needed to produce a specific product. At Fluke, workers are cross-trained, so one employee can work in several cells. On the other hand, several employees are trained to perform the same job. It gives flexibility in managing the workforce and eliminates idle time. To ensure that workers don’t get confused, each cell has a journal with detailed process description and pictures. This minimizes possibility of an error and allows different operators work in this cell. The cell is small and requires minimal setup. This setup decision results in less inventory inside the cell and shorter lead time. Each work station within a cell is placed close together to reduce movement of workers. The U-shape of the sell streamlines flow of material and increases productivity. Each cell has a performance card where key performance indicators are identified. Among the most important indicators are Material, 5S/Safety, Quality, and Productivity. Each worker 6 has to record in this card if the desired performance in each category was achieved or missed. Later, workers analyze each key performance indicator during the meeting and discuss ways to make improvements in missed categories. Because production process is constantly updated, each worker is empowered to bring his or her suggestions. At Fluke, decisions are often made from bottom-up. C. Just-In-Time Philosophy After the product is ready, Just-In-Time production concept is implemented internally. Just-In-Time production scheduling means that each product should be produced and available precisely when needed. In the case of Fluke, it means that a train comes according to schedule to pick up ready to ship products and delivers it to a distribution center. This helps each worker at the cell to follow the production schedule and supports Kanban quantities. From some of the processes we toured, Fluke is dead on when it comes to their Just-in Time processes. When products are available for delivery, a “train” comes around picking up the product and delivers it to the distribution center, where it is then ready to be sent out and delivered to their customers. Having this, helps the workers in each station at Fluke complete their processes on schedule. During our tour, we specifically viewed the AirCheck cell, which is a device used for Wi-Fi and network troubleshooting. A crucial part of this process that we saw while on this tour was the use of Kanbans. At the end of every cell, they had one with an exact schedule of when and what to make, along with how long it took to produce. We were informed that workers at Fluke often shift cells and would work on different products simultaneously to eliminate waste, in this case waiting time which is another important factor which appeared to be working well in improving efficiency. D. Kaizen Upon entering the lobby, the very first thing our group noticed was a large poster on the wall stating in bold letters, “Continuous improvement (Kaizen) is our way of life.” Our tour guides made it very clear that the company was revolved around this concept. We were shown multiple cells that were undergoing modifications, as well as some that 7 already had which shows that Fluke is always looking for ways to improve their process. When asked about Kaizen, we were given the response, “no matter where we are, we’re never good enough.” (Clarke). They weren’t afraid to point out what processes needed improvements either. On the second cell we toured which produced servers, they had two cells sharing the same equipment and it wasn’t laid out well at all. The walkway was limited and this cell was not operating a pull system as the more productive ones were. As part of Kaizen, the company is working to improve this producing method. They also have short daily meetings everyday amongst staff members to see where each and every one of them are at in their specific duties and if all is coming along on time. As noted, continuous improvement is something Fluke strives for and that is clearly shown. E. Quality Quality is also another important part of Fluke and their products. Something that goes on in the cells we noticed is the concept of poka yoke which stands for mistake proofing. They had specific spots for all of the equipment necessary and set up to where if one was out of place it would be noticeable. This is done to eliminate errors. Also they have step by step rules on how to create all products at the end of each cell so that no mistakes could be made. Jidoka, also known as autonomation was something that we also noticed on the tour. All production stations we saw were monitored by humans; they weren’t relying on machines alone. Having jidoka incorporated into these processes enables the ability to stop production if something goes wrong and ensures good quality control. If something was to go wrong, it would be fixed so that it wouldn’t happen again. 5 S’s Something that was also noticed during multiple parts of the tour was the use of the 5 S’s (Sorting, Straightening, Shine, Standardizing, and Sustain.) On our tour, we saw a sign with these 5 S’s listed which means that the company takes these seriously. All of the cells were well sorted and maintained. The necessary equipment to assemble the product was organized in such a way that was simple and easily accessible which 8 resembles the cleanliness and shine aspect of the S’s. The factory itself was also very clean, with all product names hanging above each cell. Standardization was something that each and every cell provided as well. Product guidelines were posted on the ends of all cells noting requirements and times which helps keep everything efficient and sustainable. Fluke has the reputation of having the highest quality products in the business and in using these methods; they are able to do so. F. Product Process a. Process Structure in Services – The service product structure of the air tester would be considered a back-office process. After the customer places the order there is no customer involvement needed since there is no option for customization. The process therefore is standardized and a line flow is used. In this line flow each air tester is moved through the line the same way, as opposed to a flexible flow process where the products don’t all move in the same order due to product flexibility. The lack of flexibility and customer involvement make this a back office process structure. b. Process Structure in Manufacturing – The air tester is produced using a line process. The operator moves each tester from station to station in a U-shaped cell. Each station provides everything the operator requires at that step of the process, this eliminates any time searching for necessary tools. The cells are small so the operator doesn’t have to waste time traveling. Since the product is standardized there is no variability in the process. Each is completed in a single piece flow. In a single piece flow one product is worked on one at a time. Therefore, there is little work-in-progress. According to ImprovementAndInnovation.com, the following are benefits f using single piece flow: (1) improved quality and fewer defects (2) reduced inventory (3) less space required, (4) enhancement of overall manufacturing flexibility, (5) makes the identification of future 9 kaizens simpler, (6) ensures a safer work environment, and (7) improves employee morale. (Gembutsu Consulting. August, 2007) The assemble-to-order strategy is the inventory strategy used. Fluke forecasts future orders for the air testers and places an order with their suppliers. Orders are then received within 6-8 weeks. Once Fluke receives the air testers they sit in inventory until an order from a customer is placed. Within a few days of an order being placed Fluke begins their work on the air tester, which takes around 15 minutes to complete. The Air tester is then shipped the following day. Since the air tester comes assembled already, the suppliers are an integral part of the production process. Any delays in shipment from their supplier could cause delays to the customer. Therefore, the success of their product is highly dependent on their supplier. See Figure 2 in the Appendix. VI. Recommendations TIM VII. Conclusion TIM 10 VIII. Appendix Figure 1 – Danaher’s 5-Year Sales Figure 2 – Value Stream Map SUPPLIER 6‐8 weeks Demand Forecasted PRODUCTION CONTROL CUSTOMER Orders placed Daily Schedule I 1.5 months Load Serial # Testing 1 person 1 person 47 seconds 327 seconds Load Mac address 1 person 48 secs Remove tested unit & install battery Load Case Box 1 person 1 person 1 person 55 seconds 83 seconds 75 seconds I c 11 IX. References Danaher. 21 February 2011. Retrieved from http://www.danaher.com/about/corevalues.htm Dolcemascolo, Darren. “Achieving one-piece flow”. 2 March 2011. Retrieved from http://www.reliableplant.com/Read/14703/one-piece-flow Fluke Cooperation. “Corporate Profile”. 2 March 2011. Retrieved from http://www.fluke.com/fluke/usen/about/corp/default.htm Krajewski, Lee J., Ritzman, Larry P., Malhotra, Manoj K.. (2010) Operations Management: Processes & Supply Chains. 9th ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. 12