Phylum Platyhelminythes
Platyhelminthes
~ 20,000 extant species
Parasitic + free-living
Unsegmented flatworms
Platyhelminthes
Triploblastic, acoelomate, bilaterally
symmetrical
Incomplete gut; absent in some parasitic forms
Cephalization of nervous system
Protonephridia: excretion and osmoregulation
Hermaphroditic
Support
Hydrostatic skeleton
Elastic body wall
Body musculature
Taxonomy
Class Turbellaria
Class Monogenea
Class Trematoda
Class Cestoda
Class Turbellaria
– Free-living flatworms
– Most are aquatic
– Epidermis cellular and ciliated
Feeding and digestion in
Turbellaria
Consume invertebrates (few herbivores and
omnivores)
Locate food via chemoreception
A few are symbiotic
Turbellaria digestive system
Mouth, pharynx, intestine = incomplete gut
Pharyngeal glands produce mucus and
proteolytic enzymes
Digestion extracellular, then phagocytization
in intestine
Turbellaria nervous system
Sense organs
– Tactile receptors cover body concentrated anteriorly
– Chemoreception = location of food
– Statocysts = gravity detection and
orientation
– Photoreceptors
Inverted pigment cup ocelli
Negative phototaxis
Turbellaria nervous system
Variable: simple net-like to cephalized & bilateral
Ladder-like NS = more recently evolved
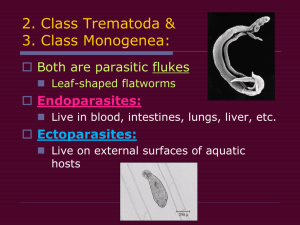
Class Monogenea
Monogenetic flukes (life cycle = one host)
– Body covered by tegument
– Oral sucker reduced or absent
– Ectoparasitic (usually fish)
Class Monogenea
Monogenetic flukes (life cycle = one host)
– Eggs hatch into ciliated larvae = oncomiracidia
– Mature and find host
Class Trematoda
Digenetic flukes (multiple hosts)
– Body with tegument
– One or more suckers present
– Internal parasite
Fluke Digestive System
Feed on host tissues and fluids (muscular
pharynx)
– Or, material in host gut
One-way digestive tract: mouth, muscular
pharynx, short esophagus, intestinal cecae
Fluke Nervous System
Ladder-like
Cerebral ganglion
Suckers with tactile receptors (bristles
and spines)
Sexual repro flukes
Hermaphroditic
Mutual cross fertilization
Male structures
– Variable testes
Monogenetic = many
Digenetic = two
– Sperm-to sperm duct, copulatory
apparatus, eversible cirrus
Sexual repro flukes
Female Structures
– Ovary to oviduct to ootype
– Oviduct joined by vitelline duct
– Seminal receptacle = blind pouch off of
oviduct
– Single uterus sometimes modified as vagina
near female gonopore
Fluke reproduction
Mutual cross-fertilization
Sperm stored in seminal receptacle
Eggs - oviduct to ootype then fertilized
r-selected strategy (high fecundity)
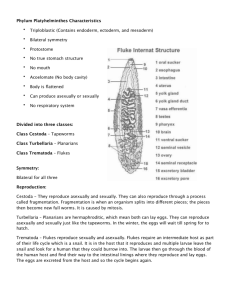
a – acetabulum
d - vitelline ducts
f - vitelline follicles
o - oral sucker
oe – oesophagus
oo – ootype
ov – ovary
ph – pharynx
sr - seminal receptable
t – testis
u - uterus
Fluke life-cycles
Monogenetic
– One host
– Mostly external parasites of fish
Digenetic
– Two or more hosts
– Mostly internal parasites
Fluke life-cycles:
Chinese liver fluke
Fluke life-cycles
Digenetic Fasciola = sheep liver fluke
– Multiple hosts
– Internal parasite of vertebrates
– Intermediate host usually gastropod
Fluke life-cycles
Schistosoma mansoni
Schistosomiasis = disease with
problems from egg production, fevers,
eggs lodged in various tissues
Schistosomiasis
Schistosoma spp. cause
swimmer’s itch
Class Cestoda
Tapeworms
– Internal parasite
– Body with tegument
– Body with anterior scolex, short neck and
proglottids
– No digestive system
Tapeworms = cestodes
Locomotion
– Sedentary: adult on host intestinal wall
– Capable of muscular undulations
Attachment
– Scolex
– Anterior with hooks or adhesive pad
Tapeworm digestion
No mouth, no digestive tract
Nutrients absorbed across tegument
Tapeworm Nervous System
Cerebral ganglion; nerve ring in scolex
Each proglottid has additional ganglia;
connect to longitudinal nerve cords
Sensory organs reduced, tactile receptors in
scolex
Sexual Repro: tapeworms
Hermaphroditic
Mutual cross-fertilization
Self-fertilization in some
Proglottids
– Numerous testes along margins
– Collecting tubules to coiled sperm duct
– Vas deferens to genital pore
Proglottids
– Two ovaries
– Uterus = blind sac
Tapeworm sex and fertilization
Cirrus of each mate inserted into genital pores
Sperm stored, eggs fertilized in oviduct
Capsule material and yolk cells stored in uterus
When mature, proglottids break free
Beef Tapeworm Life Cycle
Pork Tapeworm Life Cycle