Force Diagrams
advertisement

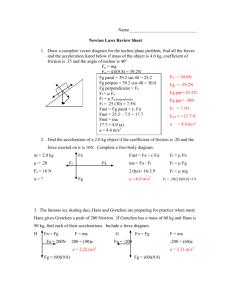
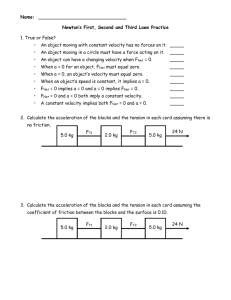
1 Force Diagrams - Class Discussion & Practice 1-23-14 1. One of the lab instruments that we will use in this packet is known by two names: F_____________ M_____________ or S______________ S____________ 2. What two units of measure do you see on this instrument? ______________ _______________ 3a. What do most people think of when they say force? 3b. What is our scientific definition of force? 4. What happens to an object whenever a force is applied to it? a. Shape can _____________________________________________________________ b. The motion 1) ___________________________ 2) ____________________________ 3) ___________________________ 4) ____________________________ 5) ___________________________ 6) ____________________________ Quick Experiment: What amount of force is required to hold a textbook in the air? _________ N What amount force is needed to pull the same book across your desk top? ________ N Why are these 2 numbers not the same? We will use the following 6 Step Procedure to draw and label Force Diagrams. 1st – Correctly draw the diagram/object. 2nd – Place each force next to the object it is acting upon. Do this by writing the abbreviation of the force. FG FN FP FT FD Ff 3rd – Write in the magnitude (_____) of each force (________) next to its abbreviation. 4th – Show the magnitude and direction of each force using arrows. Known as a ________. 5th – Calculate the sum of the forces called Net Force: Add opposite direction forces. Fnet (H) _______________ forces Direction – Fnet (V) _________ forces Forces acting to the left will be written as negative, while forces acting to the right will be written as positive. Forces acting upward will be positive while forces acting downward will be negative. 6th – If the object is moving, draw a __________________ arrow pointing in the direction of the motion. 2 Types of Forces: Abbreviations & Locations on a Force Diagram Gravitational FG - Drawn _____________ the object, pointing _____________. (Also known as _____________). Normal FN - Drawn _____________ the object, pointing _______. (All Falling objects have a F N of 0) Tension FT - Drawn in the direction that the object is being _______________. (Could be any direction.) Push FP - Drawn on the side that the force is being _______________ to. Friction – Drawn on the side that the object is being moved toward, near the surface and in the __________________ direction that the object is moving. Static Friction FSf - Friction acting on a ______________________ object. Kinetic Friction FKf - Friction acting on a _________________ object. Air Resistance (Drag) FD - Like friction, except it is drawn up in the ____________. Elastic Fe Draw in the direction the object uses its force to move an object. Compression Fc Draw in the direction the object uses its force to move an object. Magnetic Fm Drawn toward the magnet. Explanation of Support or Normal Force You sit on your chair – and your weight, due to the force of gravity pushes you downward onto the chair, while the chair supports your weight. Support forces are pretty clever – they appear only when they are needed, and only in as much amount as needed. If the person got up from the chair, the support force vanishes! The support force is called the normal force – not meaning the opposite of abnormal, but meaning perpendicular. The normal force is always perpendicular to the surface at the point where the object touches the surface. On a flat, horizontal surface, the normal force is equal to the weight of the object. It has to be! For example, in the picture above, if the weight of the apple were larger than the normal force, the apple would fall through the book. If the normal force were larger than the weight, the apple would lift up off the book. Force Diagram Practice Problems A) Soccer ball starts out not moving. FP = ______ N FF = -100 N Fnet (H) = ______ N 3 B) FN = ______ N Box starts out not moving. FP = 50 N FP = ______ N FG= -200 N Fnet (H) = - 40 N Fnet (V) = ______ N C) Car is moving at a constant velocity. A car travels down I-70 at a constant velocity. The car has a push force of (FP) of 10,000 N. The asphalt road surface exerts a 1,000 N frictional force (FF), and the air exerts a 400 N force (FD). Fnet (H) = ______ N Fnet (V) = ______ N FBD Practice Problems (These objects start out not moving.) 1. A 300 N crate is resting on the floor. Fnet (H) = ______ N Fnet (V) = ______ N 2. A person pulls a 500 N crate across the floor and meets a resistance of 35 N. Fnet (H) = ______ N 3. 4 Fnet (V) = ______ N A 5,000 N crate is pushed across a concrete floor by two people. One applies a 800 N force, the other a 600 N force (both are pushing in the same direction.) The box’s motion is opposed by a 400 N frictional force. Fnet (H) = ______ N Fnet (V) = ______ N 4. FN = _______ N FP = 300 N FP = -100 N Ff = -10 N FG= -150 N Fnet (H) = ______ N Fnet (V) = ______ N 5. You and your partner pull on a rope. You pull with a force of 30 N and your partner pulls against you with a force of 30 N. Show one of the people moving toward the other using a force diagram. Explain how this can occur. 5 6. A 800 N person tries to move a wooden crate across the floor. He pulls with a force of 75 N against a friction force of 100 N. Fnet (H) = ______ N Fnet (V) = ______ N 7. Show the forces acting on this non-moving rock. 8. Show the forces acting on this non-moving rock. More FBD Practice Problems (These objects are already moving.) 9. A ball is rolling down a ramp. (No units of force (Newtons) are needed for this problem.) Draw the force diagram. 10. Show the forces acting on this moving rock. 6 11. What is the net force acting on the people in the basket? The balloon is moving upward at a constant velocity. FT= _____ N FD = - 2 N FG = - 30 N Fnet (V) = N 12. (A falling object – gaining velocity.) FD = 20 N FP = _____ FP = _____ FG = - 25 N Fnet (H) = _______ Fnet (V) = ______ N 13. A 3,000 N crate is quickly pushed across the floor by 2 people. One applies a force of 100 N and the other a force of 50 N, both are pushing in the same direction. The box’s motion is opposed by a 25 N force from the wind. Fnet (H) = _______ Fnet (V) = ______ N 14. Draw the force diagram for the moving rock. 7 15. A balloon moving in two directions. FD = 25 N FD = -20 N FP = -50 N FP = 170 N FG = -100 N Fnet (H) = _______ Combined Net Forces = _____ N 16. Balloons in 2 directions. N Fnet (V) = _______ N Angle of the Net Forces = ______ 0 FD = 100 N FP = -200 N FP = 100 N FG = -300 N Fnet (H) = ______ N Combined Net Force = _______ N 18. Fnet (V) = _______ N Angle of the Net Forces = ________ 0 Make a Force Diagram of a Hot Air Balloon drifting to the ground while a wind of 50 N is blowing it toward the West. The balloon and the basket have a weight of 2000 N. The lift of the balloon (tension) is 1800 N and there is a drag upward of 30 N. 8 17. FT = 650 N FP = 500 N FT = 500 N FG = -300 N Fnet (H) = _______ Fnet (V) = _______ Combine Net Force = __________ N Agent – Produces the Force. Receiver – Is acted upon by the force. Effect – What the force causes to happen. Angle = _______ 0 9 1. Polar Bear – Three people attach ropes to a bear in a zoo. Two of their forces are given, what is the force of the 3rd person? (Dotted Line length does not show N.) Person A 68 N Person C ?? N Person B 88 N Rock & Feather Demonstration Task #1 - A rock and a feather are released from the same height in a 10 room that has air resistance. Both items fall to the floor with the following results. Time for the Fall Speed when it hit the Floor Rock 2.5 seconds 7 m/sec Feather 25 seconds 0.6 m/s Task #2 - A rock and a feather are released from the same height in a room that has no air resistance, known as a Vacuum. Both items fall to the floor with the following results. Time for the Fall Speed when it hit the Floor Rock 1.6 seconds 15.7 m/sec Feather 1.6 seconds 15.7 m/s What conclusions can be drawn from Task #1 and Task #2 in the Rock & Feather Experiment? FD = 45 N FD = -30 N FP = 170 N FP = -50 N FG = -100 N Fnet (H) = _______ N Fnet (V) = _______ N Combined Net Forces = ________ N 17. Angle of the Net Forces = ________ FN = 300 N FP = 200 N Fd = 120 N Fp = 200 N FG = 300 N Fnet (H) = 380 N Fnet (V) = 0 N 0 11