Momentum and Impulse
advertisement
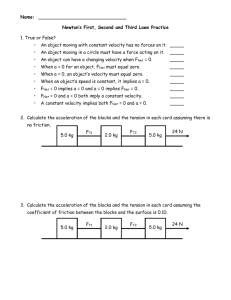
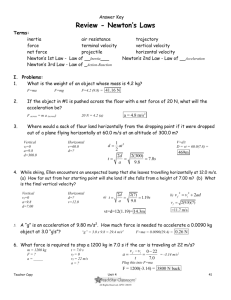
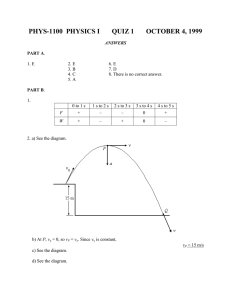
Principles of Physics Forces cause acceleration Acceleration is a change in velocity with respect to time Change in velocity results in a change in momentum Newton’s 2nd Law Fnet = ma Fnet = m(vf – vi) t Fnet t = m(vf – vi) impulse (Ns) change in momentum (kg m/s) 1Ns = 1 kg m/s Fnet = m = (vf – vi) = t = net force (N) mass (kg) change in velocity (m/s) time (s) Car crashes By increasing the time of the collision the force felt by the passengers is reduced. Airbags cushion the impact (allow impact to take longer) Ft = m(vf – vi) Why would it be better to hit a hay stack instead of a brick wall? What do catchers allow their arms to move backwards when they catch? A hockey player takes a slap shot, exerting a force of 30 N on a hockey puck for 0.16 s. If the puck had a mass of 0.115 kg and started from rest, what speed does it have as it heads towards the net? Givens: F =30 N t = 0.16 s m = 0.115 kg vi = 0 Ft = m(vf – vi) (30)(0.16 ) = 0.115(vf – 0) vf = 41.8 m/s Small rockets are used to make small adjustments in speed of satellites. One such rocket has a thrust of 35 N. If it is fired to change velocity of a 72,000 kg spacecraft by 0.63 m/s, how long should it be fired? Givens: F =35 N t=? m = 72,000 kg (vf – vi) = 0.63 m/s Ft = m(vf – vi) (35)(t) = 72,000(0.63) t = 1,296 s = 21.6 min