Force Diagram introduction practice
advertisement

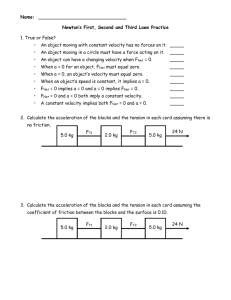
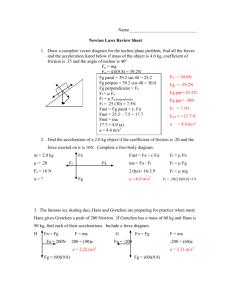
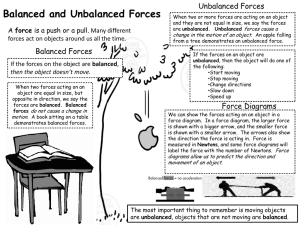
Tabletop Hovercraft Lesson 1: Activity 2 Introduction to Force Diagrams Qualitative Name________________________ Date_______________Bell_______ A force is a Push or a pull. A force diagram is a useful tool to analyze the forces acting on an object, and make predictions about its motion. Prelab – 1. What do you think it means when we say the forces acting on an object are “balanced”? Describe an example. 2. What affect do you think “balanced” forces will have on the motion of an object? 3. Describe an example of an object with “unbalanced” forces acting on it. 4. What affect do you think this will have on the motion of an object? Force Diagrams allow us to represent simply the important aspects of the forces acting on an object so it can be analyzed. 1. Use a circle to represent the object. 2. Use arrows to represent each force. All arrows should start touching the circle, and pointing away in the direction the force is acting 3. The length of the arrow represents the strength of the force. Complete the chart for the object underlined in the description for each situation below. Consider using the following to label your forces: Gravity, Tension, Friction, Air Resistance, Normal force, push, pull, buoyancy Description Ex.1) A cat sits motionless on a rug. Ex. 2) A softball player slides into home base. Force diagram (label all forces) Are forces balanced or unbalanced? (∑F=0 or ∑F≠0) Will the motion be constant or change? How will it change? Description 1. An Ice skater moves across frictionless ice with a constant speed. 2. A chandelier is suspended from the ceiling by a chain. 3. A book is being pushed across a table top with a constant speed. 3. A Bucket of water is being raised from the well at a constant speed. Force diagram (label all forces) Are forces balanced or unbalanced? (∑F=0 or ∑F≠0) Will the motion be constant or change? How will it change? Description 4. A Skydiver who has just left the plane is speeding up as he falls. 5. A skydiver is falling at a constant velocity after he has deployed his parachute 6. A ball was thrown into the air and is rising to the top of its trajectory (path). 7. A ball is at the top of a parabolic trajectory, just before it begins to fall back down. Force diagram (label all forces) Are forces balanced or unbalanced? (∑F=0 or ∑F≠0) Will the motion be constant or change? How will it change? Description 8. A cork is floating in a bowl of water. 8. An airplane is flying straight and level through the air. 9. A nail has been picked up by a magnet. 10. A hovercraft glides across a flat table Force diagram (label all forces) Are forces balanced or unbalanced? (∑F=0 or ∑F≠0) Will the motion be constant or change? How will it change? Tabletop Hovercraft Lesson 1: Activity 2 Introduction to Force Diagrams Quantitative Name________________________ Date_______________Bell_______ Find the values of the forces identified below. Be sure to pay attention to the net force as well. 1. Fnet=0 N 2. Fnet =0 N 5N 3. Fnet= 10 N upward 50 N ___ ___ 10 N ___ ___ 60 N 5. Fnet= 30 N upward 4. Fnet= 50 N right ____ 70 N ___ 60 N ___ 20 N 10 N 70 N 6. Fnet = _________ 7. Fnet= _________ 50 N 55 N 25 N 30 N 100 N 55 N 8. Fnet= 15 N left and 10 N down 9. Fnet = 0 N 115 N 115 N _____ ____ 10. Fnet= 0 N ____ 11. Fnet= 15 N down 65 N 75 N 25 N 105 N 13. Draw a force diagram that has a Net force of 50 N down 12. Fnet = 20 N right 10 N ____ 72 N ____ 30 N 45 N ____