chapter_16_review_questions_for_scantron_review_game
Chapter 16 Review
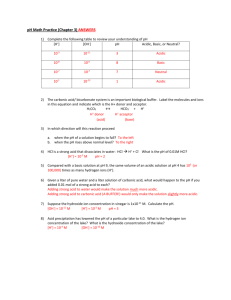
1.
Which of the following relationships is correct? a.
pH + pOH = Kw b.
Kw = -log [H+] c.
[H+] x [OH-] = 1.0 x 10
-14 d.
None of the above
2.
If pOH of a solution is 5.52, what is the hydronium concentration? a.
8.75 b.
5.25M c.
5.6x10
-6
M d.
3.3x10
-9 M
3.
Which of the following pairings is incorrect? a.
Neutral: pH = 7 b.
Acidic: [H+] > [OH-] c.
Basic: [H+] < [OH-] d.
All of the above are correct
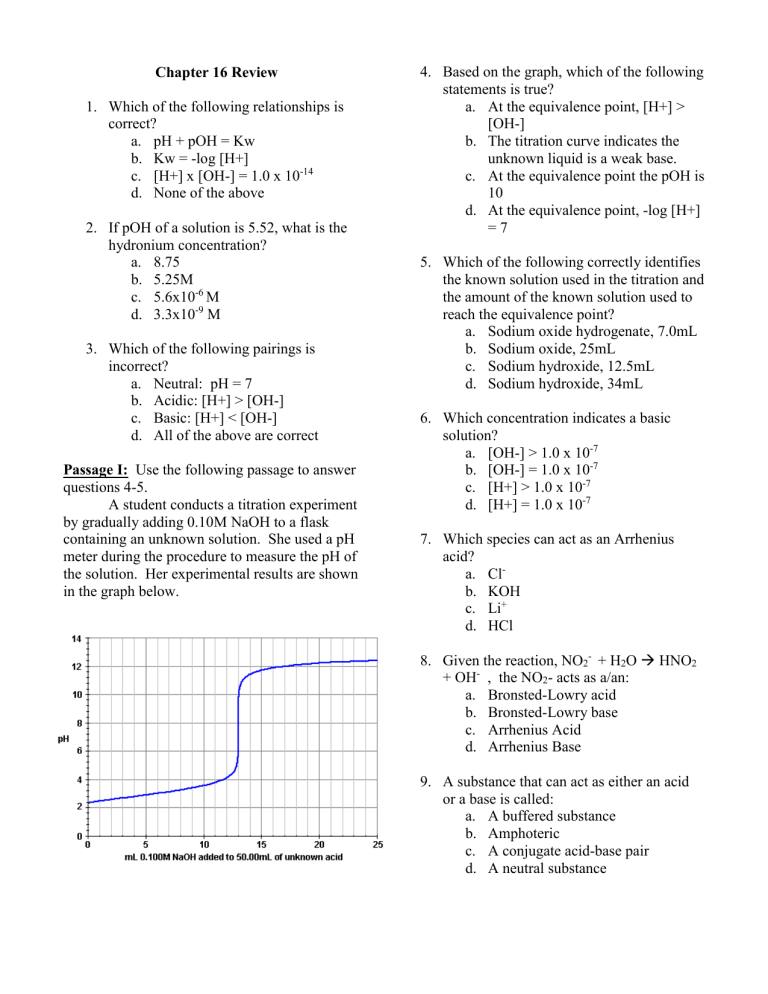
Passage I: Use the following passage to answer questions 4-5.
A student conducts a titration experiment by gradually adding 0.10M NaOH to a flask containing an unknown solution. She used a pH meter during the procedure to measure the pH of the solution. Her experimental results are shown in the graph below.
4.
Based on the graph, which of the following statements is true? a.
At the equivalence point, [H+] >
[OH-] b.
The titration curve indicates the unknown liquid is a weak base. c.
At the equivalence point the pOH is
10 d.
At the equivalence point, -log [H+]
= 7
5.
Which of the following correctly identifies the known solution used in the titration and the amount of the known solution used to reach the equivalence point? a.
Sodium oxide hydrogenate, 7.0mL b.
Sodium oxide, 25mL c.
Sodium hydroxide, 12.5mL d.
Sodium hydroxide, 34mL
6.
Which concentration indicates a basic solution? a.
[OH-] > 1.0 x 10
-7 b.
[OH-] = 1.0 x 10
-7 c.
[H+] > 1.0 x 10 -7 d.
[H+] = 1.0 x 10
-7
7.
Which species can act as an Arrhenius acid? a.
Cl
b.
KOH c.
Li + d.
HCl
8.
Given the reaction, NO
2
- + H
2
O HNO
2
+ OH
-
, the NO
2
- acts as a/an: a.
Bronsted-Lowry acid b.
Bronsted-Lowry base c.
Arrhenius Acid d.
Arrhenius Base
9.
A substance that can act as either an acid or a base is called: a.
A buffered substance b.
Amphoteric c.
A conjugate acid-base pair d.
A neutral substance
10.
What is the pH of a solution with a hydroxide ion concentration of 0.001moles per liter? a.
1 b.
3 c.
7 d.
11
11.
According to the Bronsted-Lowry theory, an acid is any species that can a.
Donate a proton b.
Accept a proton c.
Donate an electron d.
Accept an electron
12.
Choose the case that is not a conjugate acid-base pair: a.
OH , O 2b.
HCO
3
-
, CO
3
-2 c.
NH
2
OH
2
+
, NH
2
OH d.
H
3
PO
4
, HPO
4
2-
13.
The fact that HCl is a strong acid also means that Cl- is a(n) a.
Amphoteric substance b.
Weak acid c.
Weak conjugate base d.
Strong conjugate base
14.
Which of the following is not a strong acid? a.
H
2
SO
4 b.
HCl c.
HNO
3 d.
All are strong acids
15.
Find the pH of a solution which has a hydroxide concentration of 3.4x10
-5
M a.
9.53 b.
6.34 c.
10.47 d.
4.47
16.
Calculate the pH of a 0.53M HCl solution. a.
-0.53 b.
0.28 c.
0.53 d.
-0.28
17.
Determine the volume of 0.100M
Mg(OH)
2
needed to titrate 20.0mL of
0.400M HCl. a.
20.0ml b.
60.0ml c.
80.0ml d.
40.0ml
18.
Which of the following is true for a buffered solution? (Mark all that apply) a.
Any H+ ions added will react with a conjugate base of a weak acid already in solution. b.
The solution will not change its pH very much even if a strong base is added. c.
The solution resists any change in its [H+] d.
The solution will not change its pH very much even if a concentrated acid is added e.
None of the above are true.
19.
A weak acid, HF, is in solution with dissolved NaF. If HCl is added which ion will react with the extra hydrogen ions from the HCl to keep the pH from changing? a.
F- b.
Na+ c.
H
2
O d.
H+
20.
Which of the following is a method for finding the pH of a substance in the lab
(MARK ALL THAT APPLY) a.
liquid indicator b.
apple juice c.
pH paper d.
pH meter e.
sprite
21.
Which of the following is a diprotic acid? a.
hydrochloric acid b.
sulfuric acid c.
nitric acid d.
HC
2
H
3
O
2 e.
none of the above
ANSWERS ON NEXT PAGE!!
ANSWERS!!
1.
C
2.
D
3.
D
4.
D
5.
C
6.
A
7.
D
8.
B
9.
B
10.
D
11.
A
12.
D
13.
C
14.
D
15.
A
16.
B
17.
D
18.
A, B, C, D
19.
A
20.
A, C, D
21.
B