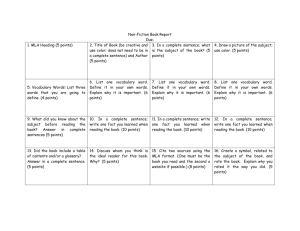
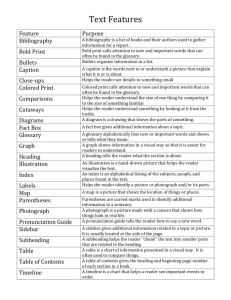
atar psychology
advertisement

ASSESSMENT OUTLINE 2016 ATAR PSYCHOLOGY YEAR 12 Semester 1 – UNIT 3 Assessment Type Task Description EGC Weighting Due Date SCaSA Weighting Investigation 15% Response 30% Project 15% Exam 40% Task 4: Psychological report Short term memory Task 2: Topic Test Biological influences Task 3: In Class Essay Cognition Task 5: Topic Test Relational influences and communication Task 1: Journal Responses to four academic articles Task 6: Semester One Exam Unit 3 content 7.5% 5% 5% 5% 7.5% 20% Term 1 Week 10 Term 1 Week 6 Term 2 Week 3 Term 2 Week 4 Term 2 Week 4 Term 2 Week 6 Semester 2 – UNIT 4 Assessment Type Task Description EGC Weighting Due Date SCaSA Weighting Investigation 15% Response 30% Project 15% Exam 40% Task 2: Psychological report Operant conditioning Task 3: Topic Test Developmental psychology Task 4: Topic Test Personality Task 5: In Class Essay Social psychology Task 6: Topic Test Culture and values Task 1: Journal Responses to three academic articles Task 7: Semester Two Exam Unit 3 and 4 content 7.5% 4% 3% 4% 4% 7.5% 20% Term 3 Week 9 Term 2 Week 8 Term 2 Week 10 Term 3 Week 3 Term 3 Week 7 Term 3 Week 6 Term 4 Week 1 It is expected that all assessments will be completed to the best of your ability and be submitted by the deadlines set. Please make yourself aware of the Assessment Policy as failure to meet deadlines has severe consequences. Student Signature: _________________ Parent/Guardian Signature: _________________ COURSE OUTLINE 2016 ATAR PSYCHOLOGY YEAR 12 Week Topics/Syllabus Assessment Resources Task 1: Journal “Brain waves forecast antidepressant effect” Week 2 Course reader Task 1: Journal Gottfried 2008 Week 3 Course reader Task 2: Topic test Week 6 Course reader Term 1 1 -2 3-4 5-6 7-8 9 - 10 Topic/s Heading: biological influences structure and function of the nervous system central nervous system brain spinal cord peripheral nervous system somatic nervous system autonomic nervous system - sympathetic and parasympathetic process of neural transmission role of synapses role of neurotransmitters – serotonin, dopamine Topic/s Heading: biological influences roles of the four lobes of the cerebral cortex frontal lobe – Broca's area, primary motor cortex parietal lobe – primary sensory cortex occipital lobe – primary visual cortex temporal lobe – Wernicke's area, primary auditory cortex Topic/s Heading: biological influences factors that affect behaviour, emotion and thought, including: heredity – the role of genetics hormones – the effects of adrenaline and noradrenaline psychoactive drugs – the effects of depressants, stimulants and hallucinogens Topic/s Heading: cognition Memory multi store model of memory (Atkinson and Shiffrin) sensory register o duration, capacity, encoding short term memory and working memory o duration, capacity, encoding o working memory model (Baddely and Hitch) Topic/s Heading: cognition long term memory o duration, capacity, encoding o procedural memory o declarative memory – semantic and episodic memory recall, recognition, re-learning forgetting retrieval failure, interference, motivated forgetting, decay Course reader Task 1: Journal Dawes 2015 Week 10 Task 4: Psychological report Week 10 Course reader Week Topics/Syllabus Assessment Resources Topic/s Heading: cognition Learning classical conditioning operant conditioning o token economies o reinforcement and punishment observational learning techniques for modifying behaviour systematic desensitization CBT Topic/s Heading: relational influences types of solutions to resolve conflict imposed distributive integrative techniques for resolving conflict mediation negotiation counseling Topic/s Heading: relational influences socialisation processes observed within families attachment – Harlow, Bowlby, Ainsworth features of different parenting styles – authoritative, authoritarian and permissive Topic/s Heading: communication communication styles impact of social background – Bernstein, Labov examples of gender differences – Tannen features of persuasive communication source of the message nature of the communication characteristics of the audience features and limitations of theories of language development innate and learned behaviours – Chomsky, Bruner Revision week Task 1: Journal Poling 2011 Week 1 Course reader End of semester exams Task 6: Exam Week 6 Term 2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 END OF SEMESTER 1 Topic/s Heading: developmental psychology stages and characteristics of developmental theories Piaget’s theory of cognitive development Kohlberg’s theory of moral development Erikson’s stage theory of identity Topic/s Heading: developmental psychology features of Bandura’s Social Learning Theory the role of observational learning and modelling Course reader Task 3: In class essay Week 2 Course reader Task 5: Topic test Week 4 Course reader Task 1: Journal Harlow 1965 Week 4 Task 1: Journal Kidwell 1995 Week 7 Course reader Task 3: Topic test Week 8 Course reader Topic/s Heading: personality features and limitations of contemporary personality theories trait theories – McCrae and Costa humanistic theories – Rogers and Maslow social‐cognitive theory – Mischel and Bandura Task 1: Journal “Humanistic approach to personality” Week 9 Course reader Topic/s Heading: social psychology Task 4: Topic Course reader Week the influence of groups on behaviour group polarisation conformity and obedience – Asch, Milgram and Zimbardo impact of the presence of others on individual behaviour – social facilitation and inhibition test Week 10 Topics/Syllabus Assessment Resources Task 1: Journal Elliot 1997 Week 2 Course reader Task 5: In class essay Week 3 Course reader Task 1: Journal Stallard 1998 Week 6 Course reader Task 6: Topic test Week 7 Course reader Task 2: Psychological report Week 9 Course reader Term 3 1 -2 3-4 5-6 7-8 9 - 10 Topic/s Heading: social psychology attribution theory Heider Kelley cognitive dissonance theory Festinger Topic/s Heading: culture and values sense of community as defined by McMillan and Chavis membership influence integration and the fulfilment of needs shared emotional connection Topic/s Heading: culture and values impact of significant events on individuals and communities positive responses – resilience and post traumatic growth negative responses – post traumatic stress disorder event characteristics contributing to stress – predictability; controllability; experience of threat or loss Topic/s Heading: research methods research terminology experimental, non‐experimental scientific, non‐scientific sample population ethics in psychology research role of the experimenter participants’ rights – privacy, anonymity, confidentiality, voluntary participation and withdrawal rights informed consent procedures deception in research professional conduct features of non‐experimental (descriptive) research methods case studies, surveys, correlational studies and archival research behavioural variables (not dependent and independent variables) in correlational studies Topic/s Heading: research methods features of experimental research methods independent and dependent variables operational hypotheses controlled and uncontrolled variables experimental and control groups placebo and experimenter effects reliability and validity longitudinal and cross‐sectional designs qualitative methods of data collection objective quantitative measures in research – physiological measures subjective quantitative measures in research – checklists and rating scales, such as Likert scales data interpretation measures of central tendency – mode, mean, median and range measures of dispersion – normal curve, variance and standard deviation role of probability use of correlation to establish association between variables sources of error in data and ways of reducing these the concept of statistical significance Week Topics/Syllabus Assessment Resources Term 4 Revision Course reader Revision Course reader 1 2 END OF SEMESTER 2