Exercise 1
advertisement

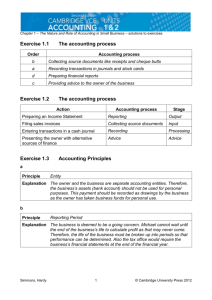
Chapter 1 The Role of Accounting – Solutions to exercises Exercise 1.1 Accounting principles a Accounting principle Entity Explanation The owner and the business are considered to be separate accounting entities, and their records should be kept on this basis. The orthodontist’s fees are an expense of the owner, not an expense of the business, and should be recorded as ‘Drawings’ b Accounting principle Consistency Explanation The same accounting methods should be applied from one period to the next so that reports can be compared between periods. The owner will be unable to identify any changes in repair or vehicle expenses. c Accounting principle Monetary Unit Explanation Transactions should be recorded in a common unit of measurement – in Australia, this means Australian dollars. d Accounting principle Reporting Period Explanation The life of the business is divided into arbitrary periods to allow for reports to be prepared. The transaction should be recorded as revenue when it was earned (when the goods were supplied), i.e. in December 2014. e Accounting principle Historical Cost Explanation Transactions should be recorded at their original purchase price as this value is verifiable by a source document. The revaluation is subject to subjectivity, and not verifiable. Simmons, Hardy 1 © Cambridge University Press 2012 Chapter 1 The Role of Accounting – Solutions to exercises f Accounting principle Going Concern Explanation The life of the business is assumed to be continuous, and its records are kept on this basis. The mortgage should be reported as a non-current liability, as it is assumed that the business will still be operating 10 years into the future. g Accounting principle Reporting Period Explanation The life of the business is divided into arbitrary periods to allow for reports to be prepared. According to tax requirements, reports must be prepared at least yearly. Exercise 1.2 Accounting principles and qualitative characteristics a Accounting principle Entity Explanation The business is assumed to be an accounting entity separate from the owner and other businesses, and its records should be kept on this basis. The holiday is an expense of the owner, not an expense of the business. b Explanation Simmons, Hardy The reports will not contain all the information that is useful for decision-making because they will not show the owner’s Drawings. 2 © Cambridge University Press 2012 Chapter 1 The Role of Accounting – Solutions to exercises Exercise 1.3 Accounting principles and qualitative characteristics a Accounting principle Historical Cost Explanation Stock should be valued at its original purchase price as this value is verifiable by a source document. OR Accounting principle Conservatism Explanation Revenues should be recognised only when certain so that assets and revenues are not overstated. There is no guarantee that the stock will be sold for its selling price, so using the selling price would recognise the revenue before it is certain and overstate sales revenue and the value of the stock (an asset). b Because the selling price is not verifiable by reference to a source document, it will mean the information in the reports is not free from bias. Explanation Exercise 1.4 Accounting principles and qualitative characteristics a Accounting principle Conservatism Explanation Losses should be recognised when probable so that expenses and liabilities are not understated. The damages should be recognised in order to present to the owner a prudent or cautious picture of the firm’s financial position. b Qualitative characteristic Relevance Justification The reports should include all information that is useful for decision-making. The probable expense of damages may affect decisions the owner makes about both profit and available cash. Simmons, Hardy 3 © Cambridge University Press 2012 Chapter 1 The Role of Accounting – Solutions to exercises Exercise 1.5 Accounting principles and qualitative characteristics a Consistency The same accounting methods should be applied from one period to the next so that reports can be compared between periods. b Qualitative characteristic Comparability Explanation Reports should be comparable over time, and between different companies through the use of consistent accounting procedures. Exercise 1.6 Accounting principles, qualitative characteristics and elements of reports a Accounting principle Reporting Period Explanation The life of the business is divided into arbitrary periods to allow for reports to be prepared. The revenue was not earned in the Reporting Period in which it was received (2014) but when the goods are provided in 2015 (a different Reporting Period). b Qualitative characteristic Relevance Explanation The reports will include some information that is not useful for decision-making about profit for the current Reporting Period (2014; i.e. the cash that has been received will not be earned until the next Reporting Period (2015). c Explanation Simmons, Hardy The inflow of economic benefits (cash) increases assets, but also increases liabilities (the goods are still owed to the customer); as a result there is no increase in owner’s equity. 4 © Cambridge University Press 2012 Chapter 1 The Role of Accounting – Solutions to exercises Exercise 1.7 Accounting principles and qualitative characteristics a Qualitative characteristic Understandability Explanation Reports should be presented in a manner that makes it readily understandable by users. As the workers have no accounting knowledge, the reports will not fulfil their function of providing information. b Use of graphs; plain language reports; explanatory notes/presentation sessions Technique Exercise 1.8 Accounting principles and qualitative characteristics a Accounting principle Historical Cost Explanation Assets and liabilities will be reported in the Balance Sheet at their original purchase price as these values are verifiable by a source document. The market value, on the other han,d represents what a potential buyer is prepared to pay for the assets. Exercise 1.9 Accounting principles, qualitative characteristics and elements of reports a Explanation As a non-current asset as it is a resource controlled by the business as a result of past events from which a future economic benefit is expected to flow to the business for more than 12 months. b Accounting principle Historical Cost Explanation The shelving should be valued at $12 500, as this is the agreed value of the asset at the time it is contributed to Max’s Mart. This agreed value becomes the Historical Cost for Max’s Mart. (The $15 000 was paid by a different entity.) Simmons, Hardy 5 © Cambridge University Press 2012 Chapter 1 The Role of Accounting – Solutions to exercises c Qualitative characteristic Reliability Explanation There is no guarantee that the shelving can be sold for its resale value, so using this figure will mean that the information in the reports is not free from bias. Exercise 1.10 Item Elements of the reports Report/classification Definition a Debtors Balance Sheet/ Asset a resource controlled by the business that is expected to provide a future economic benefit (when the cash is received) b Loan – principal Balance Sheet/ Liability a present obligation that is expected to result in an outflow of economic benefits sometime in the future (when the loan is repaid) c Interest on loan Income Statement/ Expense an outflow of an economic benefit in the form of a decrease in assets (Bank), which leads to a decrease in owner’s equity d Stock loss Income Statement/ Expense an outflow of an economic benefit in the form of a decrease in assets (Stock,) which leads to a decrease in owner’s equity e Cash sales Income Statement/ Revenue an inflow of an economic benefit in the form of an increase in assets (Bank), which leads to an increase in owner’s equity f Wages incurred Income Statement/ Expense an outflow of an economic benefit in the form of a decrease in assets (Bank,) which leads to a decrease in owner’s equity g Wages owing Balance Sheet/Liability a present obligation that is expected to result in an outflow of economic benefits sometime in the future (when the employees are paid) h Discount revenue Income Statement/ Revenue a saving in an outflow of economic benefits in the form of a reduction in a liability (Creditors), which leads to an increase in owner’s equity. Simmons, Hardy 6 © Cambridge University Press 2012 Chapter 1 The Role of Accounting – Solutions to exercises Exercise 1.11 Elements of the reports a Explanation Both represent an economic benefit, but whereas an asset represents a resource controlled by the entity that is expected to provide a future economic benefit, an expense represents an outflow or consumption of an economic benefit. b Explanation If the vehicle was purchased as stock and was intended for resale, it would be a resource controlled by the business that is expected to provide a future economic benefit in the next 12 months (when it is sold). c Explanation If the vehicle was purchased for use within the business, it would be a resource controlled by the business that is expected to provide a future economic benefit for more than 12 months. d Explanation OR Exercise 1.12 If the vehicle was sold, it would create an expense called Cost of Sales relating to the outflow of an economic benefit in the form of a decrease in assets (Stock), leading to a decrease in owner’s equity. Stock loss/Depreciation Goodwill a Discussion Simmons, Hardy The loyal clientele (goodwill) represents a resource controlled by the business that is expected to provide a future economic benefit (i.e. further sales). However, it is difficult to value this goodwill in any manner that is Reliable (accurate/free from bias) so it should not be recognised as an asset. 7 © Cambridge University Press 2012