Biology Semester 2 Final Review!
advertisement

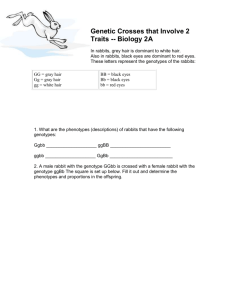
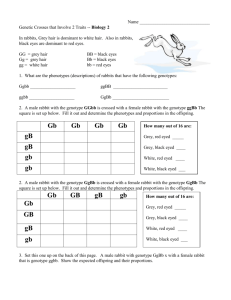
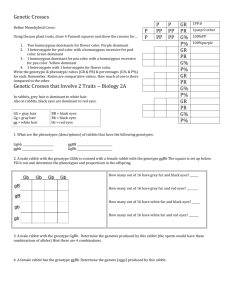
Biology Semester 2 Final Review! This does not prepare you for EVERY question on the final. You must consider questions that are related to the topics presented. DO WORK With your host…Ms. Turner! Central Reproduction Karyotypes Dogma & Genetics Evolution, Miscellaneous Cladistics, Classification 10 10 10 10 10 20 20 20 20 20 30 30 30 30 30 40 40 40 40 40 50 50 50 50 50 Central Dogma : 10 Draw a sketch of how DNA replication occurs using the following “strand” of DNA. A T T T G C A A A C G T ANSWER Central Dogma : 10 - Answer A T T G C A T A A C G T A T T G C A T A A C G T A T T G C A T A A C G T A T T G C A T A A C G T What is this mode of replication called? What enzymes are involved in this process? How is this different from transcription? Central Dogma : 20 Name at least 3 SPECIFIC differences between DNA and RNA. ANSWER Central Dogma : 20 - Answer DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose. DNA has A,T,C,G while RNA has A,U,C,G. DNA is double stranded, RNA is single stranded. DNA is replicated entiredly, RNA is only transcribed for genes. DNA replication happens once for a cell, RNA transcription happens many times. Central Dogma : 30 Draw a quick sketch of the following and label which processes are occurring where. ANSWER Central Dogma : 30 - Answer DNA Replication and Transcription both happen in the nucleus. Translation happens in the cytoplasm on ribosomes. Can you name all of the structures? Central Dogma : 40 Using the following sequence of DNA, what would the polypeptide be? ATGGGGACCAAT ANSWER Central Dogma : 40 - Answer ATGGGGACCAAT UACCCCUGGUUA Tyr – Pro – Trp - Leu Central Dogma : 50 Diagram how translation occurs. Be sure to use the following correctly: mRNA, tRNA, ribosome, codon, amino acid, peptide bond ANSWER Central Dogma : 50 - Answer mRNA docks on the ribosome. It is read one codon at a time. The anticodon on a tRNA molecule matches the mRNA and brings the correct amino acid. Amino acids are bonded together with peptide bonds. How do these peptide bonds form? Reproduction : 10 True or False: Cancer cells have a controlled rate of cell division. ANSWER Reproduction : 10 - Answer False: All cells should have a controlled rate of cell division. Cancer cells have lost the ability to control division. Mutations have occurred within the genes that code for genes that regulate cell division. Can you remember which genes these are? Reproduction : 20 How is binary fission different from mitosis? What kinds of organisms undergo each process type? ANSWER Reproduction : 20 - Answer Binary fission – prokaryotes Mitosis – eukaryotes (division of the nucleus and its contents) Reproduction : 30 Explain/draw & label the following (what is it and when is it in this form?): Chromatin Chromatids Tetrads ANSWER Reproduction : 30 - Answer Chromatin = DNA in relaxed form in Interphase Chromatid = half of a replicated chromosome, once separated (in Anaphase of Mitosis and Anaphase II of Meiosis) from sister no longer a chromatid Tetrad = pair of homologous chromosomes in Meiosis, separated in Anaphase I Reproduction : 40 What is the correct sequence that describes the development of a baby? Baby, Embryo, Fertilization, Fetus, Zygote ANSWER Reproduction : 40 - Answer Fertilization, Zygote, Embryo, Fetus, Baby How do cells become the variety of cells you have now? Reproduction : 50 Compare and contrast Mitosis and Meiosis. Include the following: Characteristics 1 Type of Cell 2 Number of Stages (does not include Interphase or Cytokinesis) 3 Number of Daughter Cells 4 Relative (to parent cell) Amount of Genetic Information (# of chrom.) 5 Daughter Cells Haploid or Diploid ANSWER Reproduction : 50 - Answer Characteristics Mitosis Meiosis Type of Cell Somatic (Body cell) Gamete (Sex cell) Number of Stages (does not include Interphase or Cytokinesis) 4 Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase 8 Prophase I & II, Metaphase I & II, Anaphase I & II, Telophase I & II Number of Daughter Cells 2 4 Relative (to parent cells) Amount of Genetic Information (# of chrom.) Identical Half Daughter Cells Haploid or Diploid Diploid Haploid Karyotypes & Genetics : 10 In Nicotiana plants, the allele for green leaves (G) is dominant over the allele for yellow leaves (g). Make a Punnett square to show the cross for a GG plant and a Gg plant and write the genotypic and phenotypic ratios. ANSWER Karyotypes & Genetics : 10 Answer G g G GG Gg G GG Gg Genotypic Ratio – 2:2:0 or 1:1:0 Phenotypic Ratio – 4:0 or 1:0 Karyotypes & Genetics : 20 In rabbits, grey hair (G) is dominant to white hair (g). Also in rabbits, black eyes (B) are dominant to red eyes (b). Use a Punnett square to show a cross between a male rabbit with the genotype GGbb with a female rabbit with the genotype ggBb. ANSWER Karyotypes & Genetics : 20 Answer gB gB gb gb Gb GgBb GgBb Ggbb Ggbb Gb GgBb GgBb Ggbb Ggbb Gb GgBb GgBb Ggbb Ggbb Gb GgBb GgBb Ggbb Ggbb Karyotypes & Genetics : 30 What sex is the individual and what genetic disorder do they have? How do you know? ANSWER Karyotypes & Genetics : 30 Answer They are female. They have Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21) Karyotypes & Genetics : 40 In rabbits, grey hair (G) is dominant to white hair (g). Also in rabbits, black eyes (B) are dominant to red eyes (b). What would be the possible gametes for a rabbit with the genotype Ggbb? ANSWER Karyotypes & Genetics : 40 Answer Gametes for Ggbb: Gb gb (use FOIL to make sure you get all the combinations) Karyotypes & Genetics : 50 If the mother of a family is „normal‟ but carries the recessive gene for cystic fibrosis and the father is also normal and does not carry the gene for cystic fibrosis, what are the chances of them having a child with a cystic fibrosis? Cystic Fibrosis (has C.F. Disease) (f) Normal (no C.F. Disease) (F) ANSWER Karyotypes & Genetics : 50 Answer Mother: Ff F f Father: FF F FF Ff F FF Ff They have a 0% chance of having a child with Cystic Fibrosis because you need to have the genotype ff to express that trait. Evolution, Cladistics, Classification : 10 Name the levels of taxonomic groups from most broad to most specific. Which two are used for an organism‟s scientific name? ANSWER Evolution, Cladistics, Classification : 10 - Answer Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Genus and species used for scientific name. Evolution, Cladistics, Classification : 20 How does variation arise? (name 2) ANSWER Evolution, Cladistics, Classification : 20 - Answer Sexual Reproduction (Meiosis, fertilization) Mutations Genetic Drift (chance) Evolution, Cladistics, Classification : 30 Use the Peppered Moths to explain how natural selection can lead to the population changing over time. (Must represent all 3 tenets) ANSWER Evolution, Cladistics, Classification : 30 - Answer 1. The population of peppered moths grows larger than the environment can support (reaches/surpasses carrying capacity). They compete for resources. 2. Some are better suited for the environment: preindustrial revolution, light colored moths were more fit, post-IR the dark moths blended in better to the dark bark (differential survival). 3. The dark color was caused by a mutation BEFORE THE IR (IR doesn‟t cause the muation) which provided the population variation in color. This trait is heritable and is passed to the next generation and becomes more common thanks to differential reproduction. Evolution, Cladistics, Classification : 40 Describe an example of artificial selection. Who acts as the “environment” in this situation? ANSWER Evolution, Cladistics, Classification : 40 - Answer Dog breeding, selecting for specific traits in crops Humans are the manipulators – they act as the “environment” Evolution, Cladistics, Classification : 50 Based on the number of amino acid differences, which organism is most closely related to the human? Name 3 other pieces of evidence scientists could use to suggest common ancestry. Bird Macaque Dog Frog Lamprey ANSWER Evolution, Cladistics, Classification : 50 - Answer The macaque – it only has 8 different amino acids whereas the dog (the next closest) has 32. Other possible evidence: Fossils, homologous structures, vestigial structures, emryology Miscellaneous: 10 How is variation important for Darwin and Wallace‟s Theory of Natural Selection? What could happen if there is no variation in a population? ANSWER Miscellaneous: 10 - Answer Populations have variation for traits that allows some to be advantageous depending on the environment and those traits enable the organism to survive, reproduce, and pass on that beneficial trait to the next generation. Over time those traits become more common. If there is no variation it is possible that a population/species go extinct if the environment changes and the population cannot adapt. Miscellaneous: 20 Who committed the crime? How do you know? ANSWER Miscellaneous: 20 - Answer Bubba – his DNA fingerprint matches the DNA from the crime scene Miscellaneous: 30 Name three properties that affect the rate of movement of molecules through agarose gel. ANSWER Miscellaneous: 30 - Answer Size Charge Shape Molecular Weight Miscellaneous: 40 Draw a representation of the cell cycle labeling the various stages. Circle the stage in which DNA is replicated. ANSWER Miscellaneous: 40 - Answer Miscellaneous: 50 Name the 6 kingdoms and an important characteristic for EACH. ANSWER Miscellaneous: 50 - Answer Eubacteria – very diverse, includes “bad” types Archaebacteria – extremophiles, includes “good” types Protista – mostly unicellular, found anywhere with water Plantae – autotrophs (capture light energy to make own food) Fungi – secrete enzymes to digest externally, decomposers Animalia – ingest and digest food within specialized cavities, sexual reproduction