Sex-Linked Traits, Polygenic Inheritance, and Dihybrid Crosses
advertisement
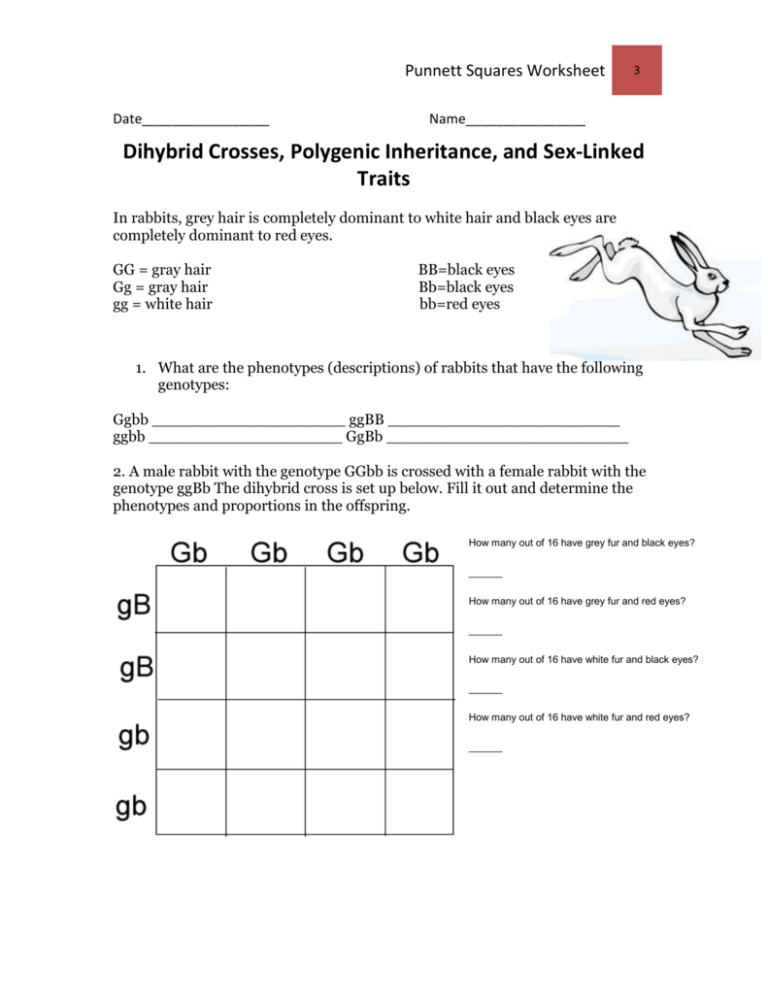
Punnett Squares Worksheet Date_________________ 3 Name________________ Dihybrid Crosses, Polygenic Inheritance, and Sex-Linked Traits In rabbits, grey hair is completely dominant to white hair and black eyes are completely dominant to red eyes. GG = gray hair Gg = gray hair gg = white hair BB=black eyes Bb=black eyes bb=red eyes 1. What are the phenotypes (descriptions) of rabbits that have the following genotypes: Ggbb ____________________ ggBB ________________________ ggbb ____________________ GgBb _________________________ 2. A male rabbit with the genotype GGbb is crossed with a female rabbit with the genotype ggBb The dihybrid cross is set up below. Fill it out and determine the phenotypes and proportions in the offspring. How many out of 16 have grey fur and black eyes? ______ How many out of 16 have grey fur and red eyes? ______ How many out of 16 have white fur and black eyes? ______ How many out of 16 have white fur and red eyes? ______ Punnett Squares Worksheet 3 3. A male rabbit has the genotype GgBb . Determine the gametes produced by this rabbit (the sperm would have these combinations of alleles) Hint there are 4 combinations. 4. A female rabbit has the genotype ggBB. Determine the gametes produced by this rabbit (the eggs would have these combinations of alleles) Hint there are 4 combinations. 5. Use the gametes from #3 and #4 to set up the dihybrid cross below. Put the male's gametes on the top and the female's gametes down the side. Then fill out the square and determine what kind of offspring would be produced from this cross and in what proportion. What is the likelihood this pair of rabbits would produce a baby with the genotype ggBb? Show your work! 6. A tall, yellow-seeded pea plant heterozygous for height and seed color (TtYy) is crossed with a tall, green-seeded pea plant that is heterozygous for height but homozygous recessive for seed color (Ttyy). If 80 offspring are produced, how many are expected to be tall and have yellow seeds? Show your work! Punnett Squares Worksheet 3 7. Hospital Mix-up Problem: There is another gene that codes for another, different antigen that also occurs on the surface of our Red blood cells, and technically, that gene also has multiple alleles. However, most people either have or do not have one particular allele called the “d” allele. This gene codes for an antigen that is called “Rh factor” because it was first discovered in Rhesus monkeys. People who have instructions to “make d antigen” are referred to as Rh+ (the allele is often symbolized by the letter “R”), while those who have “I don’t know how to make d antigen” instructions are called Rh– (the allele can be symbolized by “r”). Since this is a totally separate gene than the ABO blood group, if you’re doing a genetic cross that involves both ABO and Rh, that would be a dihybrid cross. Ms. Johnston, Ms. Johnson, and Ms. Johnstone all entered the same hospital and gave birth to baby girls on the same day, and all three babies were taken to the nursery to receive care, there. Someone later claimed that the hospital mixed up the babies. As a hospital administrator, it is your job to make sure that each pair of parents has the correct baby, so you order blood typing to be done on all the parents and all the babies. Here are the results: Ms. Johnston A+ Mr. Johnston B+ Ms. Johnson B- Mr. Johnson O+ Ms. Johnstone A+ Mr. Johnstone A- Baby 1 O+ Baby 2 AB- Baby 3 B- Your task: Create dihybrid crosses for each of the couples listed above and use your results to determine which baby belongs to each of the couples. Show your work! Punnett Squares Worksheet 3 8. In humans, one of the genes determining color vision is located on the X chromosome. This is a sex-linked trait. The dominant allele (C) produces normal color vision; red-green color blindness (c) is recessive. If a man with normal color vision marries a color-blind woman, what is the probability of their having a color-blind son? Show your work! A color-blind daughter? 9. In humans, normal color vision (C) dominates red-green colorblindness (c). Two parents produce daughters who are all carriers and sons who are all normal. What are the probable genotypes of the parents? Show your work! 10. In the couple described in the last problem, the woman gives birth to a color-blind but otherwise normal daughter. The husband sues for a divorce on the grounds of adultery. Will his case stand up in court? Explain and show your work! 11. Kathleen’s brown cat has kittens. The mother cat is heterozygous for coat color and the father cat is also. White coats are recessive. What are the chances they will have a female, white kitten? Show your work!