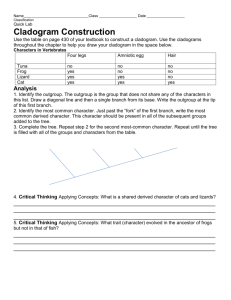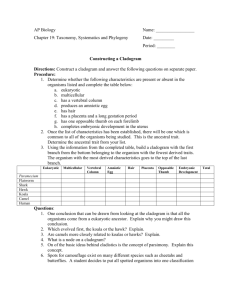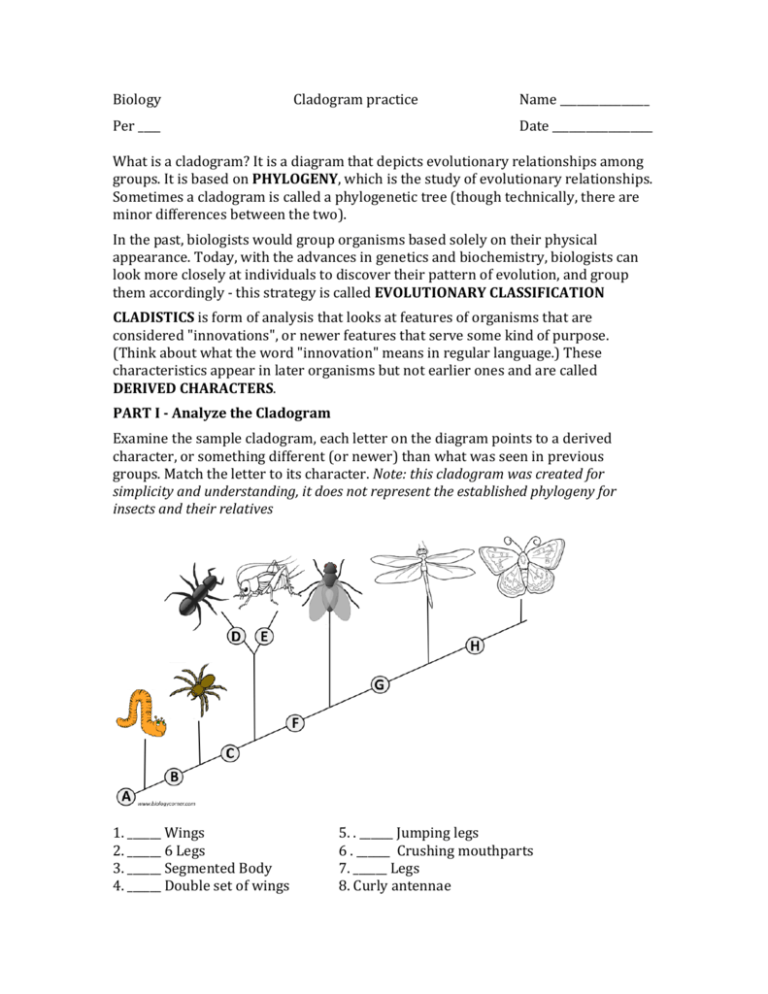
Biology Cladogram practice Name ________________ Per ____ Date __________________ What is a cladogram? It is a diagram that depicts evolutionary relationships among groups. It is based on PHYLOGENY, which is the study of evolutionary relationships. Sometimes a cladogram is called a phylogenetic tree (though technically, there are minor differences between the two). In the past, biologists would group organisms based solely on their physical appearance. Today, with the advances in genetics and biochemistry, biologists can look more closely at individuals to discover their pattern of evolution, and group them accordingly -­‐ this strategy is called EVOLUTIONARY CLASSIFICATION CLADISTICS is form of analysis that looks at features of organisms that are considered "innovations", or newer features that serve some kind of purpose. (Think about what the word "innovation" means in regular language.) These characteristics appear in later organisms but not earlier ones and are called DERIVED CHARACTERS. PART I -­ Analyze the Cladogram Examine the sample cladogram, each letter on the diagram points to a derived character, or something different (or newer) than what was seen in previous groups. Match the letter to its character. Note: this cladogram was created for simplicity and understanding, it does not represent the established phylogeny for insects and their relatives 1. ______ Wings 2. ______ 6 Legs 3. ______ Segmented Body 4. ______ Double set of wings 5. . ______ Jumping legs 6 . ______ Crushing mouthparts 7. ______ Legs 8. Curly antennae PART II -­ Create Your Own Cladogram To make a cladogram, you must first look at the animals you are studying and establish characteristics that they share and ones that are unique to each group. For the animals on the table, indicate whether the characteristic is present or not. Based on that chart, create a cladogram like the one pictured above Cells
Backbone
Legs
Hair
Opposable Thumbs
Slug
Catfish
Frog
Tiger
Human
DRAWING OF YOUR CLADOGRAM
Convert the following data table into a Venn diagram, and then into a cladogram:
Characters Sponge Cells with X flagella Symmetry Bilateral symmetry Mesoderm Head develops first Anus develops first Segemented body Calcified shell Chitonous exoskeleton Water-­‐
vascular system Vertebrae Venn diagram Jellyfish Flatworm Earthworm Snail Fruitfly Starfish Human X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X (X) X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X Cladogram The Molecular Connection 1. Find the human, rhesus monkey, kangaroo, snapping turtle, bullfrog, and tuna on the "Amino Acid Sequences in Cytochrome-­‐C Proteins from 20 Different Species" chart provided and underline their names. 2. Compare the human amino acid sequence with each of these five animals by counting the number of times an amino acid in that animal’s cytochrome c is different from the amino acid in that same position of the human sequence. For example, the number of differences between human and dog=10. Write that information below: Number of amino acid differences between human and • Rhesus monkey= • Kangaroo= • Snapping turtle= • Bullfrog=
• Tuna=
• Snapping turtle=
• Bullfrog=
• Tuna=
3. The cladogram diagram below shows the relationship of selected animals based 3. The cladogram diagram below shows the relationship of selected animals based on their shared
on their shared anatomical features. For example, out of seven key traits, all of these anatomical features. For example, out of seven key traits, all of these animals have a dorsal nerve
animals have a dorsal nerve cord, but only humans, monkeys and kangaroos have cord, but only humans, monkeys and kangaroos have mammary glands.
mammary glands. CLADOGRAM
LAMPREY
TUNA
BULLFROG
RHESUS
SNAPPING
TURTLE KANGAROO MONKEY
HUMAN
Foramen magnum forward
+ short canine teeth
Placenta
Mammary glands
Amnion
Paired legs
Paired appendages + spinal column
Dorsal Nerve cord + notochord
Record the total number of amino acid differences between humans and each Record
theshown total number
humans
and each
below.
animal below. ofWamino
rite yacid
our differences
answer i1n between
the hexagon below the animal
arrow shown
pointing to Write
your
answer
in
the
hexagon
below
the
arrow
pointing
to
the
name
of
that
animal.
WGBH
Educational Foundation and Clear Blue Sky Productions, Inc. All rights reserved.
the name ©2001
of that animal. CLADOGRAM
LAMPREY
TUNA
BULLFROG
RHESUS
SNAPPING
TURTLE KANGAROO MONKEY
HUMAN
4.4.Does
Doesthe
thedata
datafrom
fromthe
theamino
aminoacid
acidsequence
sequencegenerally
generallyagree
agree with
with the
the anatomical
anatomical data
data that
waswas
used
to make
thethe
cladogram?
that
used
to make
cladogram?
5. Do organisms with fewer shared anatomical traits also have more amino acid differences?
5. Do organisms with fewer shared anatomical traits also have more amino acid
differences?
6. Based on the molecular data, how does the "human-monkey" relationship compare to
the "duck-chicken" relationship (which shows three amino acid differences)?
20
30
40
50
- - - - - - - - G D V E K G K K I F I M K C S Q C H T V E K G G K H K T G P N L H G L F G R K T G Q A P G Y S Y T A A
- - - - - - - - G D V E K G K K I F I M K C S Q C H T V E K G G K H K T G P N L H G L F G R K T G Q A P G Y S Y T A A
- - - - - - - - G D V E K G K K I F V Q K C A Q C H T V E K G G K H K T G P N L H G L F G R K T G Q A P G F T Y T D A
- - - - - - - - G D V E K G K K I F V Q K C A Q C H T V E K G G K H K T G P N L H G L F G R K T G Q A P G F S Y T D A
- - - - - - - - G D V E K G K K I F V Q K C A Q C H T V E K G G K H K T G P N L H G L F G R K T G Q A P G F S Y T D A
- - - - - - - - G D V E K G K K I F V Q K C A Q C H T V E K G G K H K T G P N L H G L F G R K T G Q A V G F S Y T D A
- - - - - - - - G D V E K G K K I F V Q K C A Q C H T V E K G G K H K T G P N L H G L F G R K T G Q A V G F S Y T D A
- - - - - - - - G D V E K G K K I F V Q K C A Q C H T V E K G G K H K T G P N L N G I F G R K T G Q A P G F T Y T D A
- - - - - - - - G D I E K G K K I F V Q K C S Q C H T V E K G G K H K T G P N L H G L F G R K T G Q A E G F S Y T D A
- - - - - - - - G D I E K G K K I F V Q K C S O C H T V E K G G K H K T G P N L H G I F G R K T G Q A E G F S Y T D A
- - - - - - - - G D V E K G K K I F V Q K C S Q C H T V E K G G K H K T G P N L H G L F G R K T G Q A E G F S Y T D A
- - - - - - - - G D V E K G K K I F V Q K C A Q C H T V E K G G K H K T G P N L N G L I G R K T G Q A E G F S Y T E A
- - - - - - - - G D V E K G K K I F V Q K C A Q C H T C E K G G K H K V G P N L Y G L I G R K T G Q A A G F S Y T D A
- - - - - - - - G D V A K G K K T F V Q K C A Q C H T V E N G G K H K V G P N L W G L F G R K T G Q A E G Y S Y T D A
- - - - G V P A G D V E K G K K I F V Q R C A Q C H T V E A G G K H K V G P N L H G L F G R K T G Q A A G F A Y T N A
- - - - G V P A G N A E N G K K I F V Q R C A Q C H T V E A G G K H K V G P N L H G F Y G R K T G Q A P G F S Y S N A
A S F S E A P P G N P D A G A K I F K T K C A Q C H T V D A G A G H K Q G P N L H G L F G R Q S G T T A G Y S Y S A A
- - - - G F S A G D S K K G A N L F K T R C A E C H G E G G N L T Q K I G P A L H G L F G R K T G S V D G Y A Y T D A
- - - T E F K A G S A K K G A T L F K T R C E L C H T V E K G G P H K V G P N L H G I F G R H S G Q A Q G Y S Y T D A
- - P A P F E 0 G S A K K G A T L F K T R C A E C H T I E A G G P H K V G P N L H G I F S R H S G Q A Q G Y S Y T D A
[CONTINUED FROM ABOVE]
60
70
80
90
100
110
AMINO ACID SYMBOLS
Amino Acid Number-----> 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2
A = Alanine
C = Cysteine
Human ............ N K N K G I I W G E D T L M E Y L E N P K K Y I P G T K M I F V G I K K K E E R A D L I A Y L K K A T N E
D = Aspartic acid
Rhesus monkey.....N K N K G I T W G E D T L M E Y L E N P K K Y I P G T K M I F V G I K K K E E R A D L I A Y L K K A T N E
E = Glutamic acid
Horse ............N K N K G I T W K E E T L M E Y L E N P K K Y I P G T K M I F A G I K K K T E R E D L I A Y L K K A T N E
F = Phenylalanine
Pig, cow, sheep...N K N K G I T W G E E T L M E Y L E N P K K Y I P G T K M I F A G I K K K G E R E D L I A Y L K K A T N E
G = Glycine
Dog...............N K N K G I T W G E E T L M E Y L E N P K K Y I P G T K M I F A G I K K T G E R A D L I A Y L K K A T K E
H = Histidine
Gray whale........N K N K G I T W G E E T L M E Y L E N P K K Y I P G T K M I F A G I K K K G E R A D L I A Y L K K A T N E
I = Isoleucine
Rabbit............N K N K G I T W G E D T L M E Y L E N P K K Y I P G T K M I F A G I K K K D E R A D L I A Y L K K A T N E
K = Lysine
Kangaroo..........N K N K G I I W G E D T L M E Y L E N P K K Y I P G T K M I F A G I K K K G E R A D L I A Y L K K A T N E
L = Leucine
Chicken, Turkey...N K N K G I T W G E D T L M E Y L E N P K K Y I P G T K M I F A G I K K K S E R V D L I A Y L K D A T S K
M = Methionine
Penguin...........N K N K G I T W G E D T L M E Y L E N P K K Y I P G T K M I F A G I K K K S E R A D L I A Y L K D A T S K
N = Asparagine
Pekin duck........N K N K G I T W G E D T L M E Y L E N P K K Y I P G T K M I F A G I K K K S E R A D L I A Y L K D A T A K
P = Proline
Snapping turtle...N K N K G I T W G E E T L M E Y L E N P K K Y I P G T K M I F A G I K K K A E R A D L I A Y L K D A T S K
Q = Glutamine
Bullfrog..........N K N K G I T W G E D T L M E Y L E N P K K Y I P G T K M I F A G I K K K G E R Q D L I A Y L K S A C S K
R = Arginine
Tuna..............N K S K G I V W N N D T L M E Y L E N P K K Y I P G T K M I F A G I K K K G E R Q D L V A Y L K S A T S S = Serine
Screwworm fly.....N K A K G I T W Q D D T L F E Y L E N P K K Y I P G T K M I F A G L K K P N E R G D L I A Y L K S A T K T = Threonine
Silkworm moth.....N K A K G I T W G D D T L F E Y L E N P K K Y I P G T K M V F A G L K K A N E R A D L I A Y L K E S T K V = Valine
Wheat ............N K N K A V E W E E N T L Y D Y L L N P K K Y I P G T K M V F P G L K K P Q D R A D L I A Y L K K A T S S
W = Tryptohpan
Fungus 1 (Neurospora) N K Q K G I T W D E N T L F E Y L E N P K K Y I P G T K M A F G G L K K D K D R N D I I T F M K E A T A Y = Tyrosine
Fungus 2 (bkrs yeast) N I K K N V L W D E N N M S E Y L T N P K K Y I P G T K M A F G G L K K E K D R N D L I T Y L K K A C E Fungus 3 (Candida)
N K R A G V E W A E P T M S D Y L E N P K K Y I P G T K M A F G G L K K A K D R N D L V T Y M L E A S K Symbols in light blue or gray represent amino acids which show NO differences in any organism on the list, so you can ignore them.
(adapted from Strahler, Arthur, Science & Earth History, 1987, p. 348)
Human ............
Rhesus monkey.....
Horse ...........
Pig, cow, sheep...
Dog..............
Gray whale ......
Rabbit............
Kangaroo..........
Chicken, Turkey...
Penguin...........
Pekin duck........
Snapping turtle...
Bullfrog..........
Tuna..............
Screwworm fly.....
Silkworm moth.....
Wheat ............
Fungus (Neurospora)
Fungus(baker's yeast)
Fungus (Candida)
Amino Acid Number-----> 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10
AMINO ACID SEQUENCES IN CYTOCHROME-C PROTEINS FROM 20 DIFFERENT SPECIES