Third Grade Science
advertisement

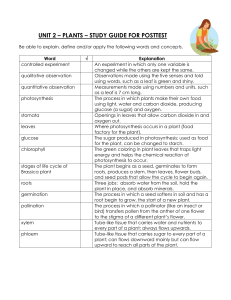
Third Grade Science PLANTS Table of Contents Introduction K-W-L Slide 3 Plant Parts Slides 4 - 13 Plant Life Cycle Slides 14 - 23 Plants and the Environment Slides 24 - 30 Plant Project Slides 30-32 K-W-L Use the K-W-L chart to brainstorm about plants. Plant Parts: Take a break and observe the inside of a seed. Now fill in the parts of a seed. PARTS OF A SEED: Plant Parts: Take a break and observe the roots of a plant. Plant Parts: Take a break and observe the stem of a plant. Plant Parts: Go to Slides 9 and 10 to learn about Photosynthesis! Go to Slide 11 to make a Photosynthesis factory. learn about Chlorophyll on slide 12! Photosynthesis: What is photosynthesis? Photo means “light” and synthesis means “to put together”. Photosynthesis means to put together with light. Photosynthesis is a process in which green plants use energy from the sun to transform water, carbon dioxide, and minerals into oxygen. Photosynthesis gives us most of the oxygen we need in order to breathe. We, in turn, exhale carbon dioxide that is needed by plants. Photosynthesis: Photosynthesis: Take a break and create a model of the “Photosynthesis Factory”. Chlorophyll: What is chlorophyll? Plants require light as a form of energy to develop and grow. The way this energy transfer happens is by using chlorophyll. Chlorophyll is the green pigment in plants that is used to trap energy from the sun. Each green part of a plant has chlorophyll. Chlorophyll helps plants absorb light and convert it into sugar through photosynthesis. It serves a key purpose in the food chain, not only by making food for plants, but by creating energy in plants for animals and humans to eat. Take a break and do a Chlorophyll rubbing. Plant Parts: Take a break and observe a Flower. PLANT LIFE CYCLE Take a break and actually plant some seeds so you can observe the plant life cycle. Assemble your Seed Observation Journal. PLANT LIFE CYCLE #1 Fill in your sequencing sheet: 1. Plants start out as seeds. A seed is planted in the soil. When it gets what it needs (water, sunlight, minerals from the soil) it will germinate. PLANT LIFE CYCLE: #2 Fill in your sequencing sheet: 2. From the seed, a tiny new plant, called a seedling, grows. You will notice roots, a curled stem and very small leaves. PLANT LIFE CYCLE: #3 YOUNG ADULT 3. Then roots grow down into the soil and the stem uncurls upward. leaves get bigger. PLANT LIFE CYCLE: #4 ADULT 4. Finally, more leaves grow and blossoms form on the plant. It is now mature. PLANT LIFE CYCLE – POLLINATION PLANT LIFE CYCLE: PARTS OF A FLOWER PLANT LIFE CYCLE: What do the flower parts do? Petals – attract pollinators with their shape, color and smell Stigma– receives the pollen from a visiting pollinator (female parts) Anther – pollen from these will stick to visiting pollinators so it can be carried to other flowers (male parts, together called stamen) Filament – holds the anther in place so the pollinator can get to the pollen (male parts, together called stamen) Sepal – protects the flower when it’s in the bud Ovary/Ovules – where the new plant is formed(female parts) Style – the stalk that supports the stigma PLANT LIFE CYCLE: PARTS OF A FLOWER PLANT LIFE CYCLE: PARTS OF A FLOWER Take a break and view some real photos of parts of a flower. Take a break and make a fold and learn about the parts of a flower. PLANTS AND THE ENVIRONMENT Check out what each plant part does to help the environment…. Leaves, twigs, branches… Leaves, twigs and branches are good at absorbing sound and block erosion-causing rainfall. They also provide shade and reduce the wind speed. Roots, leaves and trunks… Roots, leaves and trunks provide habitat for birds, animals and insects. Roots… Roots stabilize the soil and prevent erosion. Plants… Plants release oxygen after photosynthesis. Animals and people need oxygen to breathe. Fruit and Leaves… Fruit and leaves provide food for animals and people. Plants we Eat… Take a break and brainstorm ideas about the plant parts we eat. Fill in a sheet with your group. Plant Project…