Module 4
advertisement

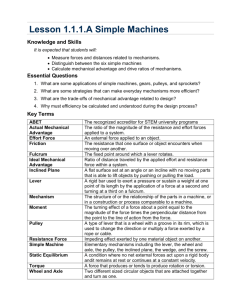
Module 6 MACHINES OVERVIEW People have been challenged to make their lives easier. One way to accomplish this was to invent tools that make jobs less difficult. These tools are machines. The tools most of us think about when we hear the word machine is actually a combination of two or more simple machines. In this module we will discuss fully and learn more about machines, its uses and importance. Scope of the Module Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Simple Machines Uses and Importance of Machines Safety Measures in Using Machines PRETEST Instruction: Which of these simple machines have you used in doing work? Tell how they helped you and your family. (15pts) _____________________ Hammer Scissors_____________________ _____________________Nails 1 Objectives Read the objectives to learn what you should be able to do in order to successfully complete this module. Identify and describe each of the six simple machines; Explain how each simple machines is used; Explain and apply the safety measures in handling machines. Learning Resources You can consult these references for further reading: Coronel, et.al. (2006). Exploring and Protecting Our World 5. Quezon City: Vibal Publishing House, Inc. Domanais, et.al. (2004). Explore and Discover 5 . Philippines: Rex Book Store, Inc. Escalde and Rasalan. (2000). Science, Health and Environment 5. Quezon City: ABIVA Publishing House, Inc. Zablan. (2001). Science and Health 5. Quezon City Philippines: SIBS publishing House, Inc. http://www.twoheartsdesign.com/images/clipart/catholic/lent/06-nails.gif http://www.clipart.com Note: Try to visit the following underlined websites for further learnings. 2 Lesson I Simple Machines Weusesimplemachineseveryday. Wearedependentin simplemachinesin manyaspectsofourlives. Butdoyouknowwhatarethesesimplemachines? Simple Machines As their name implies, are simple. The basic parts of machines. A device that helps make man's work easier. It helps us use our muscle power better to do work. It provides force and controls the direction of force but it cannot create energy. Simple machines can include common tools like knives, tweezers, scissors, ice tongs and door handles. These simple machines are practically a part of every device you can think of. They can be part of complex devices like cars and airplanes. Compound Machines All machines, no matter how many parts they have, are made up of one or more simple machines. Such as bicycles that contain many simple machines. The wheels of bicycle are examples of wheel and axle. 3 Whatarethe6 SimpleMachines? The Six Simple Machines 1. Lever 2. Wheel and Axle 3. Pulley 4. Inclined Plane 5. Wedge 6. Screw Reminders: The wheel and axle and the pulley are different forms of the lever. The wedge and the screw are different forms of the inclined plane. In thenextpage,youwilllearnmore abouteachofthesixsimplemachines andtheirexamples. 4 Lever is a rigid bar, straight or curved, that is free to turn about a fixed point called the fulcrum. It has three parts: Resistance, Effort and Fulcrum 1. Resistance force or load – what is being moved or lifted 2. Effort force - the force that the lever exerts, or the work done on the lever 3. Fulcrum-the fixed pivot point Resistance Arm- is the distance from the fulcrum to the point where the resistance or load is located. Effort Arm – The distance from the fulcrum to the point where the effort is exerted Levers are divided into three classes depending on the positions of the effort. The three classes are: 1. First-class lever – the fulcrum is located anywhere between the effort (or force) and the resistance (or load) Examples are : seesaw, crowbar, scissors, pliers, claw hammers, tack puller, tin snips 5 2. Second-class lever – the resistance is located between the effort and the fulcrum. Examples are: wheelbarrow, nutcracker, bottle opener, water pump 3. Third-class lever - the effort is located between the resistance and the fulcrum. Examples are: broom, shovel, fishing pole, tongs, tweezers, baseball bat Wheel and Axle Is a machine where a large wheel is connected to a smaller wheel or shaft called an axle. When either the wheel or the axle turns, the other part also turns. One complete turn of the wheel produces one complete turn of the axle. The wheel does not have to be a complete wheel. Instead, there may be a crank that turns and, when it turns, it makes a complete circle, just as if it were a complete wheel. The wheel and axle is basically a modified lever. The center of the axle serves as a fulcrum, making the wheel a lever that rotates around in a circle. The radius of the wheel is the effort arm and radius of the axle, the resistance arm of the lever. Examples of wheel and axle containing a crank instead of a complete wheel are pencil sharpeners, meat grinders and egg beaters. 6 The wheel and axle can change the direction of a force. Examples of wheel and axle containing complete wheels are automobile steering wheels, door knobs, gear wheels of bicycle and screw drivers. Pulley Is a wheel that turns around an axle. Usually there is a groove in the rim of the pulley so that the rope around the pulley will not slip off. The 3 types of a pulley are: fixed, movable or a combination of both called block and tackle. 1. Fixed Pulley – does not move, acts like a turning first-class lever, used with flagpoles, clothes lines, curtain rods. 2. Movable Pulley – moves along the rope, does not change the direction of the force, acts like a turning second class lever. 3. Block and Tackle – each fixed pulley changes the direction of the force and each movable pulley changes the amount of the force. - the more movable pulleys used, the less force will be needed. - used in scaffolds for painters and for billboard poster men Fixed 7 Inclined Plane Is a slanting surface that is raised at one end used for raising heavy objects It is a simple machine that gives us a gain force. Less force is used in getting an object up to the higher end of an inclined plane if the object is to be lifted directly from the lower level up to the raised end. The gain force means a longer distance for the object to travel up an inclined plane. The longer the inclined plane, the more gradual the slope becomes, and less force will be needed to move the object up the incline. The shorter the inclined plane, the steeper the slope becomes, and more force will be needed to move the object up the incline. Examples are : the plank, the sloping floor of a theater ot auditorium, a zigzag road up a mountain and stairway. Wedge Is a form of inclined plane that tapers to a sharp edge. It can be one sloping surface ( a single inclined plane) or two sloping surfaces ( a double inclined plane). It is used either to spread an object apart or raise an object. 8 The incline moves into or under the objects. The wedge gives us a gain in force and also changes the direction of the force. The longer or thinner the wedge, the greater the gain force. Examples of the wedge are the ax, knife blade, scissors blade, chisel, pin, nail and plow Screw Is a form of inclined plane wrapped in a spiral around a cylinder post. Is composed of the body (the cylinder post) and the thread, which is the spiral ridge of the screw. The threads form a tiny ramp that run around the screw from the tip to near the top. One complete turn of a screw moves it into the object a distance from one thread to another. Pitch of the screw – the distance between two consecutive thread. Example of screw are: nuts and bolts used to fasten things, drill bits used to make holes, jacks crew used to lift heavy objects, caps of jars, base of the electric light bulb. 9 Self Test Score: I. Instruction: Answer the following questions. 1. What is the difference between a simple and a compound machine? _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ 2. Describe each of the six simple machines. _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ 3. Describe the difference between a fixed and a movable pulley. _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ 4. How are the wedge and screw related to the inclined plane? _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ 10 Lesson 2 Uses and Importance of Machines Itisstatedin Lesson1,thatweare dependentonmachines,weuseiteveryday, anditisveryhelpful. Howcanmachineshelpus? Here are some ways: You need a bottle opener to open a soft drink bottle. A carpenter needs a hammer to separate two boards that have been nailed together incorrectly. A furniture mover needs to use a ramp to bring up a heavy cabinet into the back of a truck. Your father needs a jack to change a flat tire. Wow!Thosearejusta fewexamplesthatproves machinesarereallyhelpfulin manyways. Couldyouthinkoftheotheruses? 11 Man did not start using machines today. The machines that are used today have surely developed from what had already been invented in the past. In ancient times, logs were used to move huge rocks by rolling them along and these logs became the wheel and axle at around 3000 B.C. The lever before is just a large stick used to move heavy objects like rocks. The wedge before is a sharp piece of stone or rock that was used to scrape animal skins The Great Pyramids in Egypt were built using inclined planes and rollers to move 2.5 million limestone blocks some hundreds of miles over 20 years. The levers, rollers and pulleys were used to build Stonehenge in England. Simple machines were used to build magnificent buildings throughout all the early civilizations. How Can Machines Help Us? Machines can help us in four ways: 1. All machines can transfer a force from one place to another. 2. Some machines can increase the amount of a force so that we can lift heavier objects or exert greater force with the machines than we could with out it. 3. Some machines can change the direction of a force so that we can make objects move in different directions. 4. Some machines can increase the distance and speed of a force so that we can move things farther and faster. 5. Machines help make work easier but machines do not save work. 6. Machines enable people to do work with less muscular effort with greater speed. 12 How Helpful Is A Machine? Two types of work are involved in using a machine. Work Input – work that goes into the machine. It comes from the force that is applied to the machine, or the effort force. The machine does work too. It exerts a force, called an output force, over some distance. The work output is used to overcome that force you and the machine are working against. The work output is always less than the work input because of friction. Friction- is the force that acts in the opposite direction of motion and can cause an object to slow down and finally stop. Some of the work the machine does is used to overcome friction. 13 Assignment Score: I. Instruction: Identify what kind of simple machine is each of the following and give its uses. 1. Playground slide _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ 2. steering wheels of motor vehicles _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ 3. modeling ramp _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ 4. teeth _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ 5. needle _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ 14 Lesson 3 Safety Measures in Using Machines Can youplunka nailin woodwithyourbarehands? Ofcoursenot! So,thehammercanenableyoutodosomethingyou cannotdowithyourbarehands.Butthehammercan harmyou.Wouldyouagreewithme? Youmightaccidentalyhityourfingerwhiledrivinga nailwitha hammer.Anditmighthityourfootifyou accidentalydropit. While machines are very useful to us, their use can create risks if not properly handled. See the next page for some examples of risks from using work equipment or machines. 15 Some Examples or Risks 1. Using the wrong tool/machine for the job. Like using a ladder to do a long or detailed work at high place instead of an access tower. 2. Lack of guards or poor guards on machines can cause entanglement, crushing, trapping or cutting. A plastic guard is used to prevent possible cutting of fingers and other materials by the revolving blade. 3. Having inadequate controls or the wrong kind of controls needed to turn off machines quickly and safely. 4. In adequate or lack of necessary training, instruction and information for workers using equipment. Manythingscanbedonetoreducethedanger orharmfromusingworktools,equipmentsor machines.Itisbesttoremembertousetheright equipmentforthetaskandtomakesureitissafe touse. Some Safety Measures in Using Work Equipments 1. Fixed guards should be used whenever possible. 2. Control switches must be clearly marked to show that they do and don't do. 3. A competent person must be able to do a regular and thorough checkup of special kinds of machines such as the ones needed to lift equipment and passengers, scaffolding and power presses. 4. Only tools in good condition should be used. 5. Protective clothing and gadgets should be worn, if necessary. 6. Wedges should be carried with the sharp edge pointing downward. 16 7. Tools should be kept in a box or tool cabinet. 8. The sharp edges of garden tools that are temporarily not used should point downward. 9. Be sure that any simple machine is in good condition before using them. Reminder: “USE MACHINES PROPERLY TO AVOID ACCIDENTS” Instructions: Choose among six (6) simple machines, and improvised your own machine. You can make a toy, decorations, or anything useful using whatever is available. Be creative and resourceful On a separate sheet of paper, indicate the details of your project. Follow the format below: Type of Machine : Inclined Plane Materials : Block of wood Hook Decorations Uses : Raising heavy objects Student's Name : Xyle Castro Date Submitted : (m/d/y) Teacher's Name : Ginabel Bagtasos 17 SUMMARY A simple machine is a device that makes man's work easier. Machines help make work easier but do not save work. Some machines can: - transfer a force from one place to another - increase the amount of force - change direction of a force - increase the distance or speed of a force The six simple machines are classified into two main categories: levers and inclined planes. The pulley and wheel and axle are some forms of levers, while the wedge and screw are some forms of inclined planes. Levers are divided into three classes depending on the positions of the effort, resistance and fulcrum. They are named as: - First class levers where the fulcrum is between effort and resistance. - Second class levers where the resistance is between effort and fulcrum - Third class levers where the effort is between resistance and fulcrum A pulley maybe fixed, movable, or a combination of both fixed and movable called block and tackle. Safety measure should be considered in using machines to prevent risks that improper use can bring. Prepared By: Mrs. Ginabel C. Bagtasos Science Teacher Email Add: qwerbelle@yahoo.com 18