Review Vocab and Terms For Work, Power and Simple Machines
advertisement

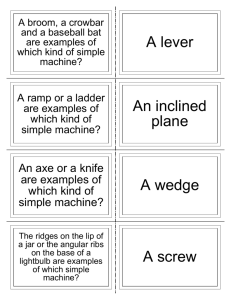
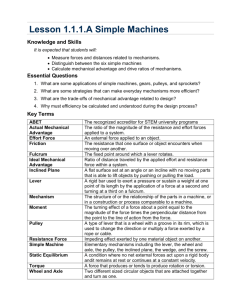
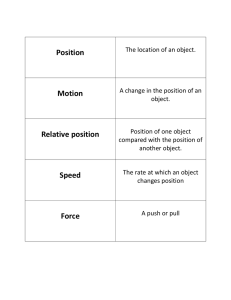
Unit 3 – Work, Power and Simple Machines NYS Standards: 5.2c Machines transfer mechanical energy from one object to another. 5.2e A machine can be made more efficient by reducing friction. Some common ways to reduce friction include lubricating and waxing surfaces. 5.2f Machines can change the direction or amount of force, or the distance or speed of force required to do work. 5.5g Simple machines include a lever, a pulley, a wheel and axle, and an inclined plane. A complex simple machine uses a combination of interacting simple machines. Ex: a bicycle Work -Occurs when a force causes an object to move in the direction of the force applied. There are two characteristics to determine if work is being done o 1. The object moves when a force is applied. o 2. The object moves in the same direction that the force is applied. Examples of work being done Pushing a desk Pushing a shopping cart Lifting a box Pulling a cart Examples of work not being done Trying to push a car and it does not move. Lifting a box and then walking with the box in your hands. Is this Work or No Work? Is this work? This is not work because the direction of the force to lift the bag and the direction of motion are not in the same direction. Calculating Work o Work = Force (N) X Distance (m) o The Unit for work is the Joules (J) Example A man applies a force of 5.0 N to push a truck 10.0m down the street. How much work does the man do? W=FxD W = 5.0N x 10.0m W = 50.0J Power -The rate at which work is done. There are two ways to increase power. o 1. Increase the work being done. o 2. Decrease the time it takes to do the work. Calculating Power o Power = Work (J) ÷ Time (s) o The Unit for power is the Watts (W) Example What is the power of a small motor that can do 2500.0J of work in 10.0 seconds? P=W÷T W = 2500.0J ÷ 10.0m W = 250.0W Simple Machines Machines transfer mechanical energy from one object to another. Machines also: Change the direction of a force. Change the amount of force. Change the distance or speed of force. Mechanical Advantage – Home many times the machine multiplies force. The larger the mechanical advantage….the easier a machine makes your work. -The main types of Simple Machines are: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Lever Pulley Wheel and Axle Inclined Plane Wedge Screw Lever – A simple machine consisting of a bar that pivots at a fixed point. o Fulcrum is the pivot point. o There are three classes of levers. 1st class lever – Ex. Seesaw 2nd class lever – Ex. Wheel barrel 3rd class lever – Ex. Arm Wheel and Axle – Consists of two circular objects of different sizes. The wheel allows the individual to spin the axle easier. Pulley – Consists of a grooved wheel that holds a rope or a cable. Inclined Plane – A simple machine that is a straight slanted surface. o The longer an inclined plane is compared to its height, the greater the mechanical advantage. Wedge – An inclined plane that moves. Screw – An inclined plane wrapped around a cylinder or post. Compound Machine Machines that are made of two or more simple machines. The more moving part, the more mechanical advantage. Efficiency in Machines Machines can be made more efficient by reducing friction. Lubricants are substances that are applied to surfaces to reduce friction between them.