Density of Common Substances
advertisement

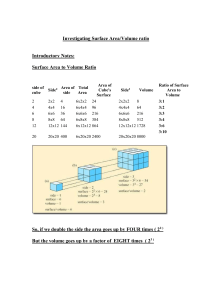
Float, Sink or ????? Student Name __Amy Wilson______________________ Ed. 2520 Directions: Write your response to each question in the space provided after determining if the ice in each beaker was observed to float, sink, or do another action. Be sure to provide a written justification for your response. 1. Using complete sentences, write the reason(s) why you feel you observed the ice to interact differently with the fluid in each of the three beakers? The ice interacted differently with each of the fluids in the beakers because the beakers contained varying fluids. The different fluids in the beakers lead to the ice melting at different rates and sink or float on the surface of the fluid. 2. What fluids have you determined are in each of the beakers? Beaker A __water_____________ Beaker B__vinegar______________ Beaker C __gel_______________ In the space provided, write using complete sentences, at least one justification for the fluid you determined to be in each of the three (3) beakers. My group decided that beaker A was, in fact, water because it was clear and had no distinct odor. We also came to the conclusion that beaker B contained vinegar, mainly because it had an odor that resembled vinegar. Finally, we decided beaker C had some sort of gel because the fluid was very dense and the ice fell in the beaker at a much slower rate because of its consistency. 3. Using the accompanying Density Chart of Common Substances found below and your responses to Question #2, what numerical densities represent the fluids in Beakers A, B, & C? Beaker A _1.00 g/ml___________________ Beaker B_0.78 g/ml______________ Beaker C _> 1.10 g/ml_________________ Density of Common Substances 4. Substance Density (g/ml) Cork 0.22 – 0.26 Pine (wood) 0.373 Ethanol Alcohol 0.78 Ice 0.917 Fresh Water 1.00 Mystery Fluid >1.10 Slate (rock) 2.6 – 3.33 Using any reference resource(s) find, then write in the available space, a general definition and arithmetic formula for DENSITY. Definition: How much something of a set volume weighs. Formula: Density = Mass/Volume (d=m/v) http://www.green-planet-solar-energy.com/definition-of-density.html 5. Write in two (2) or more complete sentences, a general statement relating to the interaction of solid materials whose density is greater than and less than of fresh water. An object that has a density less than fresh water, the object will float. An object that has a density more than fresh water, the object will sink. 6. In two (2) or more complete sentences, compare your response to Question #5 to the observations you made when cork, pine, and slate pieces were dropped into each of the beakers having a different fluid. In this response, also give a reason(s) why your Question #4 response does or does not agree with your observations. In the experiment, the slate sank to the bottom in all three of the beakers filled with varying fluids because it was denser than all three of the fluids given. Next, the cork floated when dropped in all three of the fluids because it was less dense than the three fluids. This relates with my answer to number four because if we were to follow through with the formula, the material’s mass per unit of volume is greater than the fluid, the object sinks, and if it is less, it will float. 7. Assignment: ● Complete Questions #1-#6. ● Design and provide a copy of a student response sheet for the observations, definitions, and measurements made during this activity. ● In writing, make two (2) suggestions how one might improve this activity. ● Due Date _____________________________________ Two suggestions on how to improve this activity: When putting the slate into the beakers, it was too big of a piece, so if the pieces were cut down into smaller chunks, this activity could be completed more smoothly. Also, the first group that went to observe the fluids did not know they were not supposed to touch the beakers to see the fluids’ consistency. This could be told to the class before anyone is sent up to observe the fluids so that everyone can make similar observations. Beaker A Beaker B Beaker C Cork Above 7mm 2mm 8mm Cork Below 3mm 3mm 6mm Pine Above 1mm 0 1mm Pine Below 1mm 3mm 1mm Slate Below 19mm 25mm n/a Without Ice Beaker Observations A -odorless -clear -resembles water B -has a smell that resembles vinegar -clear C -clear -appeared to be a much thicker consistency than the other two beakers -it had few bubbles throughout Adding the Ice Beaker Observations A -The ice stayed afloat on the surface, but some of it was below, resembling an iceberg -There were no bubbles present -Ice melted rapidly -The ice stayed floating near the side of the beaker B -Ice sunk in the beaker -The ice stayed near the side of the beaker -No bubbles were present C -Ice sunk in the beaker -Ice fell slower than the ice in beaker B -Ice rose back to the surface of the fluid -The ice melted rapidly, and the water created a ring on the surface, as if it would not mix well with the fluid in the beaker Name: Date: Student Response Sheet Density definition: _____________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ Density formula: ______________________________________________________________ Observations: Without Ice Beaker Observations A B C Once Ice is Added Beaker A B C Observations Student Response Sheet (cont’d.) Experiment Data: Beaker A Beaker B Beaker C Cork Above __mm __mm __mm Cork Below __mm __mm __mm Pine Above __mm __mm __mm Pine Below __mm __mm __mm Slate Below __mm __mm n/a