Cardiovascular System.key
advertisement

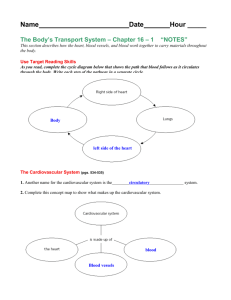
Cardiovascular System Blood vessels, heart and blood Functions • Transport oxygen, nutrients, waste, hormones • White blood cells fighting disease • Temperature regulation Blood vessels; Arteries • Arteries carry blood away from the heart • Most carry oxygen-rich blood (bright red) • except the pulmonary artery • Walls are thick and muscular • Arteries expand and relax as the heart beats • The pulse: pulse points on body surface • Arteries have high pressures Blood vessels: Veins • Veins carry blood back to the heart • Carry deoxygenated blood; little oxygen (dark reddish/blue) • except the pulmonary veins • Walls of veins are thin and pressures are low • Valves to prevent back flow of blood Blood Vessels; Capillaries • Capillaries; smallest blood vessels • Connect arteries and veins • Very thin walls – one cell layer • Diffusion of substances (e.g. oxygen) occurs through the walls Lymph Vessels • Lymph vessels travel near the veins • carry blood-like fluid; no red blood cells • These vessels empty into large veins • Lymph vessels pass through lymph nodes; of filter the lymph Heart • “cardia-” = heart • Location; slightly left of center in chest cavity; lungs on each side • Striated involuntary muscle; myocardium Heart myths • #1: I would know if I had high blood pressure or high cholesterol • #2: Heart disease treats men and women the same • #3: Younger Women Aren't at Risk • #4: Exercise is too risky if you have heart disease. • #5: Aspirin and Omega-3 fatty Acids Are All Good • #6: Once I Have Heart Disease, That's It Heart chambers contain blood • Left and right atrium (atria pl.); upper • Left and right ventricle; lower Heart valves • One way valves prevent blood back flow • As valves close, makes “lub-dupp” sound of the heart beat • Found between the atria and ventricles • Found between the ventricles and the arteries Normal Heart Sound 17 Heart murmur! valve doesn’t close properly 18 Aortic stenosis! narrowing of the aortic valve 19 Blood flow through heart • Superior & Inferior Vena Cava • Right atrium • Right ventricle • Pulmonary artery to lungs • Pulmonary veins • Left atrium • Left ventricle • Aorta to the body 21 • Vena Cava; deoxygenated blood • Pulmonary artery; deoxygenated • Pulmonary vein; oxygenated • Aorta; oxygenated Coronary arteries • These supply the heart muscle with oxygen and nutrients • What would happen if a coronary artery gets blocked? Heart Physiology • SA node is the pacemaker of the heart • Location; wall of the right atrium • SA node cardiac cells contract fastest • All cardiac cells are interconnected. • SA node sets the pace of the entire heart • about 60-80 beats per minute at rest. Heart Physiology • Heart muscle contraction is electrical • Monitored with electrodes • Recorded as an ECG or EKG - ElectroCardioGram Cardiac Cycle • One complete heart beat. • Systole = contraction phase – blood is ejected from the ventricles • Normal systolic pressure = 120 mm Hg Cardiac Cycle • Diastole = relaxation phase • Chambers refill with blood • Diastolic pressure is low in the heart • Normal is 80 mm Hg 30 Cardiovascular Pathology • Hypertension is continuous high blood pressure. • > 160/95 mm Hg • Affects 20 % of American Population Hypertension • Causes – – – – – heredity Obesity Stress Smoking Diet • Arteriosclerosis is “hardening” of the arteries • Associated with hypertension • Increased risk of an unwanted blood clot in the arteries Aneurysm • Weakening and ballooning of an artery • Associated with hypertension • Can lead to a burst artery Coronary Artery Disease • Excessive cholesterol build up in the arterial wall – especially the coronary arteries • Associated with saturated fats in the diet • Atherosclerosis – fatty plaques in the wall of an artery Heart Attack • Coronary arteries blocked; heart muscle dies from lack of oxygen and nutrients • Treatments – “clot busting” drugs – angioplasty to open up clogged arteries; – bypass surgery around the blockage Angina • Chest pains due to lack of oxygen in heart muscle cells • Often occurs after physical exertion • Forewarning of a possible heart attack 39 Varicose Veins • Damaged veins become distended • Damage to valves • Varicose veins near the anus are called hemorrhoids • Treatments – – – – anti-inflammatory drugs rest vein injections surgery