What is a wave?
advertisement

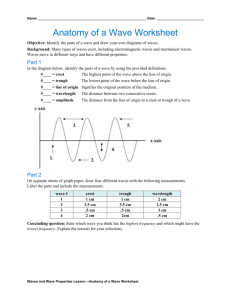
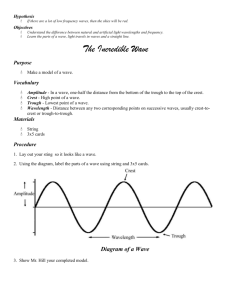
Waves What is a wave? How does it travel through space? Or is it around? Wave Transfer of energy through a medium by a disturbance. Disturbance can be repeating or a single event. Only medium is disturbed, energy is only seen in disturbance. Medium ­ substance or material through which a wave travels. Energy moves by causing a disturbance in the medium that propagates or travels through the material by movement of the medium atoms. Oscillation vs. Propagation Oscillation ­ motion that repeats in a regular cycle or time period. A sine curve shape is produced by the oscillation. Propagation ­ Transfer of energy through a medium from point to point. Energy transfers by particle vibrations http://illuminations.nctm.org/tools/soundwave/ Types of Waves Mechanical Waves ­ Caused by a disturbance of a medium by a vibration. Require a physical medium to transfer through. Speed is dependent on medium density and wave shape. Can be transverse or longitudinal. Example : Electromagnetic Waves ­ Transfer of energy through a vacuum. There is no 'physical' medium needed. A vibration of either the electric or magnetic fields. Can only be a transverse wave. Example: Anatomy of a Wave Parts, items and terms used to analyze a wave. - Line of Origin Fixed line that splits the wave in half creating a zero point for measurements. Line of Origin - Where is it above? Anatomy of a Wave Frequency ­ f ­ ­ # of complete oscillations passing a point in space in a given time ­ # oscillations per second Units : hertz (Hz) or cycles per second (s­1) Period ­ T ­ ­ Time for a single complete oscillation. ­ Units : seconds (s) Anatomy of a Wave Crest – point of maximum height above Line of Origin Trough – Point of lowest height below Line of Origin Where are they below? Crest Trough Anatomy of a Wave Amplitude – distance of crest or trough from the Line of Origin. It is the same above and below the line. Anatomy of a Wave Wavelength – Distance measured from crest to crest or trough to trough for a wave. Measured in meters. λ λ Types of Wave Waves are characterized by both what they move through and how their energy disturbs the medium they transmit through. Types of Waves Transverse Energy causes disturbance in medium perpendicular to direction of travel. Types of Waves Longitudinal Energy causes disturbance in medium parallel to direction of wave travel. Longitudinal Waves- usually created when a substance vibrates back and forth. Longitudinal waves do not have crest and troughs They have regions of: compression and rarefaction. Since Longitudinal Waves do not have easily identified crests and troughs, the wave is hard to analyze. Longitudinal waves are then converted into sine wave forms to allow easier analysis.