Types of Mollusks
advertisement

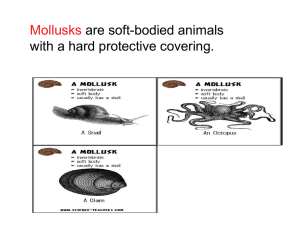
Types of Mollusks Jessica Harwood Douglas Wilkin, Ph.D. Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit www.ck12.org AUTHORS Jessica Harwood Douglas Wilkin, Ph.D. EDITOR Douglas Wilkin, Ph.D. CK-12 Foundation is a non-profit organization with a mission to reduce the cost of textbook materials for the K-12 market both in the U.S. and worldwide. Using an open-content, webbased collaborative model termed the FlexBook®textbook, CK-12 intends to pioneer the generation and distribution of high-quality educational content that will serve both as core text as well as provide an adaptive environment for learning, powered through the FlexBook Platform®. Copyright © 2015 CK-12 Foundation, www.ck12.org The names “CK-12” and “CK12” and associated logos and the terms “FlexBook®” and “FlexBook Platform®” (collectively “CK-12 Marks”) are trademarks and service marks of CK-12 Foundation and are protected by federal, state, and international laws. Any form of reproduction of this book in any format or medium, in whole or in sections must include the referral attribution link http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (placed in a visible location) in addition to the following terms. Except as otherwise noted, all CK-12 Content (including CK-12 Curriculum Material) is made available to Users in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC 3.0) License (http://creativecommons.org/ licenses/by-nc/3.0/), as amended and updated by Creative Commons from time to time (the “CC License”), which is incorporated herein by this reference. Complete terms can be found at http://www.ck12.org/about/ terms-of-use. Printed: March 2, 2015 CONTRIBUTORS Doris Kraus, Ph.D. Niamh Gray-Wilson Jean Brainard, Ph.D. Sarah Johnson Jane Willan Corliss Karasov www.ck12.org C HAPTER Chapter 1. Types of Mollusks 1 Types of Mollusks • Describe the different types of mollusks. • Distinguish gastropods from bivalves and from cephalopods. What’s the world’s largest mollusk? The colossal squid, one of the largest invertebrates, measures 14 feet in length here. Some of these squids are even larger and can grow up to almost 50 feet long! The smallest mollusks are snails that are microscopic in size. Types of Mollusks There are approximately 160,000 living species and probably 70,000 extinct species of mollusks. They are typically divided into ten classes, of which two are extinct. The major classes of living mollusks include gastropods, bivalves, and cephalopods ( Figure 1.1). Gastropods Gastropods include snails and slugs. They use their foot to crawl. They have a well-developed head. There are many thousands of species of sea snails and sea slugs, as well as freshwater snails, freshwater limpets, land snails and land slugs. Gastropods live in many diverse habitats, from gardens to deserts and mountains. They also live in rivers, lakes and the ocean. Most shelled gastropods have a one-piece shell that is typically coiled or spiraled. Gastropods have no sense of hearing, but they can see and have a keen sense of smell. In land-based gastropods, the olfactory organs (for smell) are the most important. These are located on the tentacles. Bivalves Bivalves include clams, scallops, oysters, and mussels. As their name implies, they have two parts of their shell, which can open and close. Bivalves live in both marine and freshwater habitats. Most bivalves have a pair of large 1 www.ck12.org gills that enable them to extract oxygen from the water (to breathe) and to capture food. Water is drawn into the bivalve and washes over the gills. Mucus on the gills helps capture food and cilia transfer the food particles to the mouth. Once in the mouth, food passes into the stomach to be digested. Bivalves have a mouth, heart, intestine, gills, and stomach, but no head. Bivalves have a muscular foot, which in many species such as clams, is used to anchor their body to a surface or dig down into the sand. Cephalopods Cephalopods include the octopus and squid. They have a prominent head and a well-developed brain. Typically the foot has been modified into a set of arms or tentacles. Members of this class can change color. They can also change texture and body shape, and, and if those camouflage techniques don’t work, they can still "disappear" in a cloud of ink. Cephalopods have three hearts that pump blue blood, they’re jet powered, and they’re found in all oceans of the world. Cephalopods are thought to be the most intelligent of invertebrates. They have eyes and other senses that rival those of humans. FIGURE 1.1 (left) An example of a gastropod species, the ostrich foot. (right) A Caribbean reef squid, an example of a cephalopod. Summary • Mollusks are divided into ten living classes, including the familiar gastropods, cephalopods, and bivalves. • Mollusks live in marine and freshwater habitats, as well as on land. Explore More Use the resources below to answer the questions that follow. • Mollusk Animation: Abalone Body Plan at http://vimeo.com/42588195 (1:22) MEDIA Click image to the left or use the URL below. URL: http://www.ck12.org/flx/render/embeddedobject/57281 • Mollusk Animation: Nautilus Body Plan at http://vimeo.com/42588196 (2:35) 2 www.ck12.org Chapter 1. Types of Mollusks MEDIA Click image to the left or use the URL below. URL: http://www.ck12.org/flx/render/embeddedobject/57282 • Mollusk Animation: Squid Body Plan at http://vimeo.com/37431310 (1:34) MEDIA Click image to the left or use the URL below. URL: http://www.ck12.org/flx/render/embeddedobject/57283 1. 2. 3. 4. How does the foot compare between abalone, nautilus, and a squid? How does the shell of an abalone differ from the shell of a nautilus? How many hearts does a squid have? How do these hearts help the squid? Describe the mantle of a squid. Review 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Name five examples of mollusks. What habitats do gastropods live in? What is the defining feature of a bivalve? What mollusk is through to be very intelligent? Describe the foot of a gastropod, bivalve, and cephalopod. References 1. Ostrich foot: Graham Bould; Reef squid: Jan Derk (Wikipedia: janderk). An example of a gastropod and a cephalopod . Public Domain 3