CHAPTER 6 CELLULAR RESPIRATION
advertisement

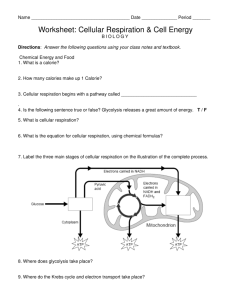
4/7/2015 Chemical Energy In Food CHAPTER 6 CELLULAR RESPIRATION Purpose of food: calorie – the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of one gram of water one degree Celsius. Cellular Respiration Overview Cellular Respiration overview Cellular Respiration – the process that releases energy by breaking down food molecules in the presence of oxygen. Contains 3 Pathways: Glycolysis Krebs cycle Electron transport The equation for cellular respiration is: 6O2 + C6H12O6 6CO2 + 6H2O + ENERGY (ATP) Step 1: Glycolysis Takes place in the cytoplasm. Glycolysis is the process in which 1 molecule of glucose is broken in half, producing 2 molecules of pyruvic acid. If cellular respiration took place in one step, all the energy would be released at once and most would be lost as heat. PROBLEM: The cell has to find a way to trap the energy a little bit at a time. SOLUTION: Each of the three stages of cellular respiration captures some of the chemical energy available in food molecules and uses it to produce ATP or energy. Step 1: Glycolysis Glycolysis is so fast that cells can produce 1000’s of ATPs in milliseconds. Glycolysis does not require oxygen. This process has to get things going so it uses 2 stored ATP molecules. 4 ATP molecules are made during glycolysis, so a total of 2 ATP molecules are released by glycolysis as energy. Cells don’t burn glucose but gradually release the energy from it. Glycolysis – chemical pathway that begins the process of releasing the energy in glucose. Source of raw materials used to make new molecules Source of energy This is only 2% of the total chemical energy in glucose. NAD+ is converted to NADH. 1 4/7/2015 OXIDATIVE RESPIRATION To get the rest of the energy from the food molecules, the cell uses oxygen. Aerobic – requires oxygen. The energy-releasing pathways require oxygen, and that is the reason we need to breathe, to respire. Respiration - process that involves oxygen and breaks down food molecules to release energy. Step 2: Krebs cycle The Krebs cycle: Takes place in the mitochondria. Also called the Citric acid cycle. The carbon contained in pyruvic acid (produced by glycolysis) is broken down into carbon dioxide. Two high energy electron carriers are also generated by the Krebs cycle: KREBS CYCLE (continued) The NADH and FADH2 go on to make huge amounts of ATP in the presence of oxygen, and the CO2 is eventually released when you exhale. ENERGY AND EXERCISE Aerobic cellular respiration produces 36 total ATP molecules from each glucose molecule (37% efficient). Remainder of energy from glucose is released as heat (body feels warm after exercise). Complex carbs are broken down into simple sugars that are converted to glucose. Lipids and proteins broken down into molecules that enter glycolysis or Krebs cycle. Breathing and respiration: Remember, the final electron acceptor for the electrons produced in respiration is oxygen. Without oxygen, all ATP synthesis in mitochondria stops and body tries to make ATP by glycolysis alone (not sufficient for most cells). Electron transport occurs in the mitochondria. The high energy electrons are passed from the carriers in the Krebs cycle (NADH, FADH2) to the electron transport chain. High energy electrons are passed from one carrier protein to the next. The electron transport chain uses these high energy electrons to convert ADP into ATP or energy. At the end of the chain, an enzyme combines the electrons with H+ and oxygen to form water, a byproduct of electron transport. Photosynthesis vs Respiration The processes are almost opposites. Eating food: NADH FADH2 Step 3: Electron Transport This CO2 is considered a waste product and is released from the cell. Equations are opposites. Photosynthesis deposits energy. Respiration withdraws energy. Cellular respiration takes place in all eukaryotes and some prokaryotes. Photosynthesis occurs only in plants, algae, and some bacteria. 2 4/7/2015 Fermentation Occurs when oxygen is NOT present. The respiration that occurs in the absence of oxygen is called anaerobic respiration or fermentation b/c it does not require oxygen. In fermentation, cells perform glycolysis followed by fermentation. Combination of glycolysis and fermentation produces 2 ATP molecules from one molecule of glucose. There are two main types of fermentation: Pyruvic Acid + NADH alcohol + CO2 + NAD+ Krebs cycle and electron transport DO NOT occur. Alcoholic Fermentation A. B. Used by yeast (facultative anaerobes). Forms ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide as wastes. CO2 produced causes bread dough to rise, bubbles in beer. Alcoholic Fermentation Lactic Acid Fermentation Lactic acid fermentation Pyruvic Acid + NADH lactic acid + NAD+ This process regenerates NAD+ so that glycolysis can continue to make small amounts of ATP. Lactic acid fermentation happens in many cells including human muscle cells during rapid exercise. Muscles are not getting enough oxygen to produce all the ATP they need through Krebs cycle and electron transport, so they use lactic acid fermentation to get ATP made. Lactic acid buildup causes the painful, burning sensation in your muscles after intense activity. Bacteria undergo lactic acid fermentation to make foods like sour cream, yogurt, buttermilk, and sauerkraut. 3