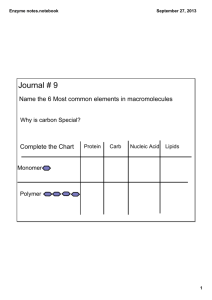
* Proteins, or polypeptides, are polymers made of monomers called
advertisement

Quick Review of Proteins * Proteins, or polypeptides, are polymers made of monomers called amino acids *There are 20 different amino acids, so there are many varieties of proteins. * They are found hair, nails, muscle, bone and in foods like meats, cheeses, and peanuts. Enzymes are special proteins that speed up chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy needed to start the chemical reaction. It takes more energy to get the reaction to happen without the enzyme (blue hill) than with the enzyme (red hill). Because enzymes lower the activation energy, reactions can happen with less energy so they can happen faster. They are biological catalysts. Catalysts are chemicals that can speed up a chemical reaction. For example – a match could be compared to a catalyst because it helps start and speed up the reaction of combustion (burning) But unlike matches,they are not used up in the chemical reaction, but are reused over and over. We could not survive without enzymes, because chemical reactions do not happen fast enough without them for our bodies to work right. An enzyme can make a reaction happen MILLIONS of times faster than it would happen without the enzyme. Enzymes do many jobs in the body, they can: • Assist in getting energy out of the foods you eat • Build cellular structure Enzymes do many jobs in the body, they can: • Transfer information throughout the body • Assist chemical pathways (the chains of chemical reactions that have to happen for living things to function) There are thousands of enzymes(proteins) in your body because each works by binding only to a specific substrate (chemical reactant). Every enzyme has a name and most end in –ASE, like the enzyme that breaks down hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), which is called catalase. Other enzymes name examples: amylase, kinase, anhydrase, protease. An important part of how an enzyme works is its shape. Enzymes have to fit their substrate perfectly, like a lock and key. Enzymes work by attracting and sticking to the reacting molecules , making it easier for them to meet. (Kind of like a dating service for molecules) Enzymes hold the reacting molecules (aka substrates) the right way so that the reactive groups are brought together. Enzymes have evolved over time to do very specific jobs in very specific environments. Changes in pH (acidity) or temperature will change the shape of the enzyme and may make it either less effective, or completely useless. Enzymes have to work at the right temperature and pH for your body, and your body has to maintain a stable internal environment (homeostasis) to keep its enzymes working properly. Since enzymes are proteins and proteins are polymers of amino acids, if the amino acid sequence is changed, then the shape of the protein changes too. leu-val-arg-iso-thr leu-lys-arg-iso-thr The other thing that affects the rate an enzyme works at is the concentration of reactants(substrates) and products of the chemical reaction it speeds up. A high concentration of reactants (substrates) makes the enzyme more effective. A high concentration of products makes the enzyme less effective. Questions: –Enzyme names end with? –What is activation energy? –What do enzymes do to activation energy? –What do enzymes bind with? Questions: –List 4 types of jobs enzymes do? –Name 3 things that affect enzyme effectiveness? –How many enzymes does your body have? Questions: –How many jobs does each enzyme do? Summary: In 1-2 sentences, summarize how enzymes work, and what you have learned about them.