what are the effects of price ceilings and price floors?
advertisement

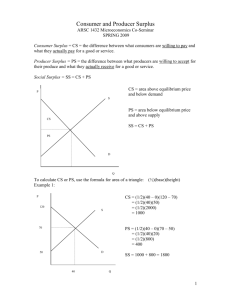
WHAT ARE THE EFFECTS OF PRICE CEILINGS AND PRICE FLOORS? Bhakti Joshi 08 Nov, 2013 Definition: Price ceilings is the maximum price for a specific good established by the government which is usually lower than the free market equilibrium price. On the other hand, price floors is the minimum price for a particular good established by the government which is usually higher than the free market price. In other words: Price ceilings give the sellers a maximum price to sell the product while price floors give the sellers a minimum price to sell the product. Why is this important?: Government could change the consumer surplus and producer surplus by making price ceilings and price floors. They are a major tool that the government will use to intervene the market. Main notes: Price Floor: We will use the market for butter in Europe to discuss the price floor. First, given the supply and demand curve of free butter market in Europe, we could get equilibrium price and quantity as Pe and Qe, which is the intersection of demand and supply curve. The price floor is usually set higher(Pf in this example) than the equilibrium price of the good, which means the price floor is used to help producers. In this butter market example, since the price is set at Pf, the production of the good will increase to Qs and the demand of the good will decrease to Qd which means there will be surplus of butter and we will have disequilibrium market for butter. Before the price floor, the total surplus of consumer and producer is the whole colored area, where the area above Pe is consumer surplus and the area below the Pe is producer surplus. But after the price floor, consumer will buy only Qd butter but at a higher price Pf. Therefore, the consumer surplus decrease to the yellow area and the producer surplus increases to the blue area. The total surplus also decreases. The purple area is the decreased total surplus, which is regarded as deadweight loss. To conclude, the effect of price floor is as follows: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. higher price lower demand higher quantity supplied surplus of butter less consumer surplus more producer surplus deadweight loss inefficiency in the market Economics > High School Micro/Macro > Micro - Market Failure & Price Controls Page 1 of 3 WHAT ARE THE EFFECTS OF PRICE CEILINGS AND PRICE FLOORS? Bhakti Joshi 08 Nov, 2013 Price ceilings: Price ceiling: We will use the market for petrol in China to discuss the price ceiling effect. Also, given the demand curve and supply curve of petrol market in China, we could identify the free market equilibrium for petrol in China, Pe and Qe. If the government imposes a lower price, say Pc, under the free market equilibrium price. Then the demand from petrol consumer in China will increase to Qd and the supply of petrol will decrease to Qs. Therefore, we have a disequilibrium market for petrol and the quantity demand is more than the quantity supplied which means a shortage. When it comes to the consumer and producer surplus, similar to the price floor, the consumers are better off since they could get the petrol at a lower price and the producers are worse off since they sell less petrol and at a lower price. The yellow area is the new consumer surplus while the blue area is the new producer surplus and the purple area is dead weight loss. To conclude, the effect of price ceiling is as follows: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. lower price higher demand lower quantity supplied shortage of petrol more consumer surplus less producer surplus deadweight loss Economics > High School Micro/Macro > Micro - Market Failure & Price Controls Page 2 of 3 WHAT ARE THE EFFECTS OF PRICE CEILINGS AND PRICE FLOORS? Bhakti Joshi 08 Nov, 2013 8. inefficiency in the market We could see from the analysis of price floor and price ceiling that although the transfer is different but they all arise deadweight loss and inefficiency of the market. Economics > High School Micro/Macro > Micro - Market Failure & Price Controls Page 3 of 3