ADVANCE ORGANISER: ABSOLUTISM / ENLIGHTENMENT
advertisement
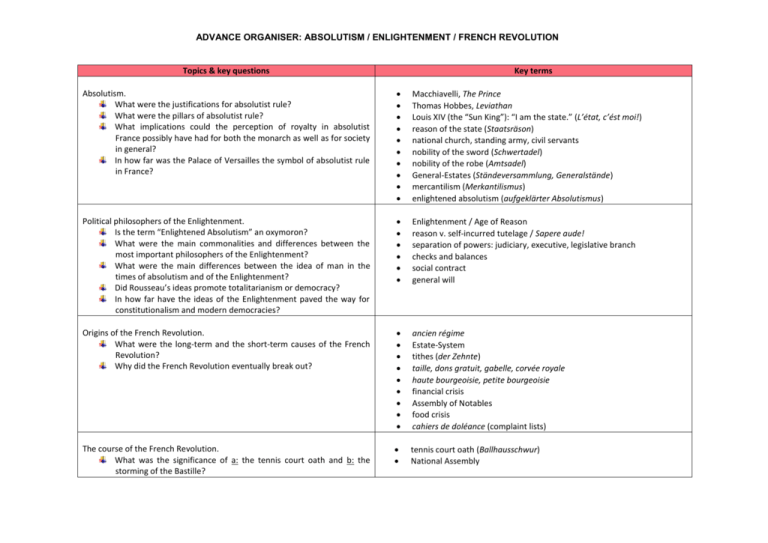
ADVANCE ORGANISER: ABSOLUTISM / ENLIGHTENMENT / FRENCH REVOLUTION Topics & key questions Key terms Absolutism. What were the justifications for absolutist rule? What were the pillars of absolutist rule? What implications could the perception of royalty in absolutist France possibly have had for both the monarch as well as for society in general? In how far was the Palace of Versailles the symbol of absolutist rule in France? Macchiavelli, The Prince Thomas Hobbes, Leviathan Louis XIV (the “Sun King”): “I am the state.” (L’état, c’ést moi!) reason of the state (Staatsräson) national church, standing army, civil servants nobility of the sword (Schwertadel) nobility of the robe (Amtsadel) General-Estates (Ständeversammlung, Generalstände) mercantilism (Merkantilismus) enlightened absolutism (aufgeklärter Absolutismus) Political philosophers of the Enlightenment. Is the term “Enlightened Absolutism” an oxymoron? What were the main commonalities and differences between the most important philosophers of the Enlightenment? What were the main differences between the idea of man in the times of absolutism and of the Enlightenment? Did Rousseau’s ideas promote totalitarianism or democracy? In how far have the ideas of the Enlightenment paved the way for constitutionalism and modern democracies? Enlightenment / Age of Reason reason v. self-incurred tutelage / Sapere aude! separation of powers: judiciary, executive, legislative branch checks and balances social contract general will Origins of the French Revolution. What were the long-term and the short-term causes of the French Revolution? Why did the French Revolution eventually break out? ancien régime Estate-System tithes (der Zehnte) taille, dons gratuit, gabelle, corvée royale haute bourgeoisie, petite bourgeoisie financial crisis Assembly of Notables food crisis cahiers de doléance (complaint lists) The course of the French Revolution. What was the significance of a: the tennis court oath and b: the storming of the Bastille? tennis court oath (Ballhausschwur) National Assembly ADVANCE ORGANISER: ABSOLUTISM / ENLIGHTENMENT / FRENCH REVOLUTION storming of the Bastille (Sturm auf die Bastille) Declaration of the Rights of Man and of Citizen Jacobins, Girondins, Sans-Culottes flight to Varennes National Convention Coalition Wars September Massacres refractory priests émigrés Reign of Terror Committee for Public Safety (Wohlfahrtsausschuss) Law of Suspects (Verdächtigengesetz) Revolutionary Tribunals / Courts Revolutionary Committees Vendée uprising mass levy (levée en masse) / conscription Law of Maximum revolutionary calendar coup de Thermidor The end of the French Revolution. Why did the Directory fail? How and why did Napoleon come to power in France? White Terror the Directory (das Direktoriat) coup d’état Napoleon’s France. France under Napoleon: A change for the better or the worse? Did Napoleon undo the achievements of the French Revolution? Code Napoléon / Civil Code Legion of Honour (Ehrenlegion) meritocracy Concordat Continental System Tricolour La Marseillaise th 14 July Eiffel Tower constitutionalism; left-wing, right-wing What are the commonalities and differences between the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of Citizen and the 1948 UN Declaration of Human Rights? What are the reasons for that? The execution of Louis XVI: An act of terror or deliverance from the evil? The Reign of Terror: Does the end justify the means? What was the British attitude towards the French Revolution and why did they see it this way? Did the revolution “devour her children”? The legacy of the French Revolution. Where can the legacy of the French Revolution still today be detected? Why is the year 1789 commonly regarded as an “epochal year”, th marking the beginning of the so-called “long 19 century”?






