Molecular Biology
advertisement
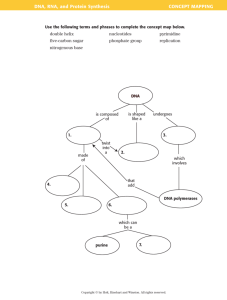
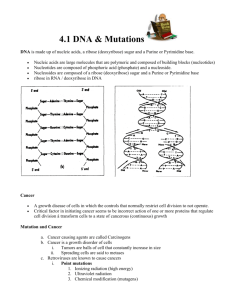
Molecular Biology • Study of Storage and Information Flow in Biology • DNA is information storage medium in cells • DNA Structure • Flow of Biological Information DNA Structure • DNA is a polymer (deoxyribonucleic acid) • Building Blocks are Nucleotides • Nucleotides composes of – A Sugar (deoxyribose) – A Phosphate – A Nitrogen Base Nitrogen Bases • In DNA, 4 types of Nitrogen Bases – – – – Adenine (A): Purine Cytosine (C): Pyrimidine Guanine (G): Purine Thymine (T): Pyrimidine • 4 types of nucleotides distinguished by their nitrogen bases Backbone • Nucleotides joined into chain by covalent bonds between phosphate and sugar units • Sugar-Phosphate-Sugar-Phosphate… • Bases extend to side joined to sugar • Chemical Direction to chain (I.e. strand) – Phosphate at one end, Hydroxyl in sugar at other – 5’ to 3’ (Carbons) by convention Base Pairing • Watson-Crick Complements (Pyrimidine to Purine) – T-A – C-G • W-C Complements pair by hydrogen bonds • Template Matching Reaction (Hybridization) • Nucleotide Bases Hydrophobic INTER-STRAND HYDROGEN BONDING (+) (-) (-) (+) to Sugar-Phosphate Backbone Adenine Thymine to Sugar-Phosphate Backbone (-) (+) (+) (-) to Sugar-Phosphate Backbone (+)(-) to Sugar-Phosphate Backbone Guanine Hydrogen Bond Cytosine Helical Structure • • • • • Flat molecules Stack and Twist upon each other DNA double-stranded molecule W-C base pairing Molecule has helical form PHYSICAL STRUCTURE OF DNA 20 Å 5’ C 34 Å 3’ OH Minor Groove 5’ 3’ 3’ 5’ Sugar-Phosphate Backbone Major Groove Nitrogenous Base C 5’ Central Axis 3’ 0H