A) 1.0 AB) 2.0 AC) 3.0 AD) 4.0 A 1. A 2.0-ohm resistor and a 4.0
advertisement

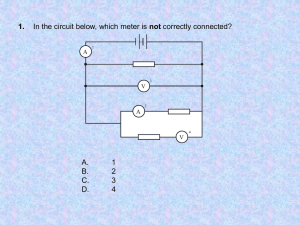
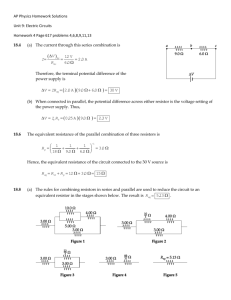
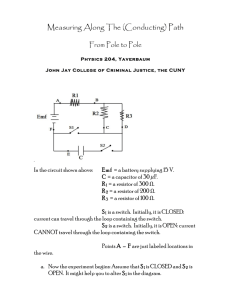
1. A 2.0-ohm resistor and a 4.0-ohm resistor are connected in series with a 12-volt battery. If the current through the 2.0-ohm resistor is 2.0 amperes, the current through the 4.0-ohm resistor is A) 1.0 A B) 2.0 A C) 3.0 A D) 4.0 A 2. Base your answer to the following question on The diagram below represents a circuit consisting of two resistors connected to a source of potential difference. What is the current through the 20.-ohm resistor? A) 0.25 A C) 12 A B) 6.0 A D) 4.0 A 3. Circuit A has four 3.0-ohm resistors connected in series with a 24-volt battery, and circuit B has two 3.0-ohm resistors connected in series with a 24-volt battery. Compared to the total potential drop across circuit A, the total potential drop across circuit B is A) one-half as great C) the same 6. A 3-ohm resistor and a 6-ohm resistor are connected in parallel across a 9-volt battery. Which statement best compares the potential difference across each resistor? A) The potential difference across the 6-ohm resistor is the same as the potential difference across the 3-ohm resistor. B) The potential difference across the 6-ohm resistor is twice as great as the potential difference across the 3-ohm resistor. C) The potential difference across the 6-ohm resistor is half as great as the potential difference across the 3-ohm resistor. D) The potential difference across the 6-ohm resistor is four times as great as the potential difference across the 3-ohm resistor. 7. Which circuit has the smallest equivalent resistance? A) B) B) twice as great D) four times as great 4. Base your answer to the following question on The circuit diagram below represents four resistors connected to a 12-volt source. C) What is the total current in the circuit? A) 0.50 A C) 8.6 A B) 2.0 A D) 24 A 5. A 3.0-ohm resistor arid a 6.0-ohm resistor are connected in series in an operating electric circuit. If the current through the 3.0-ohm resistor is 4.0 amperes, what is the potential difference across the 6.0-ohm resistor? A) 8.0 V B) 2.0 V C) 12 V D) 24 V D) 8. Which combination of resistors has the smallest equivalent resistance? A) B) C) D) 9. Three identical lamps are connected in parallel with each other. If the resistance of each lamp is X ohms, what is the equivalent resistance of this parallel combination? A) B) C) D) 10. Three resistors, 4 ohms, 6 ohms, and 8 ohms, are connected in parallel in an electric circuit. The equivalent resistance of the circuit is A) B) C) D) less than 4 between 4 and 8 between 10 and 18 18 11. A circuit consists of a 10.0-ohm resistor, a 15.0-ohm resistor, and a 20.0-ohm resistor connected in parallel across a 9.00-volt battery. What is the equivalent resistance of this circuit? A) 0.200 C) 4.62 B) 1.95 D) 45.0 12. In which circuit would current flow through resistor R 1, but not through resistor R 2 while switch S is open? A) B) C) D) 13. In the electric circuit diagram below, possible locations of an ammeter and a voltmeter are indicated by circles 1, 2, 3, and 4 Where should an ammeter be located to correctly measure the total current and where should a voltmeter be located to correctly measure the total voltage? A) B) C) D) ammeter at 1 and voltmeter at 4 ammeter at 2 and voltmeter at 3 ammeter at 3 and voltmeter at 4 ammeter at 1 and voltmeter at 2 Base your answers to questions 14 and 15 on the information below. A 15-ohm resistor and a 20.-ohm resistor are connected in parallel with a 9.0-volt battery. A single ammeter is connected to measure the total current of the circuit. 14. In the space below, draw a diagram of this circuit using symbols from the Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Physics. [Assume the availability of any number of wires of negligible resistance.] 15. Calculate the equivalent resistance of the circuit. [Show all work, including the equation and substitution with units.] Base your answers to questions 16 and 17 on the information and diagram below. A circuit contains a 12.0-volt battery, an ammeter, a variable resistor, and connecting wires of negligible resistance, as shown below. The variable resistor is a nichrome wire, maintained at 20.°C. The length of the nichrome wire may be varied from 10.0 centimeters to 90.0 centimeters. The ammeter reads 2.00 amperes when the length of the wire is 10.0 centimeters. 16. Determine the resistance of the 10.0-centimeter length of nichrome wire. _______________________ 17. Calculate the cross-sectional area of the nichrome wire. [Show all work, including the equation and substitution with units.] 18. The heating element in an automobile window has a resistance of 1.2 ohms when operated at 12 volts. Calculate the power dissipated in the heating element. [Show all work, including the equation and substitution with units.] 19. A simple circuit consists of a 100.-ohm resistor connected to a battery. A 25-ohm resistor is to be connected in the circuit. Determine the smallest equivalent resistance possible when both resistors are connected to the battery. 21. A 6-ohm resistor and a 4-ohm resistor are connected in series with a 6-volt battery in an operating electric circuit. A voltmeter is connected to measure the potential difference across the 6-ohm resistor. In the space below, draw a diagram of this circuit including the battery, resistors, and voltmeter using symbols from the Reference Tables for Physical settings/Physics. Label each resistor with its value. [Assume the availability of any number of wires of negligible resistance.] 22. In the space below, draw a diagram of an operating circuit that includes: _______________________ • a battery as a source of potential difference • two resistors in parallel with each other 20. Calculate the resistance of a 900.-watt toaster operating • an ammeter that reads the total current in the circuit at 120 volts. [Show all work, including the equation and substitution with units.] Base your answers to questions 23 through 25 on the information below. A 5.0-ohm resistor, a 10.0-ohm resistor, and a 15.0-ohm resistor are connected in parallel with a battery. The current through the 5.0-ohm resistor is 2.4 amperes. 23. Using the circuit symbols found in the Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Physics, draw a diagram of this electric circuit. 24. Calculate the amount of electrical energy expended in the 5.0-ohm resistor in 2.0 minutes. [Show all work, including the equation and substitution with units.] 25. A 20.0-ohm resistor is added to the circuit in parallel with the other resistors. Describe the effect the addition of this resistor has on the amount of electrical energy expended in the 5.0-ohm resistor in 2.0 minutes. 26. A length of copper wire and a 1.00-meter-long silver wire have the same cross-sectional area and resistance at 20°C. Calculate the length of the copper wire. [Show all work, including the equation and substitution with units.] Base your answers to questions 30 and 31 on the information and diagram below. A 10.0-meter length of copper wire is at 20ºC. The radius of the wire is 1.0 × 10-3 meter. Base your answers to questions 27 through 29 on the information and diagram below. A 15-ohm resistor R1, and a 30-ohm resistor, R2, are to be connected in parallel between points A and B in a circuit containing a 90-volt battery. 30. Determine the cross-sectional area of the wire. 31. Calculate the resistance of the wire. [Show all work, including the equation and substitution with units.] 27. Complete the diagram above, to show the two resistors connected in parallel between points A and B. 28. Determine the potential difference across resistor R 1. 29. Calculate the current in resistor R 1. [Show all work, including the equation and substitution with units.] Answer Key Circuits (AP) 1. B 2. D 3. C 4. A 5. D 6. A 7. C 8. C 9. B 10. A 11. C 12. A 13. A 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 14. The energy expended in the 5.0-ohm resistor remains the same. 26. 15. Req = 8.6 16. 6.00 17. 18. 19. 20. 20. 27. 28. 90 V 29. 6.0 A 30. 3.1 × 10 –6 m 2 31. 5.5 × 10 -2