Lit Terms SOLS Master LIST
advertisement

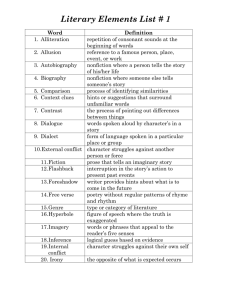
CHS Literary Terms 9th Grade Terms antagonist – a character or force in conflict with a main character, or protagonist archetype – a recurring character type in literature character – a person or animal who takes part in the action of a literary work round character – shows many different traits—faults as well as virtues flat character – shows only one trait static character – does not change during the course of a story dynamic character – develops and grows during the course of the story characterization – the act of creating and developing a character conflict – a struggle between opposing forces internal conflict – a character struggles with him or herself external conflict – a character struggles against an outside force connotation – the set ideas associated with the word in addition to its explicit meaning denotation – the dictionary meaning of a word, independent of other associations that the word may have dialogue – a conversation between characters foreshadowing – the use in a literary work of clues that suggest events that have yet to occur hyperbole – a deliberate exaggeration or overstatement imagery – the descriptive or figurative language used in literature to create word pictures for the reader. These pictures or images are created by details of sight, sound, taste, touch, smell, or movement. irony – literary techniques that portray differences between appearance and reality or expectation and result dramatic irony – a contradiction between what a character thinks and what the reader or audience knows to be true verbal irony – words are used to suggest the opposite of what is meant situational irony – an instance in which an event occurs that directly contradicts the expectations of the characters, the reader, or the audience metaphor – a figure of speech in which one thing is spoken of as though it were something else monologue – a speech by one character in a play, story, or poem narrator – a speaker or character who tells a story 1st person point of view – the point of view in which the narrator is a character in a story 3rd person limited point of view – the narrator sees the world through the eyes of only one character and reveals only the thoughts and feelings of that character 3rd person omniscient point of view – the narrator can tell readers what any character thinks and feels personification – a type of figurative language in which a nonhuman subject is given human characteristics plot – the sequence of events in a literary work exposition – the part of a plot that introduces the setting, characters, and the basic situation rising action – all the events that lead up to the climax climax – the high point of interest or suspense falling action – the happenings in a story following the climax until the resolution is reached resolution/denouement – a general insight or change that is conveyed about the main conflict in the plot protagonist – the main character in a literary work setting – the time and place of the action simile – a figure of speech in which “like” or “as” is used to make a comparison between two basically unlike ideas soliloquy – a long speech expressing the thoughts of a character while or as if alone speaker – the imaginary voice assumed by the writer of a poem symbol – anything that stands for or represents something else theme – a central message or insight into life revealed through a literary work understatement – using words that are less than what is meant in order to create emphasis stereotype – generalization of a person or group of people who share the same basic traits Archetypes Hero/heroine Villain Outsider/outcast Themes Coming of Age Good overcoming evil Power of love 10th Grade Terms alliteration – the repetition of initial consonant sounds allusion – a reference to a well known person, place, event, literary work, or work of art aside – a short speech delivered by an actor in a play which expresses the character’s thoughts to either the audience or to a select few characters onstage assonance – the repetition of vowel sounds followed by different consonants blank verse – poetry written in unrhymed iambic pentameter lines characterization – the act of creating and developing a character direct characterization – an instance when the author directly states a character’s traits indirect characterization – an instance wherein the author develops a character’s traits by showing his actions, thoughts, feelings, words, and appearance or through another character’s observations complication – an event or group of events that hinder the protagonist consonance – the repetition of similar consonant sounds at the ends of accented syllables dialect – a form of language spoken by people in a particular region or group diction – word choice fable – a brief story that teaches a moral, or practical lesson about how to get along in life figurative language – writing or speech that is not meant to be interpreted literally free verse – poetry that is not written in a regular rhythmical pattern or meter literal language – words that are used in their ordinary senses (opposite of figurative language) meter – the rhythmic pattern of a poem iambic pentameter – verse written in five-foot lines where each foot is composed of an unstressed syllable followed by a stressed syllable mood – the feeling created in a reader by a literary work or passage myth – a fictional tale that explains the actions of gods or the causes of natural phenomena onomatopoeia – the use of words that imitate sounds poetry – one of the three major types of literature usually characterized by stanzas, imagery, and emotionally charged language haiku – a three line verse form where the first and third lines have five syllables sonnet – a fourteen-line lyric poem, usually written in rhymed iambic poetry repetition – the use of any element of language- a sound, word, phrase, clause or sentence more than once refrain – a repeated word, phrase, line or group of lines rhetorical question – a figure of speech in the form of a question without the expectation of a reply rhyme – the repetition of sounds at the ends of words end rhyme – an instance when rhyming words come at the end of the line internal rhyme – an instance when rhyming words occur within a line rhythm – the pattern of beats or stresses in spoken or written language soliloquy – a long speech expressing the thoughts of a character while or as if alone stanza – a formal division of lines in a poem, considered as a unit. couplet – a pair of rhyming lines, usually of same length and meter quatrain – four line stanza sestet – six line stanza octave – eight line stanza theme – the central message or insight revealed through a literary work tone – a writer’s attitude toward his or her audience and subject universal theme – the message about life within a piece of literature that can be understood by most cultures Archetypes Hero/heroine Trickster Faithful companion Outsider/outcast Rugged individualist Shrew Innocent Villain Caretaker Earth mother Rebel Misfit Foils Themes Struggle with nature Survival of the fittest Coming of age Power of love Loss of innocence Struggle with self Disillusionment with life Effects of scientific progress Power of nature Alienation and isolation Honoring the historical past Good overcoming evil Tolerance of the atypical 11th Grade Terms analogy – an extended comparison of a relationship that is based on the idea that the relationship between one pair of things is like the relationship between another pair apostrophe – a figure of speech in which a speaker directly addresses an absent person or personified quality, object, or idea cliché – overused phrase that has lost its originality and impact denouement – any events that occur after the resolution in a plot figurative language – writing or speech not meant to be taken literally, and used to express ideas in vivid and imaginative ways flashback – a section of a literary work that interrupts the chronological presentation of events to relate an event from an earlier time oxymoron – a figure of speech that combines two opposing or contradictory ideas paradox – a statement that seems to be contradictory but that actually presents a truth parallelism – the repetition of a grammatical structure pun – a play on words; sarcasm – saying one thing but meaning the opposite satire – writing that ridicules or criticizes individuals, ideas, institutions, social conventions, or other works of art or literature style – word choice, tone, degree of formality, figurative language, rhythm, grammatical structure, sentence length, organization that a writer uses in his or her writing plain style – a type of writing in which uncomplicated sentences and ordinary words are used to make simple, direct statements Archetypes Hero/heroine Trickster Faithful companion Outsider/outcast Rugged individualist Shrew Innocent Villain Caretaker Earth mother Rebel Misfit Foils Lonely orphan looking for a home Themes The American Dream Loss of innocence Coming of age Relationship with nature Relationship with society Relationship with science Alienation and isolation Survival of the fittest Disillusionment Rebellion and protest 12th Grade Terms comedy – a literary work, especially a play, that has a happy ending epic – a long narrative poem about the adventures of the gods or of a hero essay – a short nonfiction work about a particular subject journal –a daily autobiographical account of events and personal reactions tragedy – a type of drama or literature that shows the downfall or destruction of a noble or outstanding person who possesses a tragic flaw Themes Religious diversity Political struggles Ethnic and cultural mores and traditions Individual rights Gender equity Civil rights