Microsoft Word - Ch08
advertisement

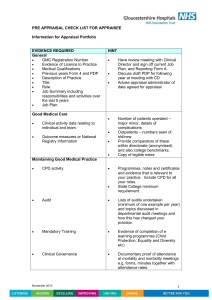
Chapter 8 Appraising and Managing Performance Learning objectives • Discuss the relationship between strategy, performance management and performance appraisal. • Understand the objectives of performance appraisal. • Identify the sources of error in performance appraisal. • Discuss the major types of performance appraisal systems. • Understand the importance of goal setting in performance improvement. • Appreciate the impact of EEO on performance appraisal. Chapter outline This chapter is divided into six sections. The first three sections introduce the topic of performance appraisal and its relationship to business strategy and various HRM activities. The third section then offers a detailed overview of the types of performance appraisal systems used by organisations and their associated problems. The remaining sections in this chapter discuss the key characteristics of an effective appraisal system and the importance of ensuring that the appraisal system satisfies all EEO requirements. Strategy, performance management and performance appraisal Organisations need ever-improving performance to survive and prosper in today’s competitive world: individual and organisational performance improvement are the keys to competitive advantage. The evaluation of organisational and employee performance permits managers to check that strategic business objectives are valid, are being successfully communicated throughout the organisation and are being achieved. Performance appraisal, by providing a dynamic link to employee recruitment, selection, training and development, career planning, compensation and benefits, safety and health and industrial relations, is a vital tool for strategy execution. It signals to managers and employees what is really important; it provides ways to measure what is important; it fixes accountability for behaviour and results; and it helps to improve performance. Performance management Organisational interest in performance management has increased as a result of competitive pressures, the influence of HRM and the individualisation of the employment relationship. The key elements of performance management are: • • • • the creation of a shared vision of the organisation’s strategic objectives the establishment of performance objectives for each function, group and individual to ensure that their performance is aligned with the needs of the business the use of a formal review process to evaluate functional, group and individual progress towards goal achievement the linking of performance evaluation and employee development and rewards to motivate and reinforce desired behaviour. Performance appraisal Performance appraisal may be viewed as an overall measure of organisational effectiveness: organisational objectives are met through the effort of individual employees. If employee performance is improved, the organisation will lift its performance. However, it should be noted that some experts do not accept these assumptions. Nevertheless, appraisal of employee performance remains a critical and ongoing management activity. This is because managers are continually observing and judging their employees. This evaluation process may be formal or informal. Either way, it has a direct impact on the employees’ salary increases, promotions, demotions, terminations, training and career development. 2 Performance appraisal objectives Discrimination A manager must be able to objectively discriminate between those who are contributing to the achievement of the organisation’s strategic business objectives and those who are not. Those who are underperforming should be given the opportunity and assistance to improve. Leaving non-performers in the organisation sends the wrong signals to other employees who are performing well. Employees who achieve want to be recognised and rewarded for their efforts. REWARD — To encourage performance it must be rewarded. Employees who have contributed the most to the achievement of the organisation’s strategic business objectives should receive the greatest rewards. DEVELOPMENT — Employee development is the third aim of performance appraisal. Performance improvement comes about by building on strengths and overcoming weaknesses. It is the manager’s job to remove blocks to employee performance and to help each employee to grow and develop. FEEDBACK—- Managers are responsible for evaluating the performance of their people and for accurately communicating that assessment. This requires the manager to identify the employee’s deficiencies and determine how they can be overcome; to know what specialised training and development are needed; and to ensure that opportunities are created for any new job experiences required. Communicating clear, specific expectations and giving both positive and negative feedback are essential parts of the performance appraisal process. Rater of employee performance The evaluation of employee performance is done by the immediate supervisor in most organisations. However, performance appraisal can be done by anyone who: • • • is familiar with the job’s responsibilities and performance objectives has sufficient opportunity to observe the employee’s job performance has the know-how to distinguish between behaviours which produce effective or ineffective job performance. SUPERVISOR EVALUATION — Overwhelmingly, performance appraisals are the responsibility of the immediate supervisor. PEER EVALUATION — Organisations employing total quality management concepts and teams are increasingly using peer evaluations. SELF-EVALUATION — This occurs where the employee evaluates their own performance. Some organisations use self-appraisals as a supplement to supervisor and/or peer evaluations. SUBORDINATE EVALUATION — Sometimes called upward performance appraisals involves the subordinate evaluating the performance of their superior. MULTISOURCE EVALUATIONS — Multi-source or 360 degree evaluations are gaining increasing popularity. It seeks performance feedback on employees from their colleagues, superiors, customers and subordinates. TEAM BASE EVALUATIONS — Are appraisals that are specially designed to evaluate how well a team has performed. 3 Sources of error in performance appraisal Research evidence indicates that managers can clearly discriminate between performing and non-performing employees. However, their ratings will not necessarily reflect their actual judgements. This is because managers often distort their evaluations when completing performance appraisal forms. Typical rater errors that occur are halo effect, central tendency, prejudice, recency effect, relationship effect, leniency/strictness bias, and emphasis on subjective performance criteria. Major types of performance appraisal systems When choosing an employee performance appraisal system to introduce, managers must consider the strategic business objectives of the organisation as well as specific performance evaluation purposes. RANKING — compares each person’s performance, with the manager ranking all subordinates from ‘best’ to ‘worst’. GRADING — compares the employee’s performance with the grade definitions, then the employee is placed in the grade that best describes his or her performance. GRAPHIC SCALES — Rating scale that evaluates employee performance using specific employee behaviour or characteristics. CRITICAL INCIDENTS — requires the manager to record those occurrences or critical incidents of employee job behaviour which highlight good or bad job performance. BEHAVIOURALLY ANCHORED RATING SCALES — a method that combines elements of the traditional rating scale and critical incidents method. BEHAVIOUR OBSERVATION SCALES — A behaviour observation scale (BOS) uses critical incidents to develop a list of the desired behaviours needed to successfully perform a specific job. ESSAY DESCRIPTION — A manager may be asked to describe, in his or her own words, the employee’s performance (covering the quantity and quality of work performed, job know-how, human relations skills, strengths and weaknesses and so on). MANAGEMENT BY OBJECTIVES (MBO) — Management by objectives is a technique whereby the manager and the subordinate mutually identify common goals, define the subordinate’s major areas of responsibility in terms of expected results, and use these as measures in assessing the subordinate’s performance. ASSESSMENT CENTRES — The primary purpose of an assessment centre is typically to identify promotable or high-potential employees. Assessment centres are rarely used for performance appraisal purposes because they are costly and time consuming. WORKPLACE SURVEILLANCE — The introduction of workplace surveillance equipment to monitor employee performance and behaviour is rapidly becoming matter of considerable controversy. Static and dynamic performance appraisals For effective performance management, performance appraisal should be dynamic. It should emphasise employee growth and development and the setting of new goals, not just judgemental decisions about performance. The characteristic feature of static appraisal programs is that they look back. They focus on the past, not the future. In contrast, a dynamic performance appraisal program helps employees know where they are going, how they are going to get there, and when they will get there. Characteristics of a dynamic performance appraisal program Dynamic performance appraisal programs are characterised by three key qualities: • • • goal establishment performance feedback performance improvement. 4 Importance of goal setting in performance improvement Employee motivation and performance are improved if the employee clearly understands and is challenged by what is to be achieved. ‘If performance appraisal is to have a developmental purpose,’ says Kearney, ‘it must concentrate on the process of getting results. That process must be examined in terms of the job related behaviours over which the individual has control.’ Performance appraisal record The performance appraisal record is the document that is used to record the ratings and comments for an employee. Properly designed, it is a valuable tool for: • • • • • defining performance levels facilitating job performance review discussion identifying training and development needs identifying low- and high-potential employees rewarding performance. Performance review discussion Research shows that three factors are important in producing effective performance appraisal interviews: 1. 2. 3. the manager’s knowledge of the employee’s job and performance the manager’s support of the employee the manager’s involvement of the employee in the discussion. The absence of any of these factors will have a negative impact on the quality of the performance appraisal interview and on its ultimate value. The performance appraisal interview should be a positive experience for the manager and the employee. The appraisal interview is often the weakest part of the whole appraisal process. Instead of generating an improvement in performance, it produces a demotivated and angry employee and results in performance decline. Preparation required for the performance review discussion Good, solid preparation leads to a successful performance review discussion. Before meeting an employee, the manager should undertake the following tasks. • • • • • • • Review the employee’s job description to ensure that it is still accurate and that nothing has been overlooked. Read the employee’s last performance appraisal report to refresh his or her memory on key points and to identify areas of improvement and areas still requiring emphasis. Check the employee’s actual performance against the mutually agreed goals. Consult with other managers who have contact with the employee in the performance of the job. Alert the employee well in advance about the forthcoming performance review discussion so he or she can undertake the necessary preparation. List all key points to be discussed in the interview. Ensure that there is sufficient time available for the appraisal discussion and that there are no interruptions. Conduct of the performance review discussion In an effective performance review discussion • • • Problems should be discussed as problems and not as criticisms. The performance appraisal review should not be used as a vehicle to attack the employee’s personality. The employee should be encouraged to talk 5 • • • Specific performance improvement objectives should be set. Discuss only those things which can be changed. The manager should avoid using positional authority. Performance appraisal and EEO Performance appraisals must satisfy EEO requirements. For example, ‘Transfer or promotion must be based on a fair assessment of an employee’s potential, ability and work record. Ideally the work record should reflect an objective assessment of the employee’s performance’. Summary Appraising and managing performance involves evaluating performance, communicating that evaluation to the employee and establishing a plan for improvement. Performance appraisal is a dynamic process with the emphasis on self-development, the establishment of performance standards and the giving and receiving of feedback. Performance appraisal is a management program; it is not just an HR department responsibility. It is also an important motivator and employee development tool. Finally, the HR manager, in searching for performance improvement, has a responsibility to ensure that management understands that an organisation’s strategic business objectives are better achieved through satisfying individual goals, and that the process of performance appraisal strongly affects how employees feel about the organisation and themselves. Terms to identify Assessment centre behaviour observation scales (BOS) behaviourally anchored rating scales (BARS) central tendency critical incidents essay description goal setting grading graphic scales halo effect management by objectives (MBO) multisource evaluations performance appraisal performance appraisal record performance management performance review discussion prejudice ranking rater errors recency effect relationship effect self-evaluation social loafing strictness bias subordinate evaluation team appraisals 360-degree appraisals REVIEW QUESTIONS Questions in bold print are recommended as exam questions 1. How often should performance reviews be conducted? There is no ideal frequency for performance reviews. Normally, formal reviews are conducted every 12 months. Some performance goals lend themselves to a longer time frame, and some to a shorter time frame. 2. Should salary increases and promotions be discussed during an appraisal interview? There is some argument that performance review should be divorced from remuneration discussion. Remuneration is an emotive issue, and discussion of it encourages defensiveness from employees. As a result, proper performance review and goal-setting is affected. On the other hand, for performance to be encouraged, it is obvious that it must be rewarded. Consequently, most organisations claim that they do just that. 6 Employees who have contributed the most to the achievement of the organisation's objectives must receive the greatest rewards. The big question is: 'If no objective measure of performance exists within the organisation, how does management know what is being rewarded?' Embarrassingly, often what is rewarded is seniority, a servile demeanour or some other factor that has little or nothing to do with the achievement of the organisation's objectives. Some employees who flatter and fawn on their supervisors receive better salary increases and promotions than their counterparts. The result can be the over-rewarding of incompetence and the under-rewarding of superior performance. In reality, there is little evidence to suggest that Australian organisations really reward performance. The key factor in determining rewards in Australian organisations is simply membership. Membership-based rewards include 'across-the-board' increases, cost-of-living increases, seniority payments and so on. Performance-based rewards include piecework payments, commissions, incentives, bonuses or other forms of merit pay plans. Performance-based rewards are 'at risk' rewards. Employees are not stupid. They quickly learn to exhibit the behaviour that they know will be recognised and rewarded by management. An objective performance appraisal system thus is essential for encouraging performance-oriented behaviour. It links employee contributions and rewards and ensures that the organisation gets maximum value for its compensation dollar. 3. How can an organisation increase its chances of having objective appraisals? Reducing the sources of error in performance appraisals will increase an organisation's chances of having objective appraisals. Research evidence indicates that managers can clearly discriminate between good and bad performing employees. It does not follow however that their ratings will reflect their actual judgments. This is because managers often distort their evaluations when completing performance appraisal forms. Managers need to recognise this when considering the validity and accuracy of their organisations performance appraisal system. Some of the main sources of error in appraisals, and which should be minimised, are: Management Attitude Where management is committed to performance appraisal it will work. However, if performance appraisal is seen by managers as something imposed on them by the human resource department, lacking the genuine support of senior management, it simply becomes a cosmetic process to be treated with indifference. Rater Errors Most managers and employees are aware of the types of problems that arise in performance appraisal. 'Easy' and 'tough' managers, and managers who play favourites, create situations that result in unfair and inaccurate ratings. Halo Effect When the manager gives an employee the same rating on all factors, through generalising from one specific factor, this causes a 'halo effect' error. Central Tendency This is a problem caused by a manager giving everyone an average or acceptable rating, regardless of actual performance. Leniency/Strictness Bias This error occurs when managers rate their employees either consistently high or low. Prejudice When the manager has a negative or positive attitude towards an individual or group, this causes a rater-generated error. 7 Recency Effect When the manager overemphasises the employee's most recent behaviour, this results in a 'recency effect' error. Other rater-related errors are produced when the manager is subjected to political influences, or varies the ratings for a specific purpose such as obtaining a salary increase or promotion for a subordinate. Emphasis On Subjective Factors An examination of many traditional performance appraisal systems reveals an emphasis on the measuring of subjective traits, such as personality, loyalty and initiative. Appraisal systems such as these are vague, subjective and open to charges of discrimination, and they should be avoided. Research indicates, moreover, that employees assessed under an objective appraisal system are significantly more satisfied with the way they were evaluated. Some examples of personal- and performance-based criteria are: Personal-based Initiative Dependability Leadership ability Attitude towards safety Willingness to cooperate Verbal communication skill Enthusiasm for job Ability to work under stress 4. Performance-based Work quantity Sales volume Earnings or profit generated Costs incurred Number of clients Number of rejects Amount of scrap produced Attendance record Can performance appraisals conflict with EEO requirements? They sure can. Today performance appraisals must satisfy equal employment opportunity (EEO) requirements. For example, transfer or promotion must be based on a fair assessment of an employee's potential, ability and work record. Ideally the work record should reflect an objective assessment of the employee's performance. In addition, it is desirable for employees to include progress in EEO as part of the performance assessment of managers. Although Australia lags behind the USA in EEO, Australian managers ultimately will have their performance evaluations subjected to public scrutiny. American managers, for example, have been involved in several court cases focusing on performance appraisal and there seems little doubt that Australian EEO authorities will refer to US legislation and court decisions for guidance. The US Equal Employment Opportunity Commission's guidelines make it clear that performance appraisals must be job related and non-discriminatory. A review of US legal cases indicates the following practices should be utilised if an organisation is to be successful in defending its appraisal system as being non-discriminatory: • • • • • Job analysis must be used to develop the system. The performance appraisal scheme must be behaviour-oriented rather than trait-oriented. Managers must be given definite instructions and training on how to make appraisals. Results must be communicated to employees. There must be a provision for appeal in the case of disagreement. According to some experts, without a valid system of performance management, organisations risk an eventuality where even unintentional discrimination may consume large amounts of time and money on 8 employee complaints, grievances and suits. The impact on public relations, managerial confidence in personnel decisions, and employee morale may be even more devastating. Thus, like it or not, managers increasingly will find their performance appraisals subject to challenge and external review. Human resource managers must not only stress this to their management but also provide the know-how within the organisation that ensures performance appraisals are objective and non-discriminatory. 5. Do you agree with the following statement? ‘Performance appraisal is simply a management technique operating under a scientific veneer to control employees by reinforcing behavioural norms that the organisation considers desirable.’ Explain your answer. Appraising and managing performance are critical management responsibilities and a vital part of the organisation’s strategic management process. However, many performance appraisal systems in practice are short term and divorced from the organisation’s strategic business objectives. Moreover, highly unionised, university and public sector organisations often have cultures that promote strong opposition to any form of performance evaluation (despite ineffective control and performance monitoring systems being an important factor in the poor performance of the public sector). Unions, for example, see performance appraisal and pay for performance as focusing on the individual, thus creating a competitive culture, coercing higher output and promoting management by control. While in the public sector, the cultural preference for collaboration rather than competition means that peer competitiveness can be seen as a strong negative factor in employee job satisfaction. One academic claims, ‘As professionals, as colleagues, as scholars, and as members of national and international discipline and research communities, performance management is not appropriate for us’. Similarly, a University of Western Australian academic argues that performance appraisal is an attack on academic freedom because it could be used to monitor and control staff and prevent the pursuit of unpopular research or public discussion of questions not supported by the university. Disagreeing, one pro-vice chancellor states, ‘Unions have carefully confused egalitarian principles, a feature of university philosophy, to obfuscate accountability and productivity…. academics are required to teach four to 12 hours a week for 30 weeks a year, prepare study materials and undertake research, often in excess of 60 hours a week all year. Other academics teach four to 12 hours for only 30 weeks and have the same salary privileges and rights as their active scholarly colleagues.’ Despite the importance of performance management, many organisations do not have any systematic method of appraisal or use a system that lacks congruence with the organisation’s culture and strategic business objectives. Not surprisingly, in a recent survey, more than half of the responding companies reported that their performance appraisal system offered little or no value to the organisation. Similarly, after a review of the literature, Newton and Findlay concluded that appraisal schemes rarely work as their formal procedures suggest because in practice they are predominantly concerned with surveillance, accountability and control. Thus, HR managers have a critical and challenging role in educating their organisation’s management and staff on the significance and use of performance appraisal in employee development, performance improvement and achievement of the organisation’s strategic business objectives. Performance appraisals are a powerful vehicle for supervisors to monitor and direct employee behaviour and to reinforce their formal authority and control. Disadvantages of this approach include the subjectivity of the supervisor (particularly if there is a personality conflict or the supervisor perceives the employee as a threat), manipulation of ratings to justify pay increases or promotions, discrimination and supervisor incompetence. To check such problems, organisations usually subject the supervisor’s evaluation to management review and/or provide a mechanism for employee appeal. 6. Should performance appraisals be conducted only by HRM specialists? This text suggests that the manager should conduct the performance appraisal. The person responsible for ensuring that the appraisal is conducted satisfactorily is the person responsible for the employee's performance. Some may conclude that the employee is responsible for the employee's own performance. This is true, but self-conduct of an objective appraisal is clearly not valid. Generally then, the people who should conduct 9 performance appraisals are 'managers'. However, information for the appraisal can and should come from several sources, only one of who is the manager of the employee whose performance is being appraised. Those sources can include: the manager, the employee, customers or clients of the employee, customers or clients of the employee's work group, peers, other managers, subordinates of the employee, other employees, objective organisational data that cannot be traced to any particular stakeholder. The HRM specialist has an important role in advising on the process, and monitoring it to see that it is conducted validly. Human resource managers thus have a critical role in educating their organisation's management and staff on the significance and use of performance appraisal in performance improvement and the achievement of corporate objectives. 7. Should an organisation show its employees their completed performance appraisal records or should these records be kept secret? If only to avoid conflict with EEO principles, the appraisal record should be mutually owned by the employee and by the organisation. Moreover, Freedom of Information (FOI) legislation in Australia ensures that employees can have access to the appraisal record if they want it. This cannot be avoided. This chapter stresses the mutuality of the determination of the appraisal document. It also stresses the importance of the appraisal for the development of the employee. Because of this, it is logical that the employee has free access to the appraisal documentation, to monitor their own development. 8. Why might a manager not want to discuss a performance appraisal with an employee? If the appraisal is not conducted correctly, and is subject to the sources of error identified in this chapter. If the appraisal is not favourable to the employee. If the appraisal will breach national security, or is outside FOI (freedom of information legislation) access guidelines. 9. What are the benefits to an organisation of having a good performance appraisal system? Performance appraisal has a dynamic link to employee recruitment, selection, training and development, career planning, compensation and benefits, safety and health and employee relations. It can be a vital tool for strategy execution by signalling what is really important, providing ways to measure what is important, fixing accountability for behaviour and results and helping to improve performance. In total, performance appraisal is a measure of organisational effectiveness. It is through the effort of individual employees that organisation objectives are met. If employee performance is improved, the organisation in turn will lift its performance. Appraisal of employee performance is thus a critical and ongoing human resource management activity. Performance appraisal helps management to discriminate between high and low performing people. A manager must be able to objectively discriminate between those who are contributing to the achievement of the organisation's objectives and those who are not. Employees who achieve want to be recognised and rewarded for their efforts. To motivate performance, outstanding performers must be identified and rewarded accordingly. Performance appraisal can achieve this. Discrimination on the basis of performance is an organisational necessity. It is part of the managerial role that cannot be avoided. If an organisation is to survive and grow, and retain and motivate its top performers, effective performance appraisal is a must. Performance appraisal helps to ensure that employees are rewarded properly. Another benefit to the organisation is that of employee development. Performance improvement comes about by building on strengths and overcoming weaknesses. It is the manager's job to remove blocks to employee performance and to help the employee to grow and develop. Performance appraisal must be a positive and dynamic process to achieve this. 10 Employee communication is an essential part of the performance appraisal process, and it is a benefit to the organisation. 10. If you were an employee, which appraisal method would you want to be evaluated by? Why? The answer to this question is determined by personal preference, and by the type of work that one might be doing. Students should be able to discriminate between the different types of performance appraisal systems. They are Ranking This is the oldest and simplest form of rating. It compares each person's performance, with the manager ranking all subordinates from 'best' to 'worst'. Grading In the grading system, specific performance levels are described, such as superior, good, acceptable, marginal, unsatisfactory. The employee's performance is compared with the grade definitions, then the employee is placed in the grade that best describes his performance. Graphic Scales This is the most common method of performance appraisal. Typically, the manager can choose one of five degrees for each specific factor. The selection of factors to be measured can be centred on subjective factors such as initiative and dependability, and/or on objective factors such as quality and quantity of work. Critical Incidents Here the manager records actual occurrences or critical incidents of employee job behaviour which highlight good or bad job performance. Incidents typically take the form of a story or anecdote and are recorded as soon as possible after they occur. Behaviourally Anchored Rating Scales (BARS) The BARS method of performance appraisal is designed to evaluate behaviour demonstrated in performing a job. Descriptions of what makes for good and bad performance in a particular job are collected from supervisors and/or people familiar with the work. These examples are then grouped into various job dimensions such as job knowledge, customer relations and safety. Next, specific examples of job behaviour are placed by a scale, which is usually graded from one to seven. Essay Description Some organisations use an essay description to try to determine performance levels. For example, a manager might be asked to describe in his or her own words the employee's performance, covering the quantity and quality of work performed, job know-how, human relations skills, strengths and weaknesses and so on. Management By Objectives (MBO) Management by objectives involves the manager and the subordinate mutually identifying common goals; defining the subordinate's major areas of responsibility in terms of expected results, and using these as measures in assessing the subordinate's performance. Assessment Centres The primary purpose on an assessment centre is typically to identify promotable or high potential employees. Performance appraisal should be dynamic and not static. It should be used to emphasise the growth and development of the employee, and not just to make a judgmental decision about performance. 11 DIAGNOSTIC MODEL 1. Identify and discuss the factors from the diagnostic model (figure 1.11) that have significance for performance appraisal. Performance improvement is a national necessity. It must become an integral part of corporate strategy. Performance appraisal is a vital part of an organisation's strategic planning and can be used as a means of achieving corporate objectives. Many performance appraisal systems, however, are not linked to an overall strategic plan. Worse, many organisations (particularly those which are highly unionised and/or in the public sector) face strong resistance to the very concept of performance appraisal. 2. Explain the impact of performance appraisal on the acquisition, development, reward, maintenance and departure of an organisation’s human resources. Performance appraisal has a dynamic link to employee recruitment, selection, training and development, career planning, compensation and benefits, safety and health and employee relations. According to Schneier, Shaw and Beatty, it can be a vital tool for strategy execution by signalling what is really important, providing ways to measure what is important, fixing accountability for behaviour and results and helping to improve performance Performance appraisal objectives are Discrimination - A manager must be able to objectively discriminate between those who are contributing to the achievement of the organisation's objectives and those who are not. In a performance-oriented organisation, there is no room for egalitarianism. Inadequate performance cannot be tolerated. Those that are under-performing should be given the opportunity and assistance to improve. Where the employee still cannot make the grade, corrective action such as transfer, demotion or termination should be taken.. Reward - For performance to be encouraged, it is obvious that it must be rewarded. Consequently, most organisations claim that they do just that. Employees who have contributed the most to the achievement of the organisation's objectives must receive the greatest rewards. If not, how are employees to be motivated to perform? Development - The third aim of the performance appraisal (and one which is often overlooked) is that of employee development. Performance improvement comes about by building on strengths and overcoming weaknesses. It is the manager's job to remove blocks to employee performance and to help the employee to grow and develop. Performance appraisal must be a positive and dynamic process to achieve this. The research evidence is clear: the higher the level of employee participation, the greater the satisfaction with the appraiser and the appraisal process. 3. Discuss the impact that performance appraisal may have on commitment, competence, cost effectiveness, congruence, adaptability, performance, job satisfaction and employee motivation. Students should examine the link between development of human resources and the outcomes like commitment, etc. Commitment can be gained through a mutual determination of developmental activities. Competence can be enhanced by the determination of developmental activities at appraisal time. Cost effectiveness and congruence are enhanced through the closer match between the person and the job. Performance is the criterion of appraisal. If performance is the subject of attention, then performance is most likely to be influenced. 12 Students should also note that these outcomes should be assessed from the organisational perspective as well as the individual perspective. If all the individuals are more committed, competent, etc., then the whole organisation will be committed and competent. Soapbox There are seldom clear answers to these questions. The idea is to stimulate debate as much as to determine an answer. Ethical dilemma 1. The sick employee If you were HR manager of Techgan, how would you handle this situation? What advice would you give to Jennifer? What would you do about James? James needs some formal counselling to determine the cause of his lowered performance. The organisation needs to find out what it can do to assist him in improving that level of performance. 2. What ethical issues, if any, are raised in this case? A manager must be able to objectively discriminate between those who are contributing to the achievement of the organisation’s strategic business objectives and those who are not. A performance-oriented organisation has no room for egalitarianism: inadequate performance cannot be tolerated. Those who are underperforming should be given the opportunity and assistance to improve. If an employee still cannot make the grade, corrective action such as transfer, demotion or termination should be taken. Ian Gow, former Ten Network Chief, says, ‘You don’t do anybody any favours by tolerating failure or incompetence. All you really do is put a lot of other people’s jobs at risk’. Leaving nonperformers in the organisation sends the wrong signals to other employees who are performing well. Leniency leading to inaccurate performance appraisals is a long-standing problem. A recent survey, for example, indicated that 20 per cent of academics had not published anything in five years despite having the same research time and sabbaticals as their more productive colleagues. The Commander of the New South Wales Police Service’s Professional Responsibility Branch states, ‘One of the problems that the Police Service has always had is that we have never been able to get rid of those officers who are simply lazy, have poor attitudes or are simply incompetent’. ‘The only way to make a business live up to its potential,’ according to one expert, ‘is to get tough.’ Former legendary Port Adelaide Football Club coach, Foster Williams, graphically illustrated this when he said, ‘Any club worth its salt will clear out its no hopers from the doorman to the head trainer to the captain. Keeping no hopers in these positions is a mark of a non-successful club. You have to weed out the people who breed an atmosphere of non-professionalism. They are there for the bloody joke, the social life, the prestige. They are not there to win’. Yet in a recent survey, 61 per cent of Australian employees felt their companies were too lenient with poorly performing employees. According to the National Commission of Audit, for example, the extraordinary complexity of the Public Service personnel system protects inefficiency because the delays in proceedings, the manipulation of rights of appeal and the frequent recourse to generous redundancy payouts make it difficult to dismiss inefficient public servants. Thus, the rigidities and lack of accountability in dealing with underperforming staff is one of the toughest issues facing public sector managers. Discrimination on the basis of performance is an organisational necessity. It is part of the managerial role that cannot be avoided. If an organisation is to survive and grow, and retain and motivate its top performers, effective performance management is a must. However, employees are not stupid. They quickly learn to exhibit the behaviour that they know will be recognised and rewarded by management. An objective performance appraisal system in which high performers receive higher rewards and low performers receive lower rewards is essential for encouraging performance-oriented behaviour and a performance-oriented culture. Linking employee contributions and rewards also ensures that the organisation gets maximum value for its compensation dollar. 13 Case study The quiet industrial relations manager This would be a good case for examination purposes. 1. What has brought about this situation? How could it have been avoided? Mary should have counselled John for his apparent lowered performance. Rating him low after the event does not improve future performance. Also, Mary needed data from a range of sources before determining whether or not to pass John over for performance increases and merit increases. The poor communication has come from Mary. She should have communicated the decision to John before announcing it on the notice board. 2. If you were Mary, how would you have handled the situation? If you were Anna, what would you have done? Mary should have acted in accordance with the advice in question 1. Anna is very much the meat in the sandwich. The problems are very much of Mary’s making. However, Anna needs now to do some goal setting, and look to the future. 3. What key elements in the appraisal process are missing in this case? What is the impact of their absence? Missing are: reward development self-evaluation peer evaluation subordinate evaluation elimination of rater bias goal/objective setting Impact: ineffective appraisal lack of performance management poor employee attitude and performance