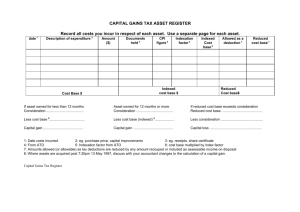
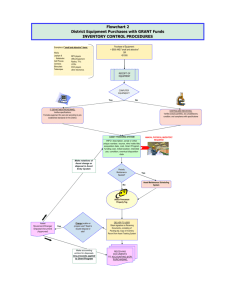
Irish Water Capital Investment Planning
advertisement

Irish Water Capital Investment Planning CIWEM/ Engineers Ireland 7th April 2014 John Casey Asset Strategy & Sustainability Manager Irish Water 1 A function based organisation with a regional presence • Irish Water – Headquarters in Dublin and a services function in Cork – Three regions and 8 regional offices 3 Regions Eastern / Midlands 8 Regional Offices Dublin City Mullingar Castlebar Connaught/Ulster Cavan Town Donegal Town Kilkenny City Southern Limerick City Mallow 2 SLA Overview Governance Arrangements Important Inputs Customer / Stakeholder Needs Develop Service Plan Rolling 5 Yr Plan Deliver Service Plan Annual Review Deliver Transformation & Change • Capital Investment Clear Roles & Responsibilities Commitment to Collaboration Commitment to Continuous Improvement Annual Service Plan • Key objectives • Performance • Activities • Change Prog. • Headcount • Budget Continuous Improvement Cycles Operate & Maintain Assets Continuous Improvement Cycles Manage Performance & Costs Dispute Avoidance & Issue Resolution 3 Decisions • Key objectives • Activities • Change Prog. • Funding Regulatory Context New Water Services Regulation CER HSA Employment & Growth DECLG IW + LA HSE EPA 4 Customer Service & Affordability Environmental Protection Balance Sustainability Objectives Building a Sustainable Water Service: Asset Management Approach Will drive Investment Planning based on asset data and defined needs Relies on full Asset data including Operations workflow & costs Makes optimum use of available resources Ensures the right projects are selected and delivered in the right way Promotes best use of existing assets – capacity & risk models Balances Capital & Operational investment – whole life view Promotes a consistent set of policies & standards across asset base Supports a sustainable business model-present & future needs Promotes risk management as a key focus to target investment Asset Management will drive both operational & capital investment based on sustainability principles 5 Building a Sustainable Water Service: Funding and Investment Drivers Drinking Water Quality Drinking Water Availability Environmental Compliance Wastewater Availability Meeting Customer Service Obligations Business Efficiencies Asset Condition & Performance 6 Enhancement Enhancement / Growth Enhancement Enhancement / Growth Enhancement Enhancement Capital Maintenance Building a Sustainable Water Service: Development of Investment Programmes Irish Water Strategic Investment Plans Water Services Strategic Plan (25 Year) This will inform / be supported by Specific Strategies: • Water Resources Management Plan • National Sludge Management Plan • Climate Change and Adaption Strategy • WSPP sets out high level strategic objectives including alignment with Economic and Spatial Plans • Will be required by legislation • Will require Ministerial approval DECLG Price Control Period – Investment Plans Capital • Stakeholders: LA’s, Regional Authorities, Customers/Citizens • • • • • Financial Regulator CER Environmental Regulator - EPA 7 Major Projects Small Capital New Connections/Developer Services Surveys & Studies • Investment plans submitted to CER First full regulatory period 2017-2021 (TBC) Interim Investment Period 2014 – 2016 Asset Management Function in Irish Water Irish Water Asset Management Asset Strategy Asset Investments Asset Programmes • • • • • • • • • • 8 Asset Policies & Standards Asset Information (Data & Models) Asset Strategies Investment Planning • • • Investment Options Analysis Portfolio Management Performance/ Benefits Review Water Supply Programme Wastewater Programme Small Capital Programme Contract Strategy Developer Services Asset Management Systems Irish Water Asset Hierarchy • Maximo • Primavera • Oracle • GIS • SCADA • Hydraulic Models Asset inventory and database Asset condition and performance Asset maintenance • Planned • Reactive Workflow management Cost Capture New connections assessment Project Management Portfolio Management BELOW GROUND WASTE WATER WATER TREATMENT L3 Business Level L3 Regional Level (SLA) FACILITIES (Buildings) L6 Process Level L7 Stage Level Cake Storage WATER SUPPLY ZONE WATER TREATMENT PLANT L5 Installation Level Abstraction & Intake Works Submersibl e Pumping Station Convey or Unit Chemica l Recepti on & Storage REGION 3 REGION 2 REGION 1 L4 Chart of Accounts Level (Financial) Chemical Prep 9 ABOVE GROUND L1 Regulatory/Tariffs Sludge Dewateri ng Plant Dirty Wash water Tank/Sy stem In-Line Pumping Station Sludge Screenin gs Handlin g Odour Treatme nt Unit PUMPING STATIONS ABSTRACTION Borehole & Adit Borehol e Pumping Station Dam Structur e Facilities Pipe Recepti on Sludge Screening Facilities Utilities •River Basin Attributes/EU Directive 2000/60/EC •Local Authority Attributes Micro Strainer Utilities Tanker Loading Power System Screening - Coarse WATER STORAGE SLUDGE MANAGEMENT Screenin g - Fine Power System Control Systems Environmental Common Site Services Dam Structur e Reservoi r Draw off & Scour Reservoir Inlet & Bye Wash Reservoi r Overflo w Water Tower Sludge Thickeni ng Plant Liquor Treatme nt Tanker Receptio n Odour Contain ment Inter Stage Transfer Control Systems Environmental Commo n Site Services Sludge Storage Approach to Investment Planning – Enduring • Previous Approach • • • WSIP high investment on relatively small number of schemes including high growth provision Under-investment on large number of schemes Under-investment in capital maintenance • Future Approach • • • • All schemes considered for investment Greater spread through small capital / more targeted investment Growth provision “just in time” Benefits of standardisation and innovation IW Future Process Assess Current Performance & Risk • Asset Management 10 Future Needs Analysis • Regional and LA consultation • EPA Engagement Gap Analysis Define and Optimise Projects • Capex • Opex • Small Capital • Bundling Finalise Investment Plan ( 6 year ) • Drivers Prioritisation • Cost Benefit Analysis Submission to CER Investment Planning Process 2014 – 2016 Project Sources • WSIP • RAL • AER • Small Capital • Strategic Studies Investment Need by Driver Project list to be prioritised Drivers Prioritisation Interim Price Control Submission Q2 2014 Project Decision Trees • First stage filter Project WSIP Readiness + WSIP in-flight Potential cashflow Further Cost Benefit Analysis and Prioritisation of Projects Finalise 2014 – 16 Investment Plan against Drivers and Funding constraints Ongoing engagement with the EPA to maximise environmental benefit within funding constraint 11 Water: Compliance Challenge 450 400 385 Active Non-Compliance (Approx. Number) 350 300 250 200 140 150 100 50 31 22 BWN Direction 0 Notification • EPA Remedial Action List • EPA Notifications • EPA Directions • EPA Audit reports 12 RAL Water: Availability Challenge • 41% UFW (LGMA 2012) • 25% of WSZs are currently operating beyond their design limits • Lack of basic infrastructure and resources to manage leakage: • • 13 – DMA setup not complete – Inconsistent and inadequate resourcing of active leakage control – Visibility of DMA performance Customer Side Leakage – Metering programme providing new data source (>140K meters installed) – 5-6% of properties experiencing significant leaks – First fix policy under consideration – Dual benefit in terms of lead non-compliance Rehabilitation contracts on-going Waste Water: Compliance Challenge • Licenced Discharges • 76% of larger urban areas complied with secondary standards in 2012 • Lower compliance rates for N and P • EPA Prosecutions (Clifden, Killybegs, Bundoran) • ECJ Prosecution under UWWT Directive • • 70 UWWT WWTPs • 39 Collection Networks • Major Data Challenge Water Framework Directive requiring Good Status by 2015 (with potential to extend to 2021/2027) • Requires potential investment of €3 - 4 billion • New EPA licences being issued based on current 2015 WFD commitments • Higher standards required under Habitats Directive • 14 E.g. Blackwater Valley Capital Investment Required • Need to ramp up investment from current approx. €300m to address compliance, capacity and capital maintenance deficits. Capital Investment • Need to develop pipeline for 2016+. 2014 2015 Available Capital 15 Capital Requirement 2016 Urban Waste Water Compliance Strategy • Minor Capital Quick Wins • ECJ Response • 16 – Engagement with DECLG and EU towards Partnership Implementation Agreement – Deliver Major Capital Projects – Collect appropriate data – Roadmap for Compliance WFD Engagement – Engagement with EPA/ DECLG/ NPWS – Development of Catchment Modelling Capability – Collaboration on River Basin Planning and Licencing approach Minor Capital Programme Example – Quick Wins • Plants that failed UWWD Standards in 2011-2012 which are not overloaded • 47 No. WWTP • Systematic bottom up data collection and analysis • Installation of appropriate monitoring • Steps – Operational assessment and resolve if possible • – Optimise and deliver minor capital solution – Confirm benefits delivered Estimated cost €3 million to bring 40 WWTP into compliance 17 Summary • Significant Investment deficit to be addressed… – – – – Compliance Capacity Asset Risk/ Asset Maintenance Business Efficiencies • …Through best practice Asset Management: – – – – – – – 18 Spending less to achieve more Stewardship of assets to keep in desired state Managing risks not resources Whole systems not their parts Whole life perspective Integrated view of operations & investment Stakeholders fully engaged