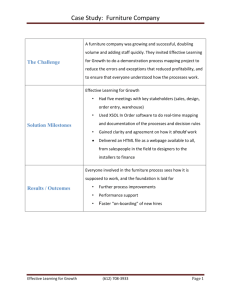
Globalization and Regional Change in the U.S. Furniture Industry
advertisement

Growth and Change Vol. 39 No. 2 (June 2008), pp. 252–282 Globalization and Regional Change in the U.S. Furniture Industry MARK H. DRAYSE ABSTRACT Furniture manufacturing has experienced rapid globalization in recent years. This is mainly the result of global production networks established by large manufacturers and retailers seeking to reduce costs in a highly competitive environment. The industry’s globalization has been facilitated by technological innovations and the global reduction of trade and investment barriers. In the U.S., furniture-producing regions are experiencing tumultuous change. Growing numbers of firms are outsourcing production to China, which is now responsible for about half of all U.S. furniture imports. Employment levels have plummeted. However, an analysis of spatial patterns of employment, output, and capital investment in U.S. furniture manufacturing shows that regional change is not uniform. Southern regions characterized by larger firms specializing in wooden case goods production have been especially vulnerable to job loss. Introduction I n October 2003, a coalition of furniture manufacturers and unions petitioned the U.S. International Trade Commission for relief under the Tariff Act of 1930, claiming material injury from Chinese imports. They argued that China was dumping furniture into the U.S. market, taking advantage of its low wages and undervalued yuan. The petitioners were supported by politicians from furniture-producing regions such as North Carolina and Virginia. Virginia Business cried “the onslaught of the Middle Kingdom is costing thousands of jobs nationwide” (Peters 2002). The petitioners and their supporters were reacting to the dramatic growth in U.S. furniture imports from China, which increased from $1.5 to $15.5 billion between 1996 and 2005.1 China’s share of U.S. furniture imports grew from 13 to 46 percent, and the U.S. furniture trade deficit quadrupled from $7.5 to $28.8 billion (U.S. Census Bureau 2006a). Chinese imports were the main reason that imports as a share of domestic shipments increased from 17 percent in 1997 to 40 percent in 2005. Meanwhile, between 2000 and 2005, average annual employment in the U.S. furniture industry fell from 641,000 to 536,000, a 16 percent decline (U.S. Census Bureau 2006b). Mark H. Drayse is an Associate Professor in the Department of Geography, California State University, Fullerton, CA 92834. His email address is: mdrayse@fullerton.edu. The author thanks Thomas Leinbach and three anonymous referees for their constructive comments on an earlier version of this paper. Submitted October 2006; revised January 2008; accepted February 2008. © 2008 Blackwell Publishing, 350 Main Street, Malden MA 02148 US and 9600 Garsington Road, Oxford OX4, 2DQ, UK. GLOBALIZATION AND THE U.S. FURNITURE INDUSTRY 253 These numbers paint a picture of another U.S. manufacturing industry succumbing to global competition. However, the antidumping petition obscures the real processes of economic globalization in the furniture industry. The driving force behind rising furniture imports is the development of global production networks by large U.S. firms. Manufacturers are outsourcing production to foreign subcontractors, and large retailers are circumventing domestic manufacturers and developing their own foreign supply networks. In fact, the Furniture Retailers of America was created expressly to fight the antidumping petition, since tariffs on furniture imports would result in higher costs for retailers and consumers. They were joined by large U.S. manufacturers with Chinese supply networks, and Chinese firms targeted for tariff penalties. Union support for the petition underscores the tenuous situation of workers in the global economy. The tension between global and local scales of economic activity is nowhere more apparent than in the loss of jobs caused by corporations shutting down plants to engage in a global sourcing strategy. From the workers’ perspective, the petition represents a defense of place in an uncertain world. Regional change has been a central theme in the evolution of the U.S. furniture industry. First taking root in the metropolitan Northeast during the early nineteenth century, the industry began shifting to small Northeastern and Midwestern cities in the latter half of the century to take advantage of cheaper labor. The early twentieth century saw the growth of regional furniture industries in the South and California. The current era of globalization continues this spatial shift of furniture production to places with less expensive, unorganized labor. This paper addresses the following questions. How is the U.S. furniture industry reorganizing in this era of rapid globalization? What is the impact of corporate reorganization on patterns of regional employment change? Regional development outcomes in the U.S. furniture industry are not uniform—for example, while North Carolina is experiencing a precipitous loss of jobs, some smaller regional industries are holding their own and performing better than the national average. What explains these different outcomes? The paper proceeds by presenting a conceptual framework for understanding regional development in an era of globalization. This is followed by a discussion of the changing patterns of global trade and the emergence of China as a pivot for the industry’s globalization. Patterns of regional change in the U.S. furniture industry are then compared and evaluated using data on capital investment, output, and employment from the Census of Manufactures and the Annual Survey of Manufactures. The connections between global production networks and regional restructuring are highlighted in a case study of Furniture Brands International’s (FBN) global strategy and its impact on employment in the North Carolina furniture industry. Economic Globalization and Regional Development Understanding the connection between economic globalization and regional development is a core research problem in economic geography. Economic globalization involves intensified international flows of capital, commodities, labor, and information as a result of 254 GROWTH AND CHANGE, JUNE 2008 converging technological, political, and economic processes operating at multiple geographical scales (Dicken 2007). Globalization is driven by firms developing global production and distribution networks to take advantage of cheaper costs of production and gain access to foreign markets. Governments in developing countries are inviting foreign investment to spur economic development, pursuing the strategy of export-led industrialization pioneered by Japan after the Second World War. Barriers to trade and investment have been reduced under the auspices of the World Trade Organization (WTO). Technological innovations in transportation and communications have lowered the costs of economic transactions and facilitated the globalization of economic activity. The concept of global value chains is a useful starting point for describing and understanding the connections between economic globalization and regional development, defined here as progressive improvement in the social and economic well-being of a region’s inhabitants. A global value chain is a linked sequence of activities involved in the production and distribution of a commodity, from raw materials extraction to final consumption (cf. Bair and Gereffi 2003). Manufacturers dominate producer-led chains, and wholesalers and retailers dominate buyer-led chains. However, the site of corporate control in different industries may be difficult to identify and can change over time (Leslie and Reimer 1999). For example, Tewari (2004) suggests that the furniture industry is evolving into a “quasi-buyer-led” value chain because of the growing influence of transnational retailers like IKEA and WalMart, alongside branded manufacturers such as FBN. Incorporated within and across global value chains are global production and distribution networks organized by corporations. These networks include horizontal and vertical linkages that may encompass local to global scales and include lead firms, suppliers, and retailers (Sturgeon 2000). While based on contractual relations between firms, global production and distribution networks are influenced by nonfirm actors, such as governments, labor unions, and nonprofit organizations (Rothenberg-Aalami 2004; Smith et al. 2002). The development and transformation of global production networks provides the crucial link between globalizing processes and regional development. Even as corporations develop global networks, production remains rooted in regional production systems where firms benefit from agglomeration. Focusing on global production networks helps to break down the false dichotomy between global flows and regional economic activity (Johns 2006), and highlights both the spatial extent (“stretching”) and territorial embeddedness (“deepening”) of corporate activity. As Dicken and Malmberg (2001) point out, firms are “intrinsically spatial and territorial” (7). Coe et al. (2004) argue that the success of regions in the global economy is related to their ability to create, enhance, and capture value through integration with global production networks. Value creation involves training and educating the workforce, promoting start-ups and supplier networks, facilitating venture capital formation, and encouraging entrepreneurial activity. Value enhancement is a result of industry learning and upgrading, and the promotion of regional assets. Regional assets include local labor markets, business associations and other organizations, cultures of learning and innovation, and the provision GLOBALIZATION AND THE U.S. FURNITURE INDUSTRY 255 of physical infrastructure (cf. Gertler 1995; Scott and Storper 2003; Storper 1997). Value capture occurs when a region’s assets are so highly valued by lead firms that they maintain or increase their activity in the region. However, changes in technological and competitive environments may result in the devaluation of regional assets by corporations, with attendant disinvestment and job loss (Coe et al. 2004). Upgrading of production—a key component of value enhancement—involves “innovating to increase value added” (Giuliani, Pietrobelli, and Rabellotti 2005). Giuliani, Pietrobelli, and Rabellotti (2005) identify four types of upgrading. Creating higher-value products is an example of product upgrading. Process upgrading is a result of innovations in production technology and more efficient organization of production. If firms concentrate on higher value activities such as design and marketing, this involves functional upgrading. The fourth type, intersectoral upgrading, occurs when firms shift industries, again resulting in a move from lower value added to higher value added activity. Downgrading is the opposite strategy, involving disinvestment or reliance on a cost-cutting strategy emphasizing low wages in the absence of innovation. Downgrading may be a consequence of functional upgrading, while product and process upgrading are complementary strategies. While upgrading can be associated with the development of regional assets, it can also result from learning that occurs within global production networks (the learning “pipelines” described by Bathelt, Malmberg, and Maskell 2004). Sacchetti and Sugden (2003) argue that globalization has promoted the development of long-term, collaborative subcontracting relationships that give lead firms a considerable degree of control over supply chain logistics and product quality, while at the same time providing subcontractors with valuable technological, managerial, and skills-related expertise that can allow them to develop their own subcontracting and distribution networks (van Grunsven and Smakman 2001). Tokatli and Kizilgun (2004) argue that firms in peripheral regions—in their case, a clothing manufacturer in Turkey—have “room for autonomous action” in upgrading and exporting their own brands. Upgrading firms may become “sources of information spillovers,” promoting innovation and growth within a regional industry (Scott 2006:1531). However, as Knutsen (2005) cautions, latecomers in buyer-driven networks may experience minimal upgrading, as lead firms exploit them for cheap wages. Growing external connections may result in regions becoming branch plant economies dependent on decisions made elsewhere (cf. Kaplinsky, Morris, and Readman 2002). Storper (1997) argues that regional competitiveness should involve increases in productivity and market share that sustain the workforce by maintaining or increasing jobs at decent wages. This is a clear indicator that firms in a regional industry are following a “high-road” development path. However, upgrading may or may not result in positive employment outcomes (cf. Bristow 2005; Kitson, Martin, and Tyler 2004). For example, capital-intensive process upgrading may result in growing sales but falling employment. Houseman (2007) argues that increased offshoring—consistent with functional upgrading—can result in increased productivity but reduced employment in the home region, as foreign workers are substituted for local workers at considerably lower wages. This can result in firms reporting growing output, while domestic employment and capital 256 GROWTH AND CHANGE, JUNE 2008 investment are declining. In their study of the textile, clothing, and footwear industries in Australia, Webber and Weller (2001) show that increased offshoring resulted in significant declines in total employment, despite growth in nonproduction jobs. A region may also experience production downgrading (plant closings, disinvestment) and consequently face severe job losses. This can result from the extensive outsourcing associated with functional upgrading, or industry decline (van Grunsven and Smakman 2001). Regional economic development in the contemporary era of globalization is influenced both by the intraregional development of industries and assets and the external connections made by firms within global production networks. Competitive pressures may contribute to different strategies of upgrading or result in industry disinvestment and decline. The development path of an industry is not uniform but influenced by regional context (cf. Smith et al. 2002). The Globalizing Furniture Industry Causes of globalization. The furniture industry had the highest trade volume of any low-technology manufacturing industry in 2001 (Kaplinsky and Readman 2005). Between 1980 and 2001, global furniture exports increased by an average of 11 percent each year, compared to a 9 percent average annual increase for all manufactured exports (United Nations Conference on Trade and Development [UNCTAD] 2004). The total value of global furniture exports increased from $54 to $95 billion (current dollars) between 1999 and 2005 (UNCTAD 2007). Compared with other labor-intensive industries, such as apparel and footwear, furniture production has been less amenable to globalization. Although the labor-intensive character of furniture production and relatively low barriers to entry have created a very competitive industry in which firms have great incentives to seek out low-wage labor, the material and cultural characteristics of furniture have mitigated long-distance subcontracting. Furniture has one of the lowest value-to-bulk ratios of any manufactured commodity, and wood and upholstered furniture can be easily damaged in transit. Furniture’s status as a cultural product has influenced industrial organization and further limited globalization. Furniture reflects the “art and expressivity” of consumers (Molotch 1996). This helped to create a labor-intensive, batch production industry based on agglomerations of small- and medium-size firms with limited capacity to develop long-distance production networks. The globalization of the furniture industry since the 1980s has occurred through a convergence of technological innovations, the implementation of economic development strategies and regulatory regimes favoring global investment and trade, and the emergence of furniture manufacturers and retailers with the capacity to develop global production and distribution networks. In recent years, a primary reason for the accelerated globalization of the furniture industry has been the establishment of global production networks using Chinese subcontractors. Innovations in transportation, packaging, and logistics have reduced shipping costs. The ability to ship furniture in containers that can be easily transferred to trucks and trains and GLOBALIZATION AND THE U.S. FURNITURE INDUSTRY 257 transported to the final destination has greatly reduced the costs of long-distance shipping. The design and packaging of knock-down furniture was pioneered by the Swedish furniture retailer IKEA. New packaging materials and product coatings reduce damage to furniture in transit. Information technology allows firms to create complex logistics systems to track orders, production, and shipments. Some firms are customizing factory-direct containers (known as mixed containers) for individual retail outlets. Political processes operating at multiple scales are promoting the globalization of furniture production. At the global scale is the phase-out of furniture tariffs under the auspices of the WTO. The integration of high-wage and low-wage countries within the European and North American economic blocs has contributed to increased production in countries such as Poland and Mexico geared toward the Western European and American markets, respectively. National governments in developing countries are opening up their borders to investment and trade in order to promote economic growth. Within countries, state and local governments are establishing policies and incentives to foster favorable local conditions for investment. The center of corporate power in the furniture industry is shifting to large transnational retailers and branded manufacturers. Since the 1980s, a wave of corporate mergers in manufacturing, combined with the emergence of megaretailers such as WalMart and Costco, created large corporations with the resources to organize global networks. After a series of acquisitions of leading North Carolina manufacturers, FBN emerged as the largest furniture manufacturer in the U.S., with $2.4 billion in revenue in 2005 (Fortune Magazine 2006). Other leading manufacturers included Steelcase and Herman Miller, both based in the Grand Rapids region in Michigan. Many traditional furniture retail chains have gone out of business in the face of stiff competition from megaretailers and manufacturers’ retail galleries. Processes of corporate consolidation and globalization are mutually reinforcing: intense competition promotes mergers and acquisitions, creating firms with greater capacity to organize global production networks. Changing patterns of global trade. Newly industrializing and transitional economies are responsible for growing shares of furniture exports. Between 1999 and 2005, the global export share of advanced industrial countries fell from 70 to 53 percent. Leading exporters were Italy, with $10.5 billion in furniture exports in 2005, followed by Germany, Canada, and the U.S. (Table 1). On the other hand, the export share of newly industrializing countries grew from 20 to 31 percent. China’s furniture exports increased from $3.5 to $16.6 billion between 1999 and 2005; in 2004, China surpassed Italy as the world’s leading furniture exporter. In 2005, China was responsible for 54 percent of furniture exports from all developing countries and 18 percent of global furniture exports. Other leading exporters from newly industrializing countries included Mexico, Malaysia, and Indonesia. The eastern expansion of the European Union has integrated lower-wage countries into the European market, resulting in greater subcontracting by firms based in Western Europe. This explains why the global export share of transitional economies increased from 10 to 15 percent between 1999 and 2005. Poland led the way with $5.6 billion in exports in 2005, 53.4 14.5 31.0 1.1 50,592,183 13,730,457 29,423,865 1,078,430 94,824,935 7.9 17.5 18.6 5.1 29.8 3.8 6.9 3.4 19.0 3.0 12.2 3.2 5.4 2.4 6.4 16.7 4.1 7.0 9.0 Average annual percent change, 1999–2005 United States Germany United Kingdom France Japan Canada Belgium Spain Netherlands Switzerland Austria Italy Sweden China Australia Country Group ADVANCED INDUSTRIAL TRANSITIONAL NEWLY INDUSTRIALIZING UNDERDEVELOPED WORLD Source: United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) (2007). Trade data for SITC (Standard Industrial Trade Classification) 821—Furniture. 17.5 11.1 8.0 5.9 5.9 5.5 4.8 3.1 2.8 2.3 2.1 2.0 2.0 2.0 1.9 16,571,814 10,538,493 7,574,119 5,641,650 5,551,047 5,190,359 4,559,805 2,970,609 2,650,578 2,141,769 2,024,695 1,902,976 1,874,510 1,856,060 1,804,620 China Italy Germany Canada Poland United States Mexico France Denmark Belgium Malaysia Czech Republic Spain Indonesia Austria Country Group ADVANCED INDUSTRIAL TRANSITIONAL NEWLY INDUSTRIALIZING UNDERDEVELOPED WORLD Percent of world 2005 exports ($millions) Country TABLE 1. GLOBAL FURNITURE TRADE, 1999–2005. 1,185,159 103,543,052 5,120,745 5,554,823 91,682,325 34,017,715 9,132,916 7,305,790 6,558,813 4,901,564 4,614,011 3,009,311 2,709,579 2,581,679 2,306,247 1,954,362 1,914,543 1,660,607 1,533,481 1,499,478 2005 imports ($millions) 1.1 4.9 5.4 88.5 32.9 8.8 7.1 6.3 4.7 4.5 2.9 2.6 2.5 2.2 1.9 1.8 1.6 1.5 1.4 Percent of world 8.9 19.3 5.7 10.1 11.8 4.5 15.2 10.6 8.7 8.6 6.4 20.0 4.4 5.2 5.3 12.5 9.4 2.5 17.3 Average annual percent change, 1999–2005 258 GROWTH AND CHANGE, JUNE 2008 GLOBALIZATION AND THE U.S. FURNITURE INDUSTRY 259 making it the fifth largest furniture exporter in the world. Other major exporters in this group were Czech Republic, Slovenia, and Romania. The advanced industrial countries absorbed 89 percent of global furniture imports in 2005. The U.S. alone imported $34.0 billion of furniture in 2005, 33 percent of total global imports. Other major importers, with much smaller volumes, were Germany, UK, France, and Japan. China was the leading furniture importer outside of the advanced industrial economies; its $1.5 billion in furniture imports in 2005 represented 13 percent of all furniture imports by developing and transitional economies. The massive scale of China’s furniture production allows it to meet most domestic demand internally while generating an enormous trade surplus. The emerging giant: the Chinese furniture industry. What explains China’s revolutionary impact on the global furniture industry? Production costs are certainly lower. Average hourly wages in Chinese furniture factories are between $0.50–$0.75, compared with $13.33 in the U.S. (Bryson et al. 2003; U.S. Census Bureau 2006b). Chinese firms also enjoy much lower overhead costs than their American counterparts. These cost savings more than compensate for the cost of shipping a container of furniture across the Pacific Ocean. For example, one study estimated that labor, overhead, and shipping costs for Chinese furniture firms are approximately 50–60 percent of the cost of labor and overhead alone for U.S. furniture firms (Bryson et al. 2003). A Wisconsin manufacturer stated that he can “ship Indiana oak halfway around the world, have it made into furniture and sent back to the Midwest—all for about 40 percent less than the cost of production here” (Schmid and Romell 2003). However, lower production costs are only part of the answer. The foundation for the industry’s modern development was laid by the strategic shift in Chinese industrial policy in the post-Mao era. Following the lead of successful Pacific Asian economies, China embarked on a strategy of export-led industrialization (cf. Naughton, 1996). The country channeled foreign investment to special economic zones in the coastal provinces. This helped the government concentrate infrastructure investments while containing foreign investment in the coastal ports that were China’s traditional gateway to the outside world. Foreign firms were allowed to invest in Chinese firms and establish joint ventures and subcontracting relationships and under certain conditions can now establish wholly owned subsidiaries (Wei 2000). Dynamic furniture manufacturing agglomerations emerged in new industrial cities such as Shenzhen, where firms have access to a growing, inexpensive labor force, massive infusions of capital and technology, and networks of suppliers and subcontractors. Annual trade marts bring together local producers and foreign firms. Furniture centers are being created to provide technical expertise and marketing services. In Shenzhen, two universities supply graduates in furniture and interior design (Carroll 2003). The significance of agglomeration is recognized in official proclamations. For example, Dayong has been designated the “Specialized Town for the Production of Redwood Furniture”; Dachong is the “Specialized Town of Mahogany Furniture Production.” The high degree of agglomeration in the Chinese furniture industry is borne out by comparisons with other industries. 260 GROWTH AND CHANGE, JUNE 2008 Of 29 Chinese manufacturing industries analyzed by Fan and Scott (2003), furniture manufacturing ranked third in geographical concentration of establishments, and seventh in geographical concentration of employment. Today, there are an estimated 50,000 furniture firms in China, employing five million workers. The core of the industry, including the major exporters, consists of more than 2,000 large state-owned companies and joint ventures (Union Européenne de l’Ameublement 2000; Xu, Cao, and Hansen 2003). The Zhu Zhiang (Pearl River) Delta in Guangdong province is the center of the Chinese furniture industry. The province accounted for 30 percent of China’s furniture output in 2002 and 51 percent of exports in 2003. Just north of Guangdong, Fujian was the source of 22 percent of output and 10 percent of exports, and the Lower Yangtze Delta region (including Shanghai, Zhejiang, and Jiangsu) was responsible for 21 percent of both output and exports (Xu, Cao, and Hansen 2003). The Chinese furniture industry has benefited greatly from Taiwanese investment. This has been a critical factor behind the country’s growing furniture industry, providing infusions of capital and technical know-how, as well as connections with customers in the U.S. and other developed countries. In the 1980s and early 1990s, Taiwan was the major source of U.S. furniture imports. As a result, Taiwanese furniture firms were experienced in producing high-quality furniture to meet the demands of U.S. customers. Once the mainland economy was opened up, Taiwanese entrepreneurs crossed the strait to take advantage of much lower production costs. The Taiwanese benefited from the relative autonomy of local authorities in Guangdong, Fujian, and other provinces eager to attract investment and create jobs (Hsing 1995; Lin 2001). China’s largest furniture manufacturer, Urumqi-based Markor Corporation, was founded by two local entrepreneurs allied in a joint venture with a Taiwanese firm (Urban 2002). The large Chinese furniture firms operate “megaplants” that employ thousands of workers living in company-owned dormitories. For example, Lacquer Craft’s 2.5 million square foot plant in Dongguan employs more than 5,000 workers. Its original brand production has been shifted to a new four million square foot plant in Shanghai (Russell 2004). Yihua International, a fully integrated firm with its own forests, is building a “3.6-million-square-foot complex in Guandong that could employ 20,000 people” (Russell 2005). Lacquer Craft’s Taiwanese founder, Samuel Ko, states that “Americans have no idea how big and well-equipped these plants are” (Becker 2003). By contrast, FBN’s 25 plants in 2005 ranged in size between 103,000 and 899,000 square feet (FBN 2006). Several large Chinese firms have established alliances with manufacturers and retailers in North America and Europe. For example, most of Lacquer Craft’s Dongguan plant output is destined for FBN and other U.S. customers (Urban 2002). While providing U.S. contractors with significant cost savings, these alliances also benefit Chinese firms through the transfer of technology and expertise. As a result of their growing capabilities, several Chinese firms are marketing brandname furniture in the U.S. For example, about 90 percent of Lacquer Craft’s U.S. sales are channeled through its own Universal Furniture and Legacy Classic divisions (Russell GLOBALIZATION AND THE U.S. FURNITURE INDUSTRY 261 2006). In May 2006, Lacquer Craft established a manufacturing base in the U.S. by acquiring North Carolina upholstery manufacturer Craftmaster Furniture Corporation (Evans 2006). Yihua International Group recently opened a distribution center in Rancho Cucamonga, California (Russell 2005). The Hong Kong manufacturer Simplified is building a distribution network among independent U.S. retailers and establishing its own licensed stores to sell branded products (Slaughter 2005). Xilinmen Group, which produces furniture for New Jersey’s Excel, plans to build a plant in the U.S. to manufacture bedding (Perry 2004). The growth of the modern Chinese furniture industry has resulted from the convergence of labor and capital in coastal cities, supportive local and national government policies, and the dynamic local and external networks established by Chinese firms. This has reoriented the geography of the global furniture value chain. For example, the forests of Siberia are being tapped to augment lumber supplies for the Chinese industry (Hashirimoto, Castano, and Johnson 2004). Foreign component and finishing suppliers are moving to China to fulfill growing demand for their products. The opening of the Chinese economy has accelerated the industry’s globalization, and connected regions and workers across the Pacific Ocean. Chinese production and American consumption is the dominant economic axis in the global furniture industry today. Regional Employment Change in the U.S. Furniture Industry Before the current era of globalization, employment in the U.S. furniture industry was predictably cyclical, tracking trends in housing and office construction that ebbed and flowed with economic recessions and expansions. But in recent years, employment has fallen precipitously in the midst of an expanding housing market because of growing reliance on Chinese suppliers by U.S. furniture manufacturers and retailers. The emerging global division of labor for the U.S. furniture industry has unhinged the connection between overall economic activity, furniture consumption and production, and domestic furniture employment. For example, between 2000 and 2005, annual housing permits in the U.S. increased 35 percent, and consumer spending on furniture grew 17 percent (U.S. Census Bureau 2006c). However, total output in U.S. furniture manufacturing increased only 2 percent between 2000 and 2005, while employment fell by 16 percent. New capital expenditures by U.S. furniture firms also declined, from $2.3 billion in 2000 to $1.4 billion in 2004 (U.S. Census Bureau 2006b). The globalization of the U.S. furniture industry is readily apparent from trade statistics. The total value of U.S. furniture imports tripled from $11.5 billion in 1996 to $34.0 billion in 2005 (Table 2). The furniture trade deficit ballooned from $7.5 to $28.8 billion (Figure 1). While China’s share of imports grew from 14 to 46 percent between 1996 and 2005, Taiwan’s import share fell from 11 to 2 percent as Taiwanese investors shifted investment to the mainland (Figure 2). The import share of Southeast Asian countries fell from 11 to 10 percent despite a rising value of imports. Vietnam is the only Southeast Asian country experiencing a growth in import share, as its furniture imports skyrocketed from a 262 GROWTH AND CHANGE, JUNE 2008 TABLE 2. US FURNITURE IMPORTS, 1996 AND 2005 (MILLIONS OF 2005 DOLLARS). Country Imports 2005 Percent Imports 1996 Percent Average annual percent change, 1996–2005 China Canada Mexico Italy Malaysia Vietnam Taiwan Indonesia Thailand Brazil Germany Philippines United Kingdom France India WORLD 15,479.9 5,202.6 4,334.0 1,185.8 908.0 850.1 801.9 729.5 531.7 529.9 365.5 330.7 254.2 237.3 233.4 34,017.7 45.5 15.3 12.7 3.5 2.7 2.5 2.4 2.1 1.6 1.6 1.1 1.0 0.7 0.7 0.7 100.0 1,478.6 3,411.4 1,779.3 858.9 500.2 0.4 1,213.2 311.8 220.7 74.6 157.8 222.1 195.5 82.1 28.5 11,544.3 12.8 29.6 15.4 7.4 4.3 0.0 10.5 2.7 1.9 0.6 1.4 1.9 1.7 0.7 0.2 100.0 29.8 4.8 10.4 3.6 6.8 134.8 -4.5 9.9 10.3 24.3 9.8 4.5 3.0 12.5 26.3 12.8 Source: US Census Bureau (2006a). negligible $392,000 in 1996 to $850 million in 2005. Vietnam now accounts for more than 25 percent of U.S. furniture imports from Southeast Asia. Import shares from developed economies are falling, although volumes are generally increasing. For example, although the total value of imports from Canada increased by an average annual rate of 4.8 percent between 1996 and 2005, Canada’s share of U.S. furniture imports fell from 30 to 15 percent. Italy and Germany, the major European sources, also saw their shares of U.S. imports decline. Production and employment change. How has the globalization of the U.S. furniture industry influenced patterns of regional production and employment? To describe regional change in production, I draw on the framework presented by Kaplinsky and Readman (2005) in their study of upgrading in the global furniture industry. They used two indicators of production upgrading: unit prices and market share. Successful upgrading was indicated by above-average change in each indicator, suggesting that firms were producing higherquality products and gaining market share. To analyze production upgrading in the U.S. furniture producing regions, I used state-level capital investment and value-added data from the Census of Manufactures and Annual Survey of Manufactures. Unit price data were not available due to the suppression of state-level shipment volume data. To analyze GLOBALIZATION AND THE U.S. FURNITURE INDUSTRY 263 FIGURE 1. THE GROWING U.S. FURNITURE TRADE DEFICIT, 1996–2005. regional employment change, a time series was created for 1997–2005 using state-level data on employment, capital investment, and value added. To dampen annual fluctuations, I compared change between 1997–1999 and 2003–2005. Regional trends are an aggregate outcome of corporate strategies and actions. As described by Giuliani, Pietrobelli, and Rabellotti (2005), upgrading strategies include 1) product upgrading, 2) process upgrading, 3) functional upgrading, and 4) intersectoral upgrading. The first three strategies are evident in furniture manufacturing. To these strategies, we can add 5) “low-road” growth based on cutting costs and 6) downgrading and disinvestment. 264 GROWTH AND CHANGE, JUNE 2008 FIGURE 2. U.S.–CHINA FURNITURE TRADE, 1996–2005. Successful product and process upgrading should be associated with above-average growth in capital investment and value added, providing evidence that firms are reaping the benefits of innovation through increased market share. Failed upgrading can be identified by increased capital investment but below-average growth or decline in value added. Functional upgrading, which may involve significant offshoring of production and concentration on design and marketing at home, is likely to result in deep cuts in capital investment. Impacts on output will vary depending on the extent of cuts in domestic production relative to the volume of imported goods. In any case, the share of a region’s GLOBALIZATION AND THE U.S. FURNITURE INDUSTRY 265 output accounted for by domestic establishments will decline as a result of widespread functional upgrading. If value added increases at an above-average rate but capital investment is well below the industry average, firms in a region may be trying to compete through price competition, a “low-road” approach unlikely to be sustained. The following hypotheses regarding corporate strategy and employment change can be proposed: 1. Successful product and process upgrading can result in different employment outcomes, although at a minimum employment change, even if negative, should be more positive than the national rate of change. On the other hand, failed product and process upgrading is likely to result in employment decline. 2. Functional upgrading should result in significant employment decline as domestic production is reduced. 3. A low-road competitive strategy may result in stable employment in the short term, although the industry is likely to decline due to lack of innovation and intense competition. In the case of a rapidly globalizing industry such as furniture, the best-case scenario may involve growing market share and above-average change in capital investment and employment, even if the latter two indicators are declining. In the case of employment, a region able to maintain stable employment levels or experience only moderate employment loss might be considered successful in the changing competitive environment. Changes in capital investment, value added, and employment are shown for the 18 major furniture manufacturing states based on employment in 2005 (see Table 3). Table 3 also includes an Upgrading Index (UI) based on percent change in value added and capital investment, where VA = value added, K = capital investment, t2 = 2003–2005, and t1 = 1997–1999: UI = [( VA t 2 VA t1 × 100 ) + ( K t 2 K t1 × 100 )] 2 Upgrading trends in the furniture-producing states are displayed graphically in Figure 3. The upper right-hand quadrant corresponds with product and process upgrading, while the upper left-hand quadrant is associated with failed upgrading. The bottom right-hand quadrant could indicate low-road growth or functional upgrading, while the bottom left-hand quadrant could represent a failed low-road strategy, aggressive functional upgrading, or simply industry decline. Looking at the dashed axes, which indicate change in value added and capital investment for the U.S. furniture industry, we can see that the “center of gravity” of the industry is in the bottom right-hand quadrant. Growing output and falling capital investment is consistent with both functional upgrading and low-road growth, suggesting that these are dominant trends in the industry. Different patterns were identified for three groups of states: a top tier with aboveaverage change in capital investment and value added, a middle tier also experiencing growth in value added but greater declines in capital investment than the top-tier states, and 266 GROWTH AND CHANGE, JUNE 2008 TABLE 3. REGIONAL CHANGE IN U.S. FURNITURE MANUFACTURING, 1997–2005 (STATES RANKED BY UPGRADING INDEX). State Employment (thousands) 2005 Florida Missouri Wisconsin Pennsylvania Minnesota Indiana Texas Ohio California Mississippi U.S. Alabama New York Illinois Georgia Michigan Virginia Tennessee North Carolina 16.0 11.7 12.8 23.2 11.9 25.6 26.0 21.7 59.4 26.5 535.8 13.4 22.9 19.0 13.5 25.9 17.4 19.8 57.5 Percent change in employment Percent change in value added Percent Upgrading change in Indexa capital investment 1997–99 to 1997–99 to 1997–99 to 2003–05 2003–05 2003–05 -10.4 -2.2 -12.8 -7.6 -2.7 -3.9 0.9 -2.6 -8.5 -17.7 -11.0 -14.6 3.4 -3.9 -10.5 -15.5 -26.4 -24.4 -26.8 20.0 17.7 14.8 9.2 4.4 15.9 16.3 17.3 8.7 4.8 10.4 4.5 16.4 -7.8 2.0 5.2 -1.0 -7.7 -10.3 52.3 -9.0 -12.4 -13.7 -7.7 -30.4 -32.8 -33.4 -29.7 -25.2 -31.9 -30.4 -45.2 -29.6 -48.0 -61.0 -55.2 -50.7 -58.3 136 105 102 98 98 93 92 92 90 90 89 88 86 81 77 72 72 71 66 a The Upgrading Index = [(VAt2/VAt1 ¥ 100) + (Kt2/Kt1 ¥ 100)]/2, where VA = value added, K = new capital investment, t2 = 2003–2005 and t1 = 1997–1999. Source: Derived from U.S. Census of Manufacturers; 1997 and Annual Survey of Manufacturers, 1998–1999 and 2003–2005 (U.S. Census Bureau 2006b). a bottom tier with above-average decline in capital investment, combined with belowaverage growth or decline in value added. The top tier, with a UI greater than 97, includes five states: Florida, Missouri, Wisconsin, Minnesota, and Pennsylvania. These states accounted for 14 percent of furniture manufacturing employment and production in 2005 and do not include the major furniture producing agglomerations. Florida was the only state with growth in both value added GLOBALIZATION AND THE U.S. FURNITURE INDUSTRY 267 FIGURE 3. UPGRADING OF REGIONAL FURNITURE INDUSTRIES IN THE U.S., 1997– 1999 TO 2003–2005. Note: Dashed axes represent U.S. industry average. (+20 percent) and capital investment (+52 percent) between the two time periods—the one unequivocal case of production upgrading. In the other four states, capital investment declined but at a much slower rate than the national average of -32 percent, suggesting a mix of production upgrading and low-road growth. Missouri and Wisconsin firms experienced increased market share, with 18 and 15 percent growth in value added. Between 1997–1999 and 2003–2005, employment fell slightly in Missouri (-2 percent), and at an average rate in Florida (-10 percent) and Wisconsin (-13 percent). The middle tier includes states with changes in capital investment and value added close to the national average: Alabama, California, Indiana, Mississippi, New York, Ohio, and Texas. The UI in these states was between 86 and 93 (the U.S. average was 89). This group includes some of the country’s largest furniture agglomerations, in Los Angeles, Southern Indiana, Northeast Mississippi, and Dallas–Fort Worth, and accounted for 36 percent of the industry’s employment and 35 percent of its output. These industries are likely 268 GROWTH AND CHANGE, JUNE 2008 experiencing a mix of functional upgrading and low-road growth. The furniture industries in Indiana, New York, Ohio, and Texas appear to be growing without upgrading (the low-road approach), because above-average increases in value added corresponded with significant decline in capital investment and stable employment levels (including modest growth in New York and Texas). However, considerable employment losses were recorded in California (-9 percent), Alabama (-15 percent), and Mississippi (-18 percent). These three states also experienced below-average growth in value added and falling capital investment, suggesting that functional upgrading may be prevalent. The bottom tier, with an UI below 82, includes Georgia, Illinois, Michigan, North Carolina, Tennessee, and Virginia. This group represented 29 percent of the industry’s employment and 30 percent of its output. The country’s leading center of household furniture manufacturing is in North Carolina, while the major office furniture agglomeration is in Michigan. North Carolina, Tennessee, and Virginia were the only states in which greater than average decline in capital investment was combined with falling value added. This trend is consistent with functional upgrading. In Georgia and Michigan, equally severe contraction in capital investment corresponded with below-average growth in value added, while in Illinois, value added declined and capital investment fell at a rate close to the national average. Employment fell considerably in each of the bottom-tier states, with the exception of Illinois. Substantial job losses occurred in North Carolina (-27 percent), Virginia (-26 percent), and Tennessee (-24 percent), while Michigan’s employment fell 16 percent. Regional shift. There is an unexpected regional shift occurring in the U.S. furniture industry, with the lower-wage, nonunion South faring considerably worse than the higherwage North and West—in 2004, average annual earnings in furniture manufacturing were $33,900 in the U.S. North, $30,190 in the U.S. West, and $27,736 in the U.S. South (U.S. Census Bureau, 2006d). Unlike the manufacturing sector as a whole, in which Southern job change closely paralleled the national trend (annual change of -2.8 and -2.7 percent, respectively), the South absorbed most of the job loss in U.S. furniture manufacturing between 1997 and 2005. The Southern furniture industry experienced a net loss of 53,700 jobs between 1997 and 2005 (mostly in North Carolina, Tennessee, and Virginia), compared to 14,100 jobs in the rest of the country. Table 3 and Figure 3 show that the Southern states (with the exception of Florida and Texas) tend to have low scores on the UI, while Northern states (with the exception of Michigan and Illinois) tend to have higher scores. This can be explained by differences in regional industry specialization and structure that have influenced corporate globalization. As furniture manufacturing evolved in the Piedmont South through the twentieth century, firms capitalized on the region’s lumber and textile supplies and woodworking skills by specializing in wooden case goods—e.g., bedroom and dining room furniture, bookcases, and desks—as well as upholstered household furniture. As it turns out, case goods today are especially prone to offshore production. Even some upholstered products are being imported in higher volumes, as foreign firms master the details of motion mechanisms for recliners. On the other hand, some industry segments remain based on domestic production, including kitchen cabinetry, custom upholstery, custom woodwork and millwork, and mattresses. These industries are well GLOBALIZATION AND THE U.S. FURNITURE INDUSTRY 269 represented in metropolitan furniture-producing regions, where firms have access to large household and business markets—especially in the Northeast and Great Lakes states. Regional industry specialization and the distribution of furniture manufacturing employment based on the import sensitivity of the industry are shown in Table 4. Industry specialization was determined based on the share of a state’s furniture employment in an industry segment, compared with the share of the nation’s furniture employment in the same industry segment. In furniture manufacturing segments classified with high import sensitivity, imports as a share of value added were greater than 60 percent in 2002. Industries with medium import sensitivity had 15–30 percent import shares, and those with low import sensitivity had import shares below 15 percent. The share of a state’s furniture manufacturing employment in industry segments with high and medium import sensitivity is shown in Figure 4. The major Southern furniture producing states, with the exception of Texas, tend to specialize in industry segments with high to medium levels of imports. For example, in North Carolina, Mississippi, Tennessee, and Virginia, between 70 and 95 percent of furniture manufacturing employment in 2002 was based in highly import-sensitive industries, especially wood household, institutional, and upholstered furniture. These four states accounted for 61 percent of all Southern employment in furniture manufacturing. By comparison, in the rest of the U.S., 55 percent of furniture workers were employed in industries with high to medium levels of import sensitivity, while the rest were in low-import industries, including kitchen cabinets, custom woodwork and millwork, and metal office furniture. Also, the Southern furniture industry is dominated by major corporations operating large factories. For example, while only 1.7 percent of U.S. furniture manufacturing establishments employed 250 or more workers in 2004, the corresponding figures for Mississippi and North Carolina were 10.6 and 6.0 percent (Table 5). Virginia and Tennessee also had an above-average number of large establishments. This is significant for two reasons. First, larger firms and plants are able to exploit scale economies and produce more standardized furniture in longer production runs. These product lines are more readily outsourced than those made in customized, small-batch production runs. Also, larger firms are in a better position to make high-volume orders and provide managerial and technical expertise to offshore suppliers than smaller firms. Outside of the South, the most significant employment decline was in Michigan. This is despite the fact that Michigan specializes in office furniture (except wood), an industry segment with a low import share in 2002. Michigan’s furniture industry is based in Grand Rapids, which gained a reputation for high-quality furniture in the nineteenth century. However, the labor-intensive wood furniture industry declined in Grand Rapids and other northern centers by the mid-1900s due to competition from Southern producers. This led to a significant regional divide, as the Grand Rapids industry shifted its focus from household to office furniture, led by companies that would become industry giants: Steelcase, Haworth, and Herman Miller. Today, these firms are developing global supply networks and closing down domestic facilities. For example, Steelcase has aggressively expanded its global supply chain since 2002, and owns factories in 12 countries in North America, 2.56 0.58 1.87 0.75 1.04 1.05 0.70 1.05 1.65 0.69 1.34 1.31 337122 4.67 2.09 337124 2.11 1.43 2.00 337127 High import sensitivityc 0.71 2.90 2.49 4.30 0.66 1.29 337121 3.57 337211 0.99 1.16 1.35 2.62 1.35 1.20 1.01 1.58 1.21 0.99 1.21 0.88 0.95 1.15 337215 Medium import sensitivityc Industry Segment 2.76 337920 0.73 1.48 0.67 1.05 1.38 1.44 1.02 0.90 1.60 1.60 1.20 1.72 1.71 337110 8.23 337214 Low import sensitivityc a Industrial specialization: cell values show Index of Industry Specialization: = (Esr/Er)/(Esn/En), where Esr = state employment in the industry segment, Er = total state of employment in the furniture industry, Esn = rational employment in the industry segement, and En = national employment in the furniture industry. b State industry segments with more than 10% of state employment in furniture manufacturaing. Shaded cells indicate index of industry specialization > 1.50. c Import sensitivity: High (> 60 percent imports in 2002): wood household furniture (NAICS 337122), metal household furniture (337124), industrial furniture (337127); medium (15–30 percent imports in 2002): upholstered furniture (337121), wood office furniture (337211), showcases, shelvings, partitions, lockers (337215), blinds and shades (337920); low (< 6% imports in 2002): wood kitchen cabinets and countertops (337110), office furniture (except wood) (337214). NAICS refers to the North American Industrial Classification System. Source: Derived by author from Census of Manufactures, 2002 (U.S. Census Bureau, 2006b). Florida Missouri Wisconsin Pennsylvania Minnesota Indiana Texas Ohio California Mississippi Alabama New York Illinois Georgia Michigan Virginia Tennessee North Carolina U.S. State TABLE 4. REGIONAL INDUSTRY SPECIALIZATION,a U.S. FURNITURE MANUFACTURING.b 270 GROWTH AND CHANGE, JUNE 2008 GLOBALIZATION AND THE U.S. FURNITURE INDUSTRY 271 FIGURE 4. PERCENT OF EMPLOYMENT IN FURNITURE INDUSTRY SEGMENTS WITH HIGH OR MEDIUM IMPORT SENSITIVITY. Europe, the Middle East, and Pacific Asia (http://www.steelcase.com). The company has dramatically reduced its manufacturing capabilities in North America while expanding them in Asia. Also, it has increased its reliance on both domestic and foreign suppliers for parts, components, and finished products. Both Steelcase and Herman Miller recently opened manufacturing plants in China and are increasing their use of Chinese suppliers. In contrast to the lower-tier Southern states and Michigan, the top-tier states and most middle-tier states are characterized by small firms and less specialized in high-import 272 GROWTH AND CHANGE, JUNE 2008 TABLE 5. INDUSTRY SIZE STRUCTURE, U.S. FURNITURE MANUFACTURING.a State Employees per establishment Establishment size distribution (%) Employment size category Mississippi North Carolina Indiana Michigan Tennessee Alabama Virginia Wisconsin Ohio Pennsylvania Texas U.S. Missouri Illinois California Georgia Minnesota New York Florida 92 52 49 43 43 36 32 28 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 20 19 18 12 1–19 20–99 100–249 250 or more 58.1 66.9 63.9 75.0 74.9 78.2 79.7 74.6 82.4 76.6 75.1 78.9 81.1 79.1 78.2 80.9 80.9 82.6 87.3 19.9 20.9 25.8 17.2 17.5 14.8 12.9 20.7 14.6 18.3 20.1 16.1 15.4 16.1 17.3 15.0 15.3 15.1 10.1 9.6 6.8 5.6 4.5 4.6 3.7 3.4 3.5 1.8 3.8 3.5 3.3 2.0 3.6 3.3 3.1 2.4 1.8 2.2 12.3 5.5 4.7 3.3 3.0 3.2 3.9 1.2 1.2 1.3 1.3 1.7 1.5 1.2 1.2 1.0 1.4 0.5 0.4 a States ranked by percent of establishments with 250 or more employees. Source: U.S. Census Bureau (2006d). industry segments. These are industries dominated by small companies catering to local metropolitan markets, without the capacity or need to develop global sources. For example, Florida has the smallest average establishment size of the leading 18 furniture-producing states, with 12 employees per establishment compared with the industry average of 25. Florida firms specialize in kitchen cabinets, millwork, and mattresses, all industries with very low import penetration. Likewise, Minnesota employs 19 per establishment, and its firms specialize in kitchen cabinets and millwork, partitions and fixtures, and institutional furniture. The Pennsylvania industry specializes in kitchen cabinets and employs 27 workers per establishment. In the case of New York, where firms specialize in the importsensitive wood household furniture industry, the small size of establishments (average of 18 workers) mitigates the development of offshore networks. GLOBALIZATION AND THE U.S. FURNITURE INDUSTRY 273 TABLE 6. REGRESSION ANALYSIS OF EMPLOYMENT CHANGE IN FURNITURE MANUFACTURING (NAICS 337) IN THE U.S. t Constant IMPORT WAGE CAPITAL Adjusted R-square n 0.647 -2.721* -0.033 2.185* 0.35 30 * p < .05. The relation between industry structure and employment change can be captured by a regression model. Using data for the 30 states with the greatest employment in furniture manufacturing, a model was created with percent employment change between 1997–1999 and 2003–2005 as the dependent variable. The independent variables included the percent of employment in high and medium import-sensitive industry segments in 2002 (IMPORT), average wage in 2004 (WAGE), and average annual capital investment between 1997–1999 and 2003–2005 (CAPITAL) (Table 6). The coefficient for IMPORT was negative and highly significant (p = 0.011). There was an inverse relationship between total employment change and the percent of workers employed in furniture manufacturing segments subject to high levels of outsourcing. The WAGE coefficient was insignificant, and the CAPITAL coefficient was positive and significant (p = 0.038). Higher rates of capital investment were associated with stable or increasing employment. Thus, although the South remains an attractive region for incoming manufacturing investment—witness the location of Japanese, Korean, and German automobile manufacturing plants—the scale and product specialization of Southern furniture manufacturers means that larger firms are likely to outsource production to reduce costs. Traditional advantages of lower wage and production costs are insufficient to prevent widespread offshoring—and have in fact contributed to it. As a result, the country’s dominant household furniture producing region, centered on North Carolina and extending into Virginia and Tennessee, absorbed most of the country’s net employment loss in furniture manufacturing between 1997 and 2005. Although the Michigan industry specializes in office furniture segments with relatively low import sensitivity, the large firms based in Grand Rapids are implementing global strategies that involve increased offshoring and foreign direct investment. As a result, employment has declined significantly in Michigan in recent years. States whose furniture industries are based on smaller firms and establishments, with less specialization in 274 GROWTH AND CHANGE, JUNE 2008 segments with high import sensitivity, were more likely to experience stable or moderate decline in employment, combined with above-average change in value added and capital investment. We can surmise that the smaller furniture industries with stronger ties to local metropolitan markets are capitalizing on customized products and short delivery times to maintain competitiveness in a fast-changing environment. Corporate Restructuring and Regional Development: The Case of FBN and North Carolina The greatest job loss in the U.S. furniture industry is occurring in North Carolina, despite well-developed institutional assets and local labor markets, and an average hourly wage of $12.90 in 2005, 6 percent below the industry average (U.S. Census Bureau, 2006d). The North Carolina case illustrates how regional context influences processes of globalization and regional employment change. North Carolina firms specialize in household and office case goods, segments of the industry experiencing growing outsourcing. The North Carolina industry is based on large firms, including the largest manufacturer of furniture in the U.S., FBN. The implementation of global sourcing strategies by FBN and other manufacturers (e.g., Lexington Industries) has been the most important reason for the collapse in employment and falling production in North Carolina. The North Carolina furniture industry is repositioning, shifting case goods production overseas and concentrating on administration, marketing, and manufacturing of upholstered goods—a classic case of functional upgrading. In the late 1800s North Carolina entrepreneurs took advantage of ample supplies of timber; skilled, relatively inexpensive labor; and improved transportation networks to produce low-price furniture for the growing Southern market (Lacy 2004; Tewari 2005). Why did North Carolina emerge as the leading Southern center of furniture production when these advantages could be found throughout the South? Tewari (2005) argues that local firms created “a set of institutions and organizational practices” that propelled them to the front ranks of furniture producers in the South and eventually the U.S. They created a biannual furniture market in High Point where manufacturers advertised their products to retailers from around the country. Furniture manufacturers organized to promote competitiveness and build the region’s reputation. The International Shoe Company, FBN’s corporate ancestor, was created in 1911 by the merger of two St. Louis shoe manufacturers. The company expanded its shoe manufacturing empire through the 1960s, becoming one of the major producers in the U.S. The next three decades would witness a tumultuous corporate restructuring. Embarking on an aggressive diversification into retail and apparel manufacturing, International Shoe Company changed its name to Interco in 1966. Interco entered the furniture industry in 1980, acquiring the well-known company Ethan Allen. The North Carolina manufacturer Broyhill was purchased in 1981, followed by the Mississippi upholstery manufacturer Lane in 1987. As happened with other companies, the 1980s merger and acquisition wave left Interco deep in debt. By the end of the decade, Interco had sold or liquidated most of its retail and apparel manufacturing holdings, and was forced to sell Ethan Allen in 1989 in a failed attempt to reduce its debt and avoid bankruptcy (FBN 2006). GLOBALIZATION AND THE U.S. FURNITURE INDUSTRY 275 Emerging from bankruptcy in 1992, Interco decided to focus on the furniture industry and sold its remaining shoe manufacturing shares in 1994. In 1995, the company bought another well-regarded North Carolina manufacturer, Thomasville, and changed its name to Furniture Brands International in 1996. FBN vaulted to the front rank of U.S. furniture manufacturers in 2001 by acquiring North Carolina’s Henredon, Drexel Heritage, and Maitland-Smith (later consolidated into its HDM subsidiary) (FBN 2006). While the corporate headquarters are in St. Louis, four of FBN’s five subsidiary offices are in North Carolina, including two in High Point, the “capital” of the household furniture industry. Twenty-one of the company’s 27 manufacturing facilities are in the state, as are six of eight distribution centers (FBN 2006). FBN is pursuing a two-pronged strategy to remain globally competitive. First, its “blended sourcing strategy” combines offshore and domestic production. In 2003, FBN imported $523 million of furniture, which represented 22 percent of sales revenue (Lorimor and Christianson 2004). Second, FBN is transitioning into a “branded consumer products” company, promoting brand name recognition and distributing furniture in dedicated retail outlets. By 2005, FBN had 244 single-brand furniture stores (Thimangu and Mueller 2005). Evidence of a shift in corporate culture was revealed in the 2005 Annual Report, in which FBN Chairman and CEO Mickey Holloman stressed that the company is “shedding the manufacturing mindset” and becoming a “true sourcing and marketing company.” FBN owns only two foreign plants, in Cebu, Philippines and Semarang, Indonesia, which it inherited when it purchased Maitland-Smith in 2001. Its global production network is based on strategic alliances forged with firms in China, Vietnam, Philippines, and Indonesia. The major alliances are with Chinese manufacturers Lacquer Craft, Kasen International, and Hong Kong Teakwood Works, all located in the Zhu Jiang Delta. The company’s goal is to concentrate its supply network on “fewer and fewer vendors”; in 2005, just five firms accounted for about 50 percent of FBN’s imports (FBN 2006). FBN is working to reduce delivery times and warehousing costs by shipping containers directly to retailers. FBN’s Pacific Asia network is managed by the independent Furniture Brands Import Services Organization (FBISO), which plays a critical operational and logistical role on FBN. FBISO ensures product quality by maintaining personnel in each source firm and operating testing facilities in China and Philippines. Back home, FBN has slashed jobs and production and closed plants. Between 2000 and 2006, the company closed 33 manufacturing plants in the U.S. The effects of plant closings and job losses were mostly felt in North Carolina’s Furniture Alley, where 24 plants were closed. FBN plant closings and layoffs were responsible for 37 percent of jobs lost in the North Carolina furniture industry (North Carolina Employment Security Commission 2006). Altogether, FBN cut 7,100 jobs in North Carolina. While net sales grew from $1.94 to $2.39 billion between 2001 and 2005, total employment fell from 23,000 to 15,200 (FBN 2006). The pattern of plant closings reveals an international division of labor in the production of FBN furniture based on industry segment. The company is outsourcing more of 276 GROWTH AND CHANGE, JUNE 2008 its case goods production to partners in China and Vietnam, while maintaining most of its upholstery manufacturing in the U.S. 17 of the company’s remaining 25 factories in the U.S. produce upholstered furniture. Though growing volumes of upholstered furniture are being imported as Chinese manufacturers improve production techniques, there are still significant advantages to producing domestically in the custom upholstery segment in which products have a variety of fabric styles and are typically made to order. The repositioning of FBN in North Carolina is reflected in the growth of office and distribution facilities. In 2001, three offices and four distribution facilities were located in North Carolina. By 2006, four offices and six distribution facilities were located in the state. As furniture firms outsource more production while maintaining head office and distribution functions in the region, the ratio of non-production to production employment is increasing. In North Carolina, furniture manufacturing, non-production workers as a share of total employment increased from 14 to 19 percent between 1997 and 2005 (U.S. Census Bureau 2006b). The growth in non-production employment has not compensated for the loss in production jobs. The restructuring of furniture firms has hit the small factory towns of the North Carolina Piedmont especially hard. In Alexander and Caldwell counties, 34 and 25 percent of the workforce, respectively, was employed in furniture manufacturing in 2005 (Table 7). In Burke, Catawba, Davidson, and Randolph counties, furniture plants employed between 10 and 15 percent of the workforce. Just four counties absorbed the loss of 12,600 furniture manufacturing jobs between 2000 and 2005: Caldwell (where production is based in Lenoir), Catawba (Hickory), Davidson (Lexington and Thomasville), and Randolph (Asheboro). This represented 56 percent of furniture manufacturing employment decline in North Carolina and almost one in seven jobs lost in the industry nationwide. Almost 2,700 jobs were lost in Lenoir, including 2,150 at FBN plants. Thomasville—“Chair City”—lost 1,700 jobs, almost all from FBN layoffs and plant closings, and Lexington lost 1,700 jobs, mostly from the restructuring of Lexington Brands (North Carolina Employment Security Commission 2006; U.S. Census Bureau 2006d). This has resulted in higher unemployment, especially in the western counties of Burke, Caldwell, and Catawba, where average annual unemployment rates between 2001 and 2005 were 7.1, 7.8, and 7.1 percent, respectively, well above the state average of 5.9 percent (which was one of the highest in the nation). Average unemployment was 5.6 percent in Randolph and 6.6 percent in Davidson. The high volume of FBN production has enabled it to enter into supply partnerships with large Chinese firms. The firm is effectively trading regions, replacing the workers, factories, and regional assets of North Carolina with those of Guangdong. A recent development has raised the intriguing possibility that the site of corporate control in the FBN network may also move across the Pacific. Samson Industries, which owns Universal and Legacy Classic, now controls 15 percent of FBN stock. In October 2007, FBN declined a merger proposal from Samson. But Samson “hasn’t ruled out a tender offer in the near future” (Furniture/Today 2007). 15,813 9,662 8,366 8,293 6,176 3,774 2,942 1,896 1,361 1,317 1,226 1,220 1,034 2000 12,794 6,390 6,349 4,030 5,872 2,874 2,647 1,415 750 750 375 801 346 2005 Employment in furniture manufacturing -3,019 -3,272 -2,017 -4,263 -304 -900 -295 -481 -611 -567 -851 -419 -688 Change -4.1 -7.9 -5.4 -13.4 -1.0 -5.3 -2.1 -5.7 -11.2 -10.6 -21.1 -8.1 -19.7 Annual change 2000–2005 Sources: Employment data: US Census Bureau (2006d). Unemployment data: US Bureau of Labor Statistics (2006). Catawba Caldwell Randolph Davidson Guilford Burke Alexander Lincoln McDowell Surry Forsyth Wilkes Montgomery County 8.94 15.33 8.61 6.25 1.37 6.72 20.80 4.76 3.29 1.43 0.13 2.18 2.40 Location quotient 2005 14.7 25.3 14.2 10.3 2.3 11.1 34.3 7.9 5.4 2.4 0.2 3.6 4.0 Share of total employment 2005 7.1 7.8 5.6 6.6 5.6 7.1 6.3 6.6 6.8 6.8 5.1 6.8 7.7 Average unemployment 2001–2005 TABLE 7. FURNITURE MANUFACTURING IN NORTH CAROLINA EMPLOYMENT CHANGE IN MAIN FURNITURE PRODUCING COUNTIES, 2000–2005. GLOBALIZATION AND THE U.S. FURNITURE INDUSTRY 277 278 GROWTH AND CHANGE, JUNE 2008 Conclusion The ability of firms to develop global production networks has been facilitated by technological change and government policy. Furniture firms use information technology to control computerized machinery on the factory floor and manage supply and distribution logistics. Innovations in shipping and packaging make it possible to ship bulky, fragile furniture across the ocean. At the same time, the global embrace of neoliberal economic policy has reduced barriers to trade and investment. The pivotal political event for the globalization of the U.S. furniture industry has been the opening of the Chinese economy and the normalization of U.S.–China trade relations. This has allowed large U.S. firms to effectively shift their labor supply from traditional centers such as North Carolina to emerging agglomerations in coastal China, where workers are paid a pittance of U.S. wages. Regional job loss and attendant social consequences are a consequence of the increasing openness of local economies to globalizing processes. However, the impact of corporate globalization on U.S. furniture-producing regions depends to a considerable degree on each region’s industry structure and the situation of its firms in global production and distribution networks. For example, the severity of job loss in North Carolina, the leading household furniture manufacturing region in the U.S., is mainly the result of regional industrial history. North Carolina developed large firms focused on the production of wooden case goods and upholstered furniture. Wooden case goods are the most feasible furniture lines to source globally, and the large size of North Carolina firms facilitates the establishment of contracting relationships based on high-volume orders and technology and information transfer. In this case, the coevolution of firms and regional assets in North Carolina created a situation in which large, industry-leading furniture firms could develop. Now, however, they are looking to China as a low-cost production alternative to North Carolina. The regional assets of North Carolina are no longer valued as highly as those of the Zhu Jiang Delta, Ho Chi Minh City, or Shanghai, where U.S. firms have cultivated offshore partners capable of producing high-volume, high-quality furniture at a relatively low cost. On the other hand, furniture-producing regions in the Northern U.S. tend to focus on customized woodworking, cabinetry, and office furniture segments closely tied to metropolitan markets. This too is a product of regional history. Through the 1900s, Northern furniture industries faced stiff competition in the case goods and upholstered good segments from Southern firms and as a result tended to shift to other industry segments. The smaller size of firms and the specialized, customized character of their products makes them less vulnerable to imports and less likely to shift production offshore. As a result, these industries have experienced lower rates of job loss, and several states are increasing market share. The main exception is Michigan, where large, capital-intensive firms carved out a dominant position in the continental office furniture industry. Their scale has enabled them to move production globally into new markets and outsource the production of standardized components and products for the U.S. market. What policy options are available to regions faced with industry change? Protectionist petitions are likely to have little if any effect, especially as they tend to mask underlying GLOBALIZATION AND THE U.S. FURNITURE INDUSTRY 279 globalizing processes. The U.S. Department of Commerce supported the antidumping petition, stating that Chinese producers sold furniture in the U.S. at “less than fair values.” Seven companies, representing about 40 percent of U.S. wood furniture imports, were assessed preliminary tariffs between 4.9 and 24.3 percent. These included large manufacturers such as Lacquer Craft, Starcorp, Markor, and Shing Mark. An additional 82 “Section A” companies that cooperated with the Department’s investigation received a tariff of 10.9 percent, and all other Chinese firms were assessed a rate of 198.1 percent (U.S. Department of Commerce 2004a). After further review, though, the tariffs for the “Big Seven” were reduced to 0.8 to 15.8 percent, and the Section A companies saw their tariff reduced to 6.7 percent (U.S. Department of Commerce 2004b). These tariffs were much lower than the level demanded by the petitioners and had a negligible effect on rising furniture imports. More than anything, the petition revealed the divide in the U.S. furniture industry between transnational retailers and manufacturers, on the one hand, and smaller companies concentrating on domestic production, on the other. To effectively compete in the global economy, furniture firms need to develop and sell high-quality products, offer diverse styles, ensure quick delivery, and provide personal customer service. Furniture remains a bulky fashion product subject to significant transportation costs; rising production costs in China or changes in the regulatory landscape could reduce the cost savings associated with offshore production. Regions could try to encourage the growth of small- and medium-size firms in segments of the furniture industry focused on customization and less vulnerable to imports. There are a number of actions governments could take to promote entrepreneurialism and industry growth, including 1) working with colleges and businesses to match vocational training programs with the labor needs of local firms, 2) promoting innovation through financial and technical assistance, and 3) assisting firms in marketing and distributing their products. The example of the Québec furniture industry is instructive. Several industry-specific institutions support innovation and growth, such as L’Ecole québécoise du meuble et du bois ouvré, which provides technical assistance, applied research, worker training, and assistance with production organization. There is still space for regional policy in a globalizing economy. NOTE 1. Unless otherwise noted, all monetary values are in constant 2005 U.S. dollars. REFERENCES Bair, J., and G. Gereffi. 2003. Upgrading, uneven development, and jobs in the North American apparel industry. Global Networks 3: 143–169. Bathelt, H., A. Malmberg, and P. Maskell. 2004. Clusters and knowledge: Local buzz, global pipelines, and the process of knowledge creation. Progress in Human Geography 28: 31–56. Becker, D. 2003. The giant awakens: The plants. Greensboro News & Record, March 2. http:// www.news-record.com (accessed June 17, 2004). Bristow, G. 2005. Everyone’s a “winner”: Problematising the discourse of regional competitiveness. Journal of Economic Geography 5: 285–304. 280 GROWTH AND CHANGE, JUNE 2008 Bryson, V., G. Lanzillotti, J. Myerberg, E. Miller, and F. Tian. 2003. The furniture industry (case goods): The future of the industry, United States versus China. Unpublished manuscript. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina, Kenan-Flagler Business School. Carroll, B. 2003. Shenzhen flexes furniture muscles. Furniture Today, January 6. http://www. furnituretoday.com (accessed December 12, 2005). Coe, N.M., M. Hess, H.W. Yeung, P. Dicken, and J. Henderson. 2004. “Globalizing” regional development: A global production networks perspective. Transactions of the Institute of British Geographers 29: 468–484. Dicken, P. 2007. Global shift: Transforming the world economy, 5th ed. London: Routledge. Dicken, P., and A. Malmberg. 2001. Firms in territories: A relational perspective. Economic Geography 77: 345–363. Evans, G. 2006. Lacquer Craft acquires Craftmaster Furniture. Furniture/Today, May 2. http:// www.furnituretoday.com (accessed May 2, 2006). Fan, C.C., and A.J. Scott. 2003. Industrial agglomeration and development: A survey of spatial economic issues in East Asia and a statistical analysis of Chinese regions. Economic Geography 79: 295–319. Fortune Magazine. 2006. Fortune 1000. April 17. Furniture Brands International (FBN). 2006. Annual reports and 10-K reports. http://www. furniturebrands.com (accessed August 26, 2006). Furniture/Today. 2007. Samson Holdings get 14.9 percent stake in Furniture Brands. http:// www.furnituretoday.com (accessed October 1, 2007). Gertler, M. 1995. “Being there”: Proximity, organization, and culture in the development and adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies. Economic Geography 71: 1–26. Giuliani, E., C. Pietrobelli, and R. Rabellotti. 2005. Upgrading in global value chains: Lessons from Latin American clusters. World Development 33: 549–573. Hashirimoto, O., J. Castano, and S. Johnson. 2004. Changing global picture of trade in wood products. Unasylva 55(219): 19–26. High Point Economic Development Corporation. 2006. Legacy Classic Furniture chooses High Point. http://www.high-point.net/edc (accessed June 22, 2006). Houseman, S. 2007. Outsourcing, offshoring, and productivity measurement in U.S. manufacturing. Upjohn Institute Staff Working Paper No. 06–130. Kalamazoo, MI: W.E. Upjohn Institute for Employment Research. Hsing, Y. 1995. Taiwanese guerrilla investors in southern China. Review of Urban and Regional Development Studies 7: 24–34. Johns, J. 2006. Video games production networks: Value capture, power relations and embeddedness. Journal of Economic Geography 6: 151–180. Kaplinsky, R., M. Morris, and J. Readman. 2002. The globalization of product markets and immiserizing growth: Lessons from the South African furniture industry. World Development 30: 1159– 1177. Kaplinsky, R., and J. Readman. 2005. Globalization and upgrading: What can (and cannot) be learnt from international trade statistics in the wood furniture sector? Industrial and Corporate Change 14: 679–703. GLOBALIZATION AND THE U.S. FURNITURE INDUSTRY 281 Kitson, M., R. Martin, and P. Tyler. 2004. Regional competitiveness: An elusive yet key concept? Regional Studies 38: 991–999. Knutsen, H.M. 2005. Industrial development in buyer-driven networks: The garment industry in Vietnam and Sri Lanka. Journal of Economic Geography 4: 545–564. Lacy, R.L. 2004. Whither North Carolina furniture manufacturing? Federal Reserve Bank of Richmond Working Paper No. 04-07, Richmond, VA. Leslie, D., and S. Reimer. 1999. Spatializing commodity chains. Progress in Human Geography 23: 401–420. Lin, G.C.S. 2001. Metropolitan development in a transitional socialist economy: Spatial restructuring in the Pearl River Delta China. Urban Studies 38: 383–406. Lorimor, S., and R. Christianson. 2004. State of the industry: Furniture sales and imports on a growth path. Wood & Wood Products, June. http://www.iswonline.com (accessed February 10, 2005). Molotch, H. 1996. L.A. as design product: How art works in a regional economy. In The city: Los Angeles and urban theory at the end of the twentieth century, ed. A.J. Scott and E. Soja, 275. Berkeley and Los Angeles: University of California Press. Naughton, B. 1996. Growing out of the plan: Chinese economic reform, 1978–1993. Cambridge and New York: Cambridge University Press. North Carolina Employment Security Commission. 2006. Announced business closings and permanent layoffs. http://www.ncesc.com (accessed August 6, 2006). Perry, D. 2004. Chinese manufacturer eyes U.S. Furniture/Today, 18 October. http://www. furnituretoday.com (accessed November 10, 2004). Peters, J. 2002. Furniture under fire. Virginia Business, August. http://www.virginiabusiness.com (accessed July 20, 2004). Rothenberg-Aalami, J. 2004. Coming full circle? Forging missing links along Nike’s integrated production networks. Global Networks 4: 335–354. Russell, T. 2004. Lacquer Craft’s Dongguan plant set to begin production in September. Furniture/ Today, May 31. http://www.furnituretoday.com (accessed May 31, 2004). ———. 2005. New classic sets big China plant. Furniture/Today, January 31. http://www. furnituretoday.com (accessed January 31, 2005). ———. 2006. Lacquer Craft parent reports higher sales, profits. Furniture/Today, May 9. http://www. furnituretoday.com (accessed May 9, 2006). Sacchetti, S., and R. Sugden. 2003. The governance of networks and economic power: The nature and impact of subcontracting relationships. Journal of Economic Surveys 17: 669–690. Schmid, J., and R. Romell. 2003. China turns the tables. Milwaukee Journal Sentinel, December 28. http://www.jsonline.com (accessed June 22, 2004). Scott, A.J.. 2006. The changing global geography of low-technology, labor-intensive industry: Clothing, footwear, and furniture. World Development 34: 1517–1536. Scott, A.J., and M. Storper. 2003. Regions, globalization, development. Regional Studies 37: 579–593. Slaughter, P. 2005. China manufacturer targets U.S. Furniture/Today, April 18. http://www. furnituretoday.com (accessed April 18, 2005). Smith, A., A. Rainnie, M. Dunford, J. Hardy, R. Hudson, and D. Sadler. 2002. Networks of value, commodities, and regions: Divisions of labor in macro-regional economies. Progress in Human Geography 26: 41–63. 282 GROWTH AND CHANGE, JUNE 2008 Storper, M. 1997. The regional world: Territorial development in a global economy. New York and London: The Guilford Press. Sturgeon, T. 2000. How do we define value chains and production networks? Working Paper 00-0010. Boston: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Industrial Performance Center. Tewari, M. 2004. Outsourcing in North Carolina’s furniture industry. Paper presented at Duke University, Panel on Global Outsourcing, April 13. http//www.soc.duke.edu (accessed February 14, 2005). ———. 2005. Nonlocal forces in the historical evolution and current transformation of the North Carolina furniture industry. In The American South in a global world, eds. J.L. Peacock, H.L. Watson, and C.R. Mattews, 113–137. Chapel Hill and London: University of North Carolina Press. Thimangu, P.L., and A. Mueller. 2005. Holliman rebuilds furniture brands. St. Louis Business Journal, May 27. http://www.bizjournals.com (accessed June 5, 2006). Tokatli, N., and O. Kizilgun. 2004. Upgrading in the global clothing industry: Mavi Jeans and the transformation of a Turkish firm from full-package to brand-name manufacturing and retailing. Economic Geography 80: 221–240. U.S. Census Bureau. 2006a. Foreign trade statistics. http://www.census.gov (accessed February 15, 2006). ———. 2006b. Annual survey of manufactures 1997–2001, 2003–2005, and census of manufactures 2002. http://www.census.gov (accessed February 15, 2006). ———. 2006c. Housing units authorized by building permits. http://www.census.gov (accessed September 1, 2006). ———. 2006d. County business patterns. http://www.census.gov (accessed September 1, 2006). U.S. Department of Commerce. 2004a. Preliminary determination of antidumping investigation: Wooden bedroom furniture from the People’s Republic of China. http://ia.ita.doc.gov/download/ factsheets/factsheet-prc-bedroom-furniture-061704.pdf (accessed July 6, 2006). ———. 2004b. Amended final determination in the antidumping investigation on imports of wooden bedroom furniture from the People’s Republic of China. http://www.trade.gov/media/FactSheet/ 1204/furniture_122804.html (accessed July 6, 2006). Union Européenne de l’Ameublement. 2000. Monitoring of the Chinese furniture sector. United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD). 2004. Trade and development report. http://www.unctad.org (accessed January 21, 2005). ———. 2007. International trade statistics. http://www.unctad.org (accessed August 1, 2005). Urban, H., 2002. U.S. furniture makers heed the great call of China. Wood & Wood Products, April. http://www.iswonline.com (accessed June 7, 2006). van Grunsven, L., and F. Smakman. 2001. Competitive adjustment and advancement in global commodity chains: I. Firm strategies and trajectories in the East Asian apparel industry. Singapore Journal of Tropical Geography 22: 173–188. Webber, M., and S. Weller. 2001. Trade and inequality: Australia’s textile, clothing, and footwear industries, 1986–1996. Journal of Economic Geography 1: 381–403. Wei, Y.D. 2000. Regional development in China: States, globalization, and inequality. London and New York: Routledge. Xu, M., X. Cao, and E. Hansen. 2003. China’s wood furniture industry. Asia Timber Magazine, September–October. http://www.asiatimber.net (accessed January 24, 2005).