Dihybrid Cross Worksheet In peas, round seed
advertisement
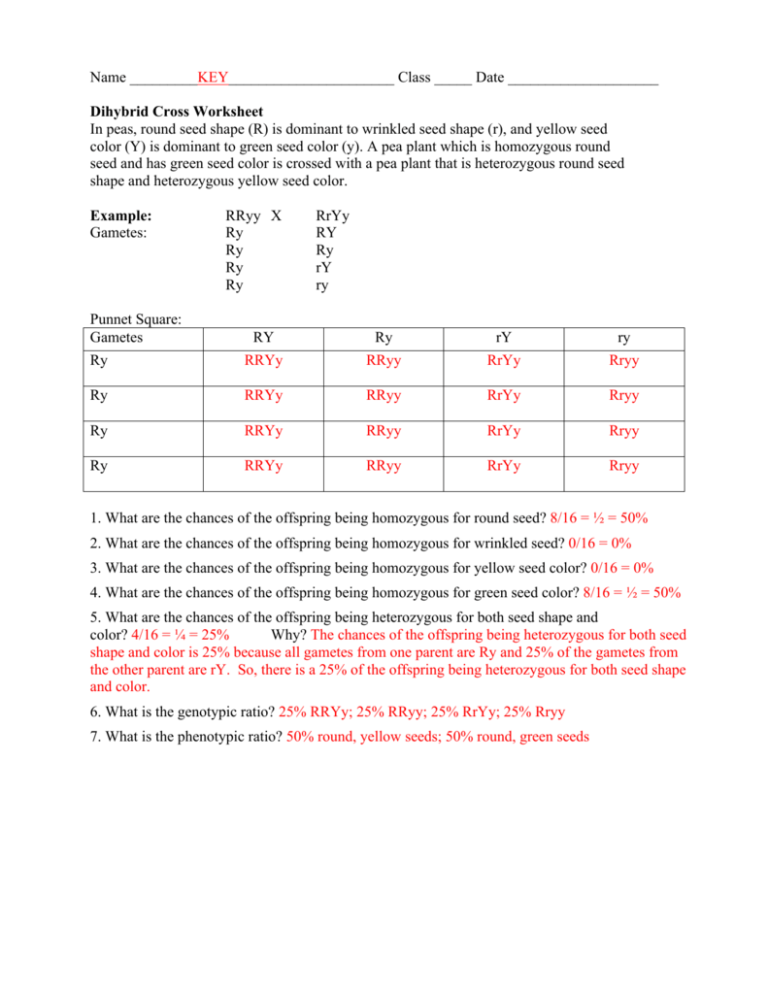
Name _________KEY______________________ Class _____ Date ____________________ Dihybrid Cross Worksheet In peas, round seed shape (R) is dominant to wrinkled seed shape (r), and yellow seed color (Y) is dominant to green seed color (y). A pea plant which is homozygous round seed and has green seed color is crossed with a pea plant that is heterozygous round seed shape and heterozygous yellow seed color. Example: Gametes: RRyy X Ry Ry Ry Ry RrYy RY Ry rY ry Punnet Square: Gametes Ry RY RRYy Ry RRyy rY RrYy ry Rryy Ry RRYy RRyy RrYy Rryy Ry RRYy RRyy RrYy Rryy Ry RRYy RRyy RrYy Rryy 1. What are the chances of the offspring being homozygous for round seed? 8/16 = ½ = 50% 2. What are the chances of the offspring being homozygous for wrinkled seed? 0/16 = 0% 3. What are the chances of the offspring being homozygous for yellow seed color? 0/16 = 0% 4. What are the chances of the offspring being homozygous for green seed color? 8/16 = ½ = 50% 5. What are the chances of the offspring being heterozygous for both seed shape and color? 4/16 = ¼ = 25% Why? The chances of the offspring being heterozygous for both seed shape and color is 25% because all gametes from one parent are Ry and 25% of the gametes from the other parent are rY. So, there is a 25% of the offspring being heterozygous for both seed shape and color. 6. What is the genotypic ratio? 25% RRYy; 25% RRyy; 25% RrYy; 25% Rryy 7. What is the phenotypic ratio? 50% round, yellow seeds; 50% round, green seeds In the following plants round seed shape is dominant over wrinkled seed shape and yellow seed color is dominant over green seed color. Determine the offspring expected when two pea plants, each heterozygous for seed shape and seed color, are crossed. R = round seed shape r = wrinkled seed shape Parents: R r Yy Gametes: RY Ry rY ry Y = yellow seed color y = green seed color X R r Yy RY Ry rY ry Punnett Square: Gametes RY RY RRYY Ry RRYy rY RrYY ry RrYy Ry RRYy RRyy RrYy Rryy rY RrYy RrYy rrYY rrYy ry RrYy Rryy rrYy rryy 8. What are the chances of the offspring being homozygous for both round seed shape and yellow seed color? 1/16 = 6.25% RRYY 9. What are the chances of the offspring being homozygous for both wrinkled seed shape and green seed color? 1/16 = 6.25% rryy 10. What are the chances of the offspring being heterozygous for both shape and seed color? 4/16 = 25% RrYy 11. What is the genotypic ratio? 1/6 RRYY; 2/16 RRYy; 2/16 RrYY; 1/16 RRyy; 4/16 RrYy; 1/16 rrYY; 2/16 Rryy; 2/16 rrYy; 1/16 rryy 12. What is the phenotypic ratio? 9:3:3:1 9/16 round, yellow seeds (DOM-DOM) 3/16 round, green seeds (DOM-REC) 3/16 wrinkled, yellow seeds (REC-DOM) 1/16 wrinkled, green seeds (REC-REC) A purebred wingless red-eyed fruit fly is crossed with a purebred winged sepia-eyed fruit fly to produce F1 flies. A = wings Parents: a a E E X A A e e a = wingless E = red-eyes e = sepia-eyes Gametes: aE Ae aE Ae aE Ae aE Ae Punnett Square: Gametes Ae aE AaEe aE AaEe aE AaEe aE AaEe Ae AaEe AaEe AaEe AaEe Ae AaEe AaEe AaEe AaEe Ae AaEe AaEe AaEe AaEe Two of the F1 flies are mated to produce an F2 generation of flies. What is the phenotypic ratio of the F2 flies? F2 Parents: A a E e Gametes: X AE Ae aE ae A a E e AE Ae aE ae Punnett Square: Gametes AE AE AAEE Ae AAEe aE AaEE ae AaEe Ae AAEe AAee AaEe Aaee aE AaEE AaEe aaEE aaEe ae AaEe Aaee aaEe aaee Genotypic ratio: 1/16 AAEE; 2/16 AAEe; 2/16 AaEE; 1/16 AAee; 4/16 AaEe; 1/16 aaEE; 2/16 Aaee; 2/16 aaEe; 1/16 aaee Phenotypic ratio: 9/16 winged with red eyes (DOM-DOM) 3/16 wingless with red eyes (REC-DOM) 3/16 winged with sepia eyes (DOM-REC) 1/16 wingless with sepia eyes (REC-REC)