Hydraulics Laboratory Experiment # "Flow over triangular V-notch weir"
advertisement

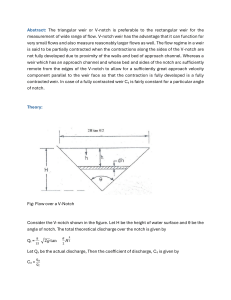
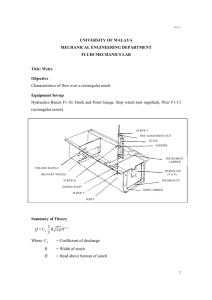
Hydraulics Laboratory Experiment # "Flow over triangular V-notch weir" Flow over triangular V-notch weir Introduction: Weirs are generally used to measure discharge in open channels were accuracy is required. Weirs are sometimes used in hydraulic engineering to regulate the flow in rivers and channels. Discharge over sharp crested weirs is a device used to measure Q accuracy +- 2% A sharp crested weir is formed from a steel or thin stainless steel (rectangular, triangular, trapezoidal, V notch). Objective: To determine the coefficient of discharge and the head-discharge relationship for Vnotch weir. Equipment: Hydraulic bench, hook and point gauge. Theory: The theoretical discharge for triangular notch is given by Qtheo = 8/15 (2g)1/2 tan(ө/2)H5/2 Where; H: height of flow over notch. ө: angle of the V-notch which was 90 To obtain the actual discharge, a coefficient of discharge Cd Qactual = Cd 8/15(2g)1/2 tan(ө/2)H5/2 Procedure: 1- Set a slope degree below 2% 2- Fit the selected weir plate at the channel discharge end 3- Start the pump and regulate the discharge value in order to reach the required flow rate 4- Measure the difference between the water surface height (m) against the bed upstream of the weir plate, and the weir height p (m) 5-Calculating the static head value H (m) by h = H-p, where p is the still height against the channel bed 6- Measure and record H and Q Analysis: Results # 1: Q (m3/h) Table (1): Q & H Q (m3/s) H (m) Results # 2: Table (2): H5/2-vs-Q Q (m3/s) H5/2 (m)