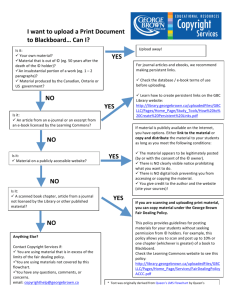
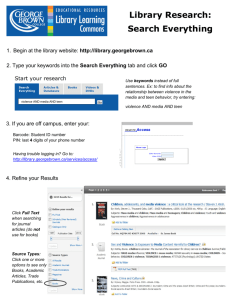
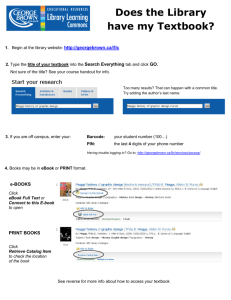
notes - Centre for Instructional Development
advertisement

What is Accessible Media? Learn @ Lunch Anne Villahermosa March 13, 2012 W5H What? universally designed course content that fosters an inclusive and equitable learning environment Who? All Members of the College Community: o Learners o Faculty & Staff o Administrators o Guest Speakers o Vendors Why? Meets a diverse range of learners needs & preferences from the start Where? o In the classroom o On-line courses o College-wide events o Professional development workshops o College website o Service areas When? Now! Video Why Captioned Media? How? Accessible Media Policy http://researchguides.georgebrown.ca/captionedmedia SITE SEARCH Ask a Librarian... Home Find Materials Study Tools Services Contact Us Help Library » Research Guides » Captioned Media & E-Text Captioned Media & E-Text Last Updated: Mar 8, 2012 Admin Sign In Tags: research guide URL: http://researchguides.georgebrown.ca/captionedmedia Captioned Media & E-Text Why Captioned Media? "Why Captioned Media" Video (wmv) "Why Captioned Media?" (Transcript) Comments (0) Conferences 2011 Monday, Jun 20, 2011: CACUSS 2011 ASEUCC at Ryerson University, Toronto Co-Presenting:"Enhancing the Accessibility of Your Postsecondary Library by Maximizing Partnerships within the Institution" at the Canadian Association of College and University Student Services (CACUSS) annual conference. Monday, Jul 11, 2011 to Saturday, Jul 16, 2011: AHEAD 2011: Sustainable Access through Partnership The 34th Conference of the Association of Higher Education and Disability in Seattle, Washington. Comments (0) Comments(0) Print Page Print Guide RSS Updates Search: Accessible Media This Guide !Search My Profile All media newly acquired by the Library is either closed captioned or permission to caption has been obtained. Currently 50% of the Library’s media collection is closed captioned. Closed captioned media displays the audio content as text on-screen in synchronization with dialogue, narration and sound effects. This feature provides equitable access to media by all students. In accordance with the regulations of the Accessibility for Ontarians with Disabilities Act (AODA), all Divisions are required to adhere to accessibility standards and principles when designing, adopting and procuring educational materials and resources for the delivery of course curricula. This includes, but is not limited to, the following: E-books, course-packs, e-learning platforms, interactive and instructive online learning management systems, audio-visual and multi-media. The College has a Captioned Media and E-text Policy which stipulates that all media produced or purchased for instructional, informational or marketing purposes must be captioned or permission to caption must be granted as a condition of purchase. Divisions must allocate a budget for making resources accessible, such as captioning audio-visual media. Anne Villahermosa, MA Ed. Contact Info Accessible Media Co-ordinator Educational Resources George Brown College 200 King Street East Toronto, ON M5A 3W8 Tel. 416.415.5000 ext. 2782 TTY 1.877.515.5559 Faculty members may contact the Accessible Media Co-ordinator to review the media used in their curricula to determine if it is closed captioned, if a closed captioned version exists or if a suitable alternative is available. Assistance is available to all members of the College community using audio-visual resources for instructional purposes, college-wide events or websites to facilitate the closed captioning of the material. Send Email Links: Profile & Guides Subjects: Accessible Media In The News CACUSS 2011 Presentation Comments (0) Universally Design Transit Pass Books CACUSS 2011 Presentation Comments (0) Conferences 2010 Tuesday, Jun 8, 2010: Aiming for Accessibility Conference - University of Guelph, Ontario Panelist: Making Media Accessible in Educational Environments Wednesday, Jul 14, 2010: AHEAD Conference - Denver, Colorado Co-Presenter: Accessible Media Policies: A Canadian Model for Development, Implementation and Sustainability in PostSecondary Institutions Comments (0) Universal Design Handbook, 2E - Wolfgang Preiser and Korydon H. Smith (2010) ISBN: 9780071629232 The book provides an overview of universal design premises and perspectives, and performance-based design criteria and guidelines. Public and private spaces, products, and technologies are covered, and current and emerging research and teaching are explored. This unique resource includes analyses of historical and contemporary universal design issues from seven different countries, as well as a look at future trends. World Report on Disability - June 9, 2011 Integrated Accessibility Regulation - June 3, 2011 May 29th - June 4th 2011 National Access Awareness Week Braille Newspapers in India Design Meets Disability - Graham Pullin (2009) ISBN: 9780262162555 Eyeglasses have been transformed from medical necessity to fashion accessory. This revolution has come about through embracing the design culture of the fashion industry. Why shouldn't design sensibilities also be applied to hearing aids, prosthetic limbs, and communication aids? In return, disability can provoke radical new directions in mainstream design. November 29, 2010 Federal Court of Canada's landmark decision concerning the rights of Canadians with disabilities to access government websites 21st Century Communications & Video Accessibility Act of 2010 (U.S.) George Brown College How? 8 Tips for Accessible Course Materials & Universal Design Resources Contact Anne Villahermosa, MA Ed. Accessible Media Co-ordinator 200 King Street East Toronto, ON M5A 3W8 416.415.5000 ext 2782 1.800.265.2002 Toll Free TTY 1.877.515.5559 ext. St. James Library avillahe@georgebrown.ca www.georgebrown.ca Captioned Media and E-text Policy: http://researchguides.georgebrown.ca/captionedmedia Eight Tips for Making Your Course Content Accessible 1. Make textbook adoption decisions as early as possible (before any established college deadline for textbook adoptions). 2. Request an electronic version and/or additional desk copy of your textbooks. Use publishers who offer electronic copies. 3. Caption all videos used for instruction and provide transcripts for audio-only materials. 4. Provide students with alternative methods to receive lecture materials, including posting lecture notes online, providing transcripts, etc. 5. Be open to communicating with students about their learning styles and using multiple instructional methods to address their needs. 6. Create or convert and post electronic course materials online in accessible formats. Make materials available as soon as possible to facilitate student learning. 7. Provide "clean" copies of class handouts or use materials already in electronic format, and make them available to students before the material is covered in class. 8. Use the campus course / learning management system to post the syllabus and other important class information and course materials electronically. Source: http://ctfd.sfsu.edu/feature/eight-specific-steps-faculty-cantake-for-making-your-courses-accessible.htm Universal Design Resources “Making online teaching accessible: inclusive course design for students with disabilities.” Written by Norm Coombs (2010) Published by Jossey-Bass. ISBN 9780470499047. Universal Design in Education: Principles and Applications: http://www.washington.edu/doit/Brochures/Academics/ud_edu.html Center for Applied Special Technology (CAST) – Universal Design for Learning: http://www.cast.org/ National Center on Accessible Instructional Materials: http://aim.cast.org/ National Center for Accessible Media – WGBH NCAM http://ncam.wgbh.org/invent_build/web_multimedia/tools-guidelines University of Victoria – Moodle accessibility and on-line learning content (course design tips for instructors) http://elearning.uvic.ca/moodle/instructors/best-practices/310accessibility How-to guide for creating accessible online learning content: http://projectone.cannect.org/ George Brown College: Guide to Creating Accessible Documents: http://www.georgebrown.ca/AODA/documents/GBC-AccessibilityBooklet.pdf