Circulatory System Consists of the following main organs: 1. Heart 2
advertisement

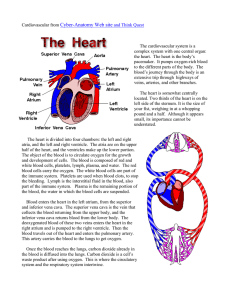
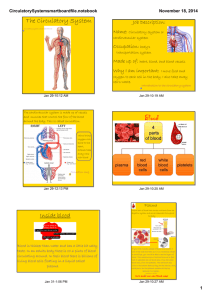
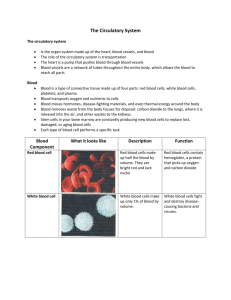
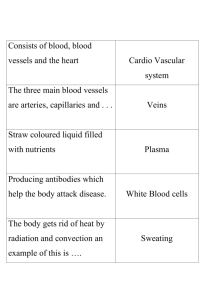
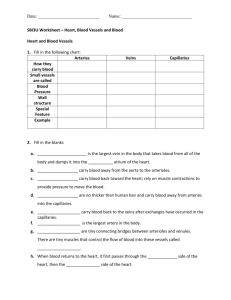
Circulatory System Consists of the following main organs: 1. Heart 2. Lungs 3. Blood Vessels 3. Transports white blood cells to defend the body against disease (immune system). Transport system reaching every cell in the body. 1. Blood delivers nutrients absorbed by the digestive system and oxygen absorbed by the respiratory system. 2. Transports waste products from cells for removal by the excretory and respiratory systems. Heart Muscle that contracts and relaxes to pump blood around the body. Each side of the heart is a separate pump. The right side pumps blood to your lungs, where it receives oxygen and gives off carbon dioxide. The left side of the heart receives blood from the lungs and pumps the blood around the body. 1 Each side of the heart is divided into 2 chambers: http://heart.healthcentersonline.c om/heartvalve/valvulardiseaseov erview.cfm Top two chambers are called Atria and the bottom two chambers are called Ventricles. Draw and label Figure 3.17 on page 137. 3 Types of Blood Vessels 1. Arteries – Transport oxygenated blood away from the heart, to the rest of the body. Veins – Transports deoxygenated blood (high in carbon dioxide) from the cells to the heart. Veins have valves that stop the blood from flowing backwards. 2 Vericose Veins Capillaries – very small, thin blood vessels. This is where the blood gasses and nutrients are exchanged with cells. 1. Capillaries are made up of specialized epithelial tissue that is only one cell layer thick. 2. Capillaries are very narrow, so that the blood cells must go through in single file. Skin Capillaries 3 Blood Consists of: 1) 1. Red blood cells ( hemoglobin) – carries oxygen to the cells. 1) 2. White blood cells ( immune system) 3. Platelets – help to stop bleeding (clotting) 4. Plasma – liquid portion (55% of blood volume), transports nutrients and carries waste, such as carbon dioxide away. 4