Reproductive Anatomy: Male & Female
advertisement

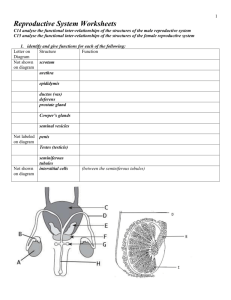
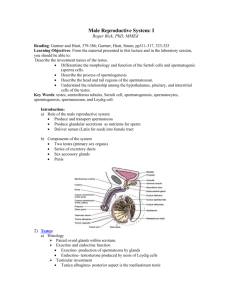
Reproductive Anatomy: Male & Female 1. Both the male and female reproductive systems contain the same basic parts, fill in their functions: Gonads: Ducts: Accessory Glands: External Genitalia: 2. What are the male gonads called? 3. How does sperm differ from semen? 4. What are the female gonads called? The Male: 5. Use figure 19-1 to help you draw a diagram of the male reproductive system that includes all of the following: Testis Epididymis Ductus deferens (vas deferens) Ejaculatory duct Urethra Seminal vesicles Prostate gland Bulbourethral glands Scrotum Penis 6. If one testis becomes infected, will it generally spread to the other testis? Why or why not? 7. What are the two muscles associated with the male testes and what do they do? 8. Why are these muscles necessary? 9. Look at figure 19-2a. Notice how the testes are separated into small areas called lobules. A membrane called septa separates each lobule. Coiled inside each lobule are small tubules called _________________________. What occurs within these tubules? 11. The seminiferous tubules in each lobule connect to a maze of passageways known as the rete testis and this in turn connects to the epididymis. On your diagram above add the following structures: lobules, septa, seminiferous tubules, and rete testes. 12. Located between the seminiferous tubules are blood vessels and cells that secrete the dominant male sex hormones called androgens. What is the most important androgen? 13. Read about spermatogenesis on pages 616-617. Fill in the missing areas on the flow chart and add notes in the margins about each step. Outermost layer of cells in the seminiferous tubules spermatogonia Mitosis Meiosis spermatozoa Fluid of lumen inside the seminiferous tubule 14. A spermatozoon (singular for spermatozoa) has three distinct regions, label the picture and state the function of each part. 15. Is a spermatozoon newly formed from the testes capable of fertilizing an oocyte? 16. Once spermatozoa are released into the lumen of the seminiferous tubules they are transported to the epididymis. What are the three functions of the epididymis? 17. Spermatozoa leaving the epididymis are still not able to fertilize an oocyte. They must first undergo capacitation. What are the two steps of capacitation? 18. Next the spermatozoa enter the ductus deferens. How does spermatozoa move through the ductus deferens? ______________________ How long can it stay here? ____________________ 19. Spermatozoa coming from the ductus deferens are joined by fluid from the seminal vessicles. What is this fluid and what does it do? 20. The prostate gland also secretes fluid called prostatic fluid. What is it and what does it do? 21. The final glands to add fluid to semen are the bulbourethral glands. What is this fluid and what does it do? 22. An ejaculate (2-5ml of semen) contains what? 23. The penis contains two types of erectile tissue. Describe what they are and how erection occurs. THE FEMALE 24. Use figure 19-8 to help you draw a diagram of the female reproductive system that includes all of the following: ovaries uterine tubes uterus vagina cervix clitoris 25. What are the functions of the ovaries? 26. Ovum production, or oogenesis begins __________________________________, accelerates at ______________________________, and ends at ___________________________________. Between puberty and menopause, oogenesis occurs on a monthly basis as part of the ovarian cycle. Explain how oogenesis occurs in the female. 27. What is an ovarian follicle? Where are they located and what do they contain? 28. The Ovarian cycle is concerned with what happens to the ovarian follicle each month. Complete the flow chart below for the Ovarian cycle and take notes on each step. Primordial follicles in egg nest Step 1: formation of primary follicles Primary follicles Step 2: formation of secondary follicles Step 3: formation of tertiary follicles Step 4: Ovulation Ovulation Step 5: formation and degeneration of corpus luteum Step 6: Corpus albicans 29. At puberty each ovary contains about 200,000 primordial follicles, about 500 of them are ovulated during a females life. What happens to the rest of them? 30. When the secondary oocyte is released during ovulation it leaves the ovaries and travels along the uterine tubes for 3-4 days. If the oocyte is to be fertilized it needs to happen between ______________ and _____________________? 31. If an oocyte is fertilized by a spermatozoon the result is a pre-embryo that will develop into an embryo and enventually a fetus. The Pre-embryo will leave the uterine tube and enter the Uterus. What does the uterus do? 32. The uterus has two main layers, the myometrium and the endometrium. What are these two layers made of and what is their function? Myometrium Endometrium 33. What is the uterine cycle and how long does it last? 34. The uterine cycle has three phases: (1) menses, (2) proliferative phase, and (3) secretory phase. How do these phases correspond to the phases of the ovarian cycle? 35. Read about and take notes on each stage of the uterine cycle. (1) menses (2) proliferative phase (3) secretory phase 36. What are menarche and menopause? 37. What are the three functions of the vagina? 38. The area containing the external genitalia of the female is called the vulva. Located in the vulva anterior to the opening of the vagina and urethra is a small organ called the clitoris. What is this organ? 39. Various glands discharge secretions into the vagina and vulva. Name them and the function of their secretions. 40. Read about the physiology of sexual intercourse and summarize the following Male Sexual Function: Female sexual function: 41. Both the male and female reproductive systems rely heavily on hormones. Both systems are regulated by hormones and movement from one phase to another is dependant on the level of specific hormones present in the body. Use the text and the chart on page 635 to summarize the hormones of the reproductive system. Hormone Effect in Males Effect in Females GnRH FSH LH Androgens Estrogens Progestins Inhibin