WEMS Standard Operating Procedures
advertisement

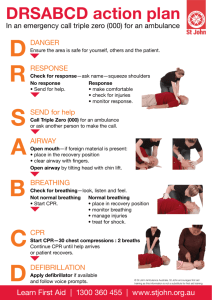
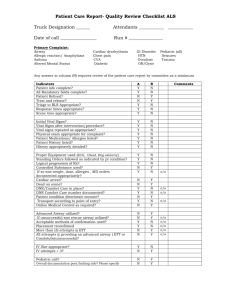
WEMS Standard Operating Procedures Standard Patient Assessment 1. Scene Size-Up and Body Substance Isolation Precautions 2. If Scene Unsafe Allow Public Safety to Correct and Control Hazard(s) 3. If Scene Safe Conduct Initial Assessment 4. Form a General Impression 5. Assess Mental Status 6. Assess Airway 7. Assess Breathing 8. Assess Circulation 9. Determine Priority for Treatment and Transport to the Hospital 10. Treat with Appropriate Interventions Patient Priority for Transport The following patients will be transported to Sturdy Memorial Hospital by Rescue immediately: 1. Unresponsive or altered mental status 2. Unstable vital signs 3. Any patient over 50 with chest pain 4. Major trauma (punctures, avulsions, amputations, chest injury) 5. Any patient with a suspected C-Spine injury 6. Obvious fractures or dislocations 7. Severe asthma complications 8. Cardiac /respiratory arrest 9. Obstructed airway 10. Seizure 11. Burn 12. Birth 13. Suspected stroke 14. GI bleed The following patients will be treated by WEMS and are eligible for transport to Sturdy Memorial Hospital by Rescue: 1. Minor trauma 2. Abdominal pain (unless signs of shock or internal injury) 3. Menstrual cramps 4. UTI 5. Minor asthma complications 6. Headache 7. General psychological problems unless clearly psychotic, suicidal, or homicidal 8. Nausea and vomiting The patient may sign a Refusal of Care Form and decline an ambulance for transport to Sturdy Memorial Hospital if: 1. The patient is of legal age or an emancipated minor 2. The patient is mentally competent and Awake and Oriented x 4 3. The patient is fully informed of the risk 4. The patient is willing 5. If there is any doubt regarding the above criteria, summon Norton FD for assistance WEMS - Approved Interventions for non-Norton FD calls Minor Trauma: 1. Assess Patient 2. If the wound is open (abrasion, laceration), clean and cover 3. Use direct pressure by applying a gauze bandage to the wound 4. Elevate the wound as long as there is no suspected musculoskeletal injury 5. Cover with appropriate gauze and/or bandage 6. If bleeding does not diminish, summon Norton FD Abdominal Pain: 1. Assess Patient 2. Obtain SAMPLE History and OPQRST 3. If female patient, determine birth control use and possible pregnancy (male EMT/Public Safety Officer can be asked to leave as long as a female Public Safety Officer, RA, AC, or student remains in the room with the female EMT) 4. Physically examine the abdomen for discoloration, distension, bloating, and protrusion 5. Monitor vital signs every 5 minutes 6. Encourage ER visit by ambulance or private transportation Minor Breathing Emergencies: 1. Assess Patient 2. Monitor breath sounds 3. Summon Norton FD if breathing <12 or >20 times/minute 4. Provide Oxygen at 15 LPM in a non-rebreather mask or through the bag-valve mask if patient cannot breath on his or her own 5. If Anaphylaxis, give one dose of Epinephrine auto-injector (provided EMT has undergone required in-service training) 6. Monitor vital signs every 5 minutes 7. Encourage ER visit by ambulance or private transportation Diabetic Emergencies: 1. Assess Patient - look for medical tags 2. Determine if patient is alert enough to swallow oral glucose 3. Administer oral glucose, if possible 4. Monitor vital signs every 5 minutes 5. Encourage ER visit by ambulance or private transportation Intoxication: 1. Assess Patient 2. If Patient is unconscious or has difficulty breathing, summon Norton FD 3. Ensure airway is clear and patient is breathing normally 4. Suction vomit and provide oxygen if necessary 5. If patient is conscious, determine L.O.C. 6. Monitor vital signs every 5 minutes 7. Patient must be Awake and Oriented x 4 to refuse transport by Norton FD 8. Monitor patient and establish history of intoxication to determine whether the patient’s condition is presently deteriorating or will likely in the future 9. Contact Public Safety for assistance in patient interventions