Data Analysis Practice Test for High School Students
advertisement

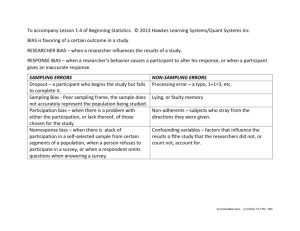
11. Data Analysis Practice Test For #1 to 4, select the correct answer. 1. Claire selects every tenth name from an alphabetical list of students in grade 9. Which sampling method is this? A convenience sample B random sample C stratified sample D systematic sample 2. A naturalist wants to count the population of a rare plant. He throws a peg into the area where they grow, and then uses where the peg landed as one corner of a 100 cm by 100 cm square. He will count the plants inside the square. Which sampling method is this? A convenience sample B random sample C systematic sample D voluntary response sample 3. Which of the following survey questions is biased? A Who is your favourite musician? B What movies have you watched in the past month? C What do you like about Smiley’s Toothpaste? D What brand of ice cream do you prefer? 4. For which situation would a survey of the population be most appropriate? A the kind of pizza your class will order for lunch B the number of drivers in western Canada who wear seat belts C the percent of junior high students who plan to attend college D the most popular brand of soft drink Complete the statements in #5 and 6. 5. Daniel plans to determine the average height of grade 9 male students in his school. He decides to record the height of every male grade 9 student. Daniel’s survey group represents the ______________________. 6. A city planner wanted to determine if a traffic light is necessary at a new intersection. He set up a camera and recorded the traffic flow from 7:30 a.m. to 8:30 a.m. Based on the results, he installed a traffic light. A factor that may have influenced the results is ______________________. Short Answer 7. A random sample shows that 0.05% of tennis balls are defective. How many are likely to be defective in a container of 1200 tennis balls? Include any assumptions in your prediction. 8. Sara plans to survey grade 9 students about where to hold the year-end party. For each description: • Identify the type of sample. • Identify any bias in each sample. a) Sara uses a computer program to generate names from a list of students. b) Sara surveys students who have lockers near her locker. c) Sara leaves ballots in the cafeteria for students to complete and then place in a drop box in the office. 9. For each survey question, identify any influencing factors. Then, reword the question so it is free of any influencing factors. a) Do you prefer to drink watered down 1% milk or creamy and smooth 2% milk? b) Is the loud, heavy beat of rap music damaging to the human body? Extended Response 10. A marketer wants to determine the music preferences of girls between the ages of 14 and 17 in Manitoba. a) Identify the population. b) Decide if she should survey the population or a sample. Give a reason. c) Describe two sampling methods she could use. d) Write a survey question that is free from bias. 11. The school canteen offers four flavours of frozen ice treats. The table shows sales of frozen ice treats for one week. Flavour Banana Cherry Grape Pear Monday 10 8 17 12 Tuesday 9 10 22 8 Wednesday Thursday 12 8 7 7 15 25 10 13 Friday 14 6 20 7 a) Predict the theoretical probability that someone will buy a grapeflavoured ice treat. b) List at least two assumptions you made. c) Based on sales, predict the probability that someone will buy a grapeflavoured ice treat. d) Which type of probability would you use to order frozen treats? Explain. e) The students plan to order 500 treats. About how many of each flavour of ice treat would you recommend they order? Show your work. 11. Data Analysis Practice Test Answers 1. D 2. B 3. C 4. A 5. Population 6. Timing 7. 60. Example: There is an assumption that the sample represents the actual production of tennis balls. 8. a) random sample; no bias b) convenience sample; Example: Not all students have an equal opportunity of participating. c) voluntary response sample; Example: Only students who are interested would vote. 9. a) Example: There is a bias toward 2% milk. Which type of milk do you prefer to drink—1% or 2%? b) Example: There is a bias against rap music. How does rap music affect the human body? 10. a) All girls between the ages of 14 and 17 in Manitoba b) Sample. Example: It would be too costly and time consuming to survey the population. c) Look for any two reasonable sampling methods and a description. Examples: • stratified sample: Divide girls registered in schools into groups by region. Then, randomly select 10% of the girls from each region. • systematic sample: Select every tenth girl from a list of all girls registered in schools. d) Example: Which is your favourite type of music? A Alternative B Country C Rap D Rock and Roll E Other ______ 11. a) 25% b) Examples: • The sales for one week represent the sales for all weeks. • Every flavour is equally popular. c) 99 240 × 100 = 41.25% d) Experimental probability is closer to actual student behaviour. e) Banana: 53 240 × 100 = 22.08%; 110; Cherry: Grape: 41.25%; 205; Pear: 50 240 38 240 × 100 = 15.83%; 80; × 100 = 20.83%; 105