CHEMISTRY FIRST SEMESTER FINAL REVIEW READ THE
advertisement

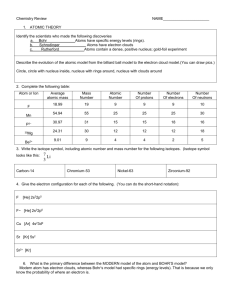
CHEMISTRY FIRST SEMESTER FINAL REVIEW READ THE FOLLOWING PARAGRAPH BEFORE YOU START! How to prepare: I would first order my notes, problem sets, labs, etc. by the dates on them or by chapter. Then I would look at the topic statement below (The capital letter phrases) for the first topic. Find this topic and all related information or materials in your possession and study them thoroughly! Rework old problems, think about application to daily life, etc. When you feel you have the topic well reviewed and understood THEN and ONLY THEN work the topic problems or questions on this sheet. If you don’t go them right, go back and spend more time reviewing your old materials. If you do get them right go on to the next topic and repeat the process. After you do all topics this way, start over! AS ALWAYS: You will be required to show work and units where needed! USE AND REPORT ANSWERS TO CORRECT SIGNIFICANT FIGURES IN ALL MATH PROBLEMS! SIGNIFICANT FIGURES, SCIENTIFIC NOTATION, AND SI UNITS 1. How many significant figures in: a. 1234 b. 123.0 c. 123400 d. 0.001234 e. 0.01230 2. Report the above a-e in correct scientific notation. 3. What are the common SI Units? Know the prefixes from milli to kilo and be able to convert between units in the metric system. 4. What is the difference between mass and weight? 5. Multiply: 5.98 mm x 3.2 mm = ? Add 3.258 + 12.0 = ? 6. Give an example of a qualitative observation 7. . Give an example of a quantitative observation. DENSITY Report answers with correct number of significant figures! 8. How many grams of mercury would you have if you had 32 cm3 of mercury? The density of mercury is 13.6 grams/cm3. 9. Bob has a piece of aluminum which has a mass of 10.8 grams and a volume of 4 cm3. Calculate the density of aluminum. EVIDENCE USED TO IMPLY A CHEMICAL REACTION OCCURRED. 10. Which of the following observations is evidence used to imply that a chemical reaction has occurred? a. gas evolution b. a precipitate forms c. the color changes d. the temperature changes e. the odor changes f. a sound is produced g. change in taste 11. What is the difference between a physical change and a chemical change? Identify each type of change. a. boiling water b. rusting iron c. burning candles d. breaking glass e. melting wax 12. Identify each as an element, compound or mixture. a. lead b. water c. kool-aid d. table salt e. soda f. oxygen 13. What are the characteristic of a metal, metalloid and non-metal? Identify each type of element: a. Zn b. As c. S d. Ne e. Na THE ATOM – Define the atomic number, mass number, average atomic mass and isotopes, # neutral atoms, ions, cations, anions. 14. Fill in the blanks for the following: 37 29 79Br 137Ba2+ Cl -1 Al 35 56 17 atomic number _____ _____ _____ _____ mass number _____ _____ _____ _____ # protons _____ _____ _____ _____ # neutrons _____ _____ _____ _____ # electrons _____ _____ _____ _____ type of ion? _____ _____ _____ _____ State whether each of the above is neutral or an ion. If it is an ion, state whether it is a cation or anion. Be sure you know the CHARGE LOCATION AND SIZE OF THE three SUBATOMIC PARTICLES!!! 15. Which of the following is an isotope of the element which has atomic number 28 and a mass number of 58? What can information can you tell from an isotope structure? 28Si 58Co 57Ni 142Ce 14 27 28 58 16. An element has 30 protons, 35 neutrons, and 30 electrons. What element is this? 17. An ion of an element has 29 protons, 35 neutrons, and 27 electrons. What ion is this? Write its symbol with the correct charge. 18. List the 5 parts to Dalton’s Atomic Theory. Which parts are held true today? 19. State the Law of Conservation of Mass (Matter). 20. How many particles are there in 1 mole of anything? What is the name for this number of particles? MOLAR MASS/ATOMIC WEIGHT Report in the correct units! 21. Determine the molar mass for: a. ZnS b. FeCl2 c. Co(NO 3)3 22. What is average atomic mass/atomic weight and how is it calculated? 23. How many moles are in 36 g of carbon dioxide? 24. What is the mass of 4.00 moles of ammonia (NH3) ? ELECTRON STRUCTURE, OUTER ELECTRONS, AND ELECTRON DOT STRUCTURE 25. What is the chemical family name for column: I, II, VII, and VIII? 26. Write the full electron configuration for: C, As, and S227. How many outer electrons does each of the following have? a. Na b. As c. Br d. O-2 28. Draw the electron dot structure for each of the following: a. C b. Sr c. Al d. N e. N -3 f. Na+ 29. How many electrons must each of the following lose or gain to achieve an octet? (State whether it loses or gains and how many) a. Cl b. Ca c. Ga d. Xe e. P 30. Which element has similar chemical properties like Si? Why? a. At b. Al c. N d. C 31. Draw the covalent bond structure for H2O and POBr, use dashes for bonding e- pairs and dots for nonbonding pairs. 32. When electrons absorb energy, what is the result? What color of light has the most energy per photon? What is the probability map for an electron called? Describe discrete vs. continuous energy levels. 33. What occurs when an electron moves from a higher energy level to a lower energy level in an atom? PERIODIC TABLE 34. What are the names of the familes in the following columns of the periodic table? What charge do all elements in that column form when they are ions? I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII, VIII 35. Write the complete electron structure for a neutral sodium atom. According to its electron structure, what row (period) of the periodic table should sodium be in? How many valence electrons does it have? What ion will sodium tend to form? 36. How many elements fill the second principal energy level as their highest energy level? 37. What is meant by a noble gas electron configuration? Why are they more stable? 38. Who is Dmitri Mendeleev? COUNTING ATOMS AND MOLECULES 39. Indicate the number of molecules, and the total number of each type of atom for each of the following: a. 4 H2O b. 2 Al2(SO4)3 MAKING FORMULAS FROM IONS 40. Use the following ions and write the correct formula for the compound made from them: a. Na+ and Brb. Mg2+ and I2+ -1 c. Ca and NO 3 d. Fe3+ and SO 4-2 41. Name the above compounds and the following: e. KOH f. CuF g. CuSO 4 42. Which compounds below are ionic? Which are molecular (covalently bonded/2 nonmetals)? a. Ar b. CaF2 c. NO 2 d. CuSO4 e. CCl4 43. Given SO42- and the compound Zr 2(SO 4)3 , what is the charge on Zirconium? 44. List the diatomic elements. 45. What is the difference between ionic compounds and molecular compounds? Identify each as ionic or molecular. a. NaI b. SO2 c. CCl4 d. CaCl2 46. Name each acid: a. HCl b H2SO 4 c. HNO 3 BONDING 47. Draw the electron dot structure for Li C F Ne 48. State the octet rule. 49. What type of bond (ionic, covalent) will form in the following compounds? Draw the bonding that occurs using arrows, dashes, and dots where appropriate. Are any polar covalent? CO2 NaCl F2 gas 50. List some diatomic molecules. 51. What is the big difference between ionic and covalent bonding? Be able to show Ionic and Covalent bonding on paper using dots, arrows, and dashes when necessary. 52. Use the electronegativity chart to identify each type of bonding: a. Cs – Cl b. H -O c. Br - I MISCELLANEOUS 53. 54. 55. 54. 56. What is the difference between accuarcy and precision? What is Avogadro’s number? What is the significance of it? Describe Dalton’s Atomic Theory. All types of electromagnetic radiation have the same _________. Describe the trends in the periodic table for: Across a period (row) Down a column (group) a. Atomic radius b. Ionization energy c. Electronegativity 57. Name the following common polyatomic ions: SO 42NO3-1 OH-1 FO4-1 ClO4-1 PO43- 58. Name the following common acids a. HCl b. HNO 3 c. H2SO 4 d. H3PO4 59. Most of the volume of the atom is taken up by the electron cloud. True or False? 60. Who originally constructed the Periodic Table? Dalton / Newton / Darwin / Mendeleev or Rutherford 61. The change of an atom from excited state down to ground state always involves an emission of some type of electromagnetic radiation. True or False? 62. All types of electromagnetic radiation have the same speed. True or False? 63. Identify the parts of an electromagnetic wave on a diagram, including wavelength, frequency, and amplitude. 64. Give an example of a binary compound.