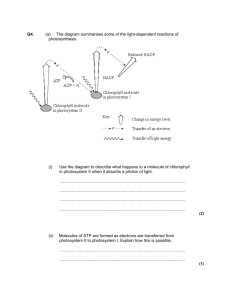
Light-dependent reaction Photosynthesis
advertisement

Monday COPY BAT: Explain what is meant by oxidation and reduction. Explain how ATP is made during the lightdependent reaction. Starter Write down what you can remember about oxidation and reduction reactions. Oxidation - this is when a substance combines with oxygen • The substance to which oxygen has been added is said to be oxidised • When one substance gains oxygen from another, the one losing the oxygen is said to be reduced. • This process is known as reduction. Another way of looking at it .... • When a substance is oxidised it loses electrons • When a substance is reduced it gains electrons • This is in fact the more usual way to define oxidation Oxidation and Reduction always take place together. • Oxidation results in energy being given out. • Reduction results in energy being taken in Write down the 3 ways that oxidation and reduction can be described - copy and complete table. electrons Oxidation Reduction hydrogen oxygen Gain of oxygen electrons hydrogen oxygen Oxidation Loss of electrons Loss of hydrogen Gain of oxygen Reduction Gain of electrons Gain of hydrogen Loss of oxygen For GCSE Chemistry you may have learnt OILRIG - Oxidation Is Loss (of electrons) Reduction Is Gain The Making of ATP • When a chlorophyll molecule absorbs light energy it boosts a pair of electrons in the chlorophyll molecule and raises them to a higher energy level • These electrons are said to be in an ‘excited’ state The electrons become so excited that they leave the chlorophyll molecule all together. • They are taken up by a molecule called an electron carrier. • The chlorophyll molecule has lost electrons so we say it has been __________. • The electron carrier has gained electrons so it has been __________. The electrons are now passed along a number of electron carriers in a series of oxidation-reduction reactions. • These electron carriers form a transfer chain located in the thylakoid membranes. • Each electron carrier is at a slightly lower energy level than the previous one and so the electrons lose energy at each stage. What is lost energy used for? • It is used to make ATP • It is used to combine an inorganic phosphate molecule Pi with a molecule of ADP. COPY BAT: Explain the role of photolysis in the lightdependent reaction. Describe how chloroplasts are adapted to carry out the light-dependent reaction Starter Explain what is meant by ‘photolysis’. The loss of electrons when light strikes a chlorophyll molecule leaves it short of electrons. • What would happen if these were not replaced? If the chlorophyll molecule is to continue absorbing light energy, these electrons must be replaced. • The replacement electrons are provided from the water molecules that are split using light energy. • This photolysis of water also produces hydrogen ions what is another name for a hydrogen ion? 2H2O > 4H + + 4e- + O2 water protons • The hydrogen ions or protons are taken up by an electron carrier called NADP • As the NADP has had hydrogen added to it we say it has become ____________ electrons oxygen The reduced NADP then enters the light INDEPENDENT reactions along with electrons from the chlorophyll molecules. • The reduced NADP (NADPH) is important because it is a further potential source of chemical energy to the plant. • What do you think happens to the oxygen byproduct from the photolysis of water? It is either used in respiration or diffuses out of the leaf as a waste product of photosynthesis. Label diagram ‘ Photosynthesis: light-dependent stage’ Now answer the following questions fully: • 1. Where precisely within a plant cell are the electron carriers involved in the light-dependent reaction found? • • 2. Describe what happens in the photolysis of water. 3. In each of the following, state whether the process involves oxidation or reduction of the molecule named: ..................................................................... a) An unsaturated fat molecule gains a hydrogen atom. b) Oxygen is lost from a carbon dioxide molecule c) Light causes an electron to leave a chlorophyll molecule. Where does the light-dependent reaction take place? • In the thylakoids of chloroplasts. How are chloroplasts adapted to their function? • 1. The thylakoid membranes provide a large surface area for the attachment of chlorophyll, electron carriers and enzymes that carry out the lightdependent reaction. • 2. A network of proteins in the grana hold the chlorophyll in a very precise manner that allows maximum absorption of light. • 3. The granal membranes have enzymes attached to them, which help manufacture ATP. 4. Chloroplasts contain both DNA and ribosomes - why is this useful? • So that they can quickly and easily manufacture some of the proteins needed for the lightdependent reaction What is lost energy used for? • It is used to make ATP • It is used to combine an inorganic phosphate molecule Pi with a molecule of ADP. Other useful Sources http://preuniversity.grkraj.org/html/7_PHOTOSYNTHESIS.htm http://www.ftexploring.com/photosyn/chloroplast.html http://youtu.be/C1_uez5WX1o - photosynthesis song http://youtu.be/mYbMPwmwx88 - photosynthesis http://www.biologymad.com/master.html?http://www.biologymad.com/A2Biology.htm photosynthesis and respiration http://www.biology.arizona.edu/biochemistry/problem_sets/photosynthesis_1/ photosynthesis_1.html - Photosynthesis questions. References Glenn Toole, Susan Toole (2008). A2 Biology. Cheltenham: Nelson