Nursing Flashcard - Infective Endocarditis - Af
advertisement

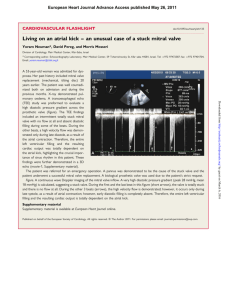
Nursing Flashcard – Infective Endocarditis background 1) Condition characterized by infection of the endothelium lining of the heart. The characteristic lesion is the vegetation. 2) Most patients have a pre-existing cardiac pathologic condition (prosthetic heart valve or patch, congenital heart disease mainly cyanotic or with left-to-right shunt) or are drug addicts (IV users endocarditis of the tricuspid valve). 3) Valve involvement: i) left sided : mitral > aortic ii) right sided: tricuspid > pulmonary etiology S. aureus, Strep. epidermidis, gram-negative bacilli, enterococci, Hemophilus influenzae symptoms 1) fever (low-grade or >100,4°F), chills, night swe ats 2) malaise, weakness, anorexia, weight loss, pallor 3) myalgia, arthralgia 4) progressive valve dysfunction heart failure 5) petechial hemorrhages in the retina (Roth’s spots) 6) tender subcutaneous nodes on finger and toes (Osler’s nodules) 7) symptoms due to organ infarction (cerebral, renal) or peripheral arteries occlusion diagnostic evaluation 1) echocardiography is the test of choice (identifies vegetations / abscesse) 2) lab: anemia, leukocytosis, blood cultures positive for micro-organisms, elevated ESR & CRP, proteinuria, microscopic hematuria complications 1) septic embolic phenomena (cerebral, coronary, peripheral, pulmonary, visceral) 2) perivalvular or myocardial abscess formation with evidence of new heart block 3) dehiscence of a prosthetic valve 4) heart failure (with acute or progressive valve dysfunction, or new valvular insufficiency) 5) uncontrolled sepsis 6) multi-system organ dysfunction treatment 1) antibiotic prophylaxis before dental, gastrointestinal, gynaecological, and urological procedures 2) medical therapy i) stabilize the patient before surgery ii) organism specific IV antibiotics 3) surgical i) excision of all infected native / prosthetic infected material ii) valve or prosthesis repair or replacement iii) extracardiac (splenic / vertebral / cerebral abscess and mycotic aneurysms)