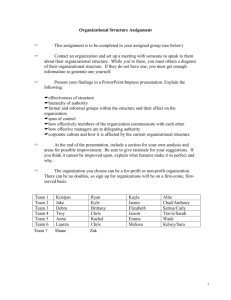
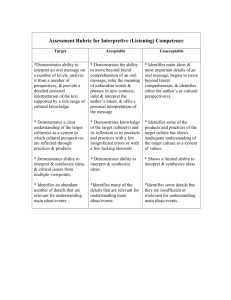
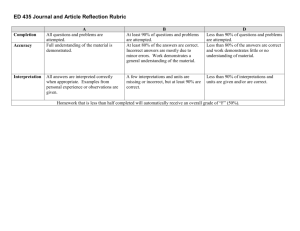
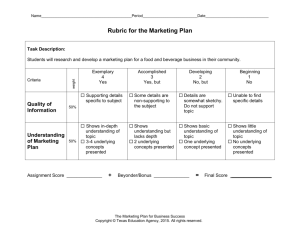
See the Eight Elements of Thought Rubric
advertisement

Critical Thinking Rubric developed by the PRISM Collaborative PRISM Experience, Meredith College, Raleigh NC 1 2/12/13 DRAFT Rubric for Critical Thinking Learning Outcomes Levels and Learning Outcomes Exemplary Apply skills of reason, critique and creative thought Competent/Proficient Developing Beginning See the Eight Elements of Thought Rubric Use & communicate critical thinking skills through reading, writing, & speaking (See * below) Clearly states thesis or purpose; develops ideas that are well organized, substantial, logical and concrete; explicitly identifies and states assumptions; integrates/considers multiple points of view; uses appropriate vocabulary and avoids stereotypical language; focuses content to topic at hand. Thesis is stated but may be unclear; ideas that are somewhat organized, substantial, logical and concrete; assumptions not always recognized or made explicit; considers multiple points of view but fails to integrate into argument; generally uses appropriate vocabulary and to a large extent avoids stereotypical language; generally focuses content to topic at hand. Thesis attempted but not clearly stated; ideas are somewhat organized but lacking detail and may be repetitive; loosely identifies assumptions; demonstrates beginning understanding of multiple points of view; uses somewhat appropriate vocabulary but may fall back on stereotypical language or clichés; incomplete attempt to focus content on topic at hand. Does not state thesis or purpose; ideas that are poorly organized, insubstantial, illogical and not concrete; does not identify or state assumptions; egocentric does not consider multiple points of view; uses inappropriate vocabulary and stereotypical language; content lacks focus and rambles. Integrate & evaluate knowledge from a variety of sources and disciplines Thoroughly analyzes & integrates sufficient, credible, relevant knowledge from a variety of sources and disciplines Knowledge is evaluated from multiple credible sources but without a thorough analysis or integration. Knowledge taken from sources without any interpretation/evaluation; relies on insufficient, irrelevant, or unreliable knowledge. Does not identify any supporting knowledge or evidence. Questions: Clearly defines issue or problem; accurately identifies the core issues; appreciates depth & breadth of problem Questions: Defines the issue; identifies the core issues, but may not fully explore their depth & breadth Questions: Defines the issue, but poorly (superficially, narrowly); may overlook some core issues Questions: Fails to clearly define the issue or problem; does not recognize the core issues Solutions: Solutions & consequences are logical and reflect student's informed evaluation and ability to place evidence & perspectives discussed in priority order. Solutions: Solutions consider logical consequences, but solutions lack informed evaluation. Solutions: Formulation of solutions considers consequences, but solutions are improbable, unclear, illogical, inconsistent, and/or superficial. Solutions: No viable solutions explored; formulation of solutions does not include consideration of consequences. Raise important questions & formulate solutions to complex problems Critical Thinking Rubric developed by the PRISM Collaborative PRISM Experience, Meredith College, Raleigh NC 2 2/12/13 Levels and Learning Outcomes Exemplary Competent/Proficient Develop intellectual curiosity by thinking independently and being active in the learning process Fully engaged in the learning process; achieves depth of understanding by exploring a topic prompted through one's own initiative; depth & breadth of understanding is achieved by evaluation of knowledge and taking the next step to draw logical, well-developed conclusions. Active in the learning process; takes initiative to explore a topic with minimal prompts from others; demonstrates the ability to focus on pertinent knowledge anddraws thoughtful conclusions. Somewhat active in the learning process; takes some initiative to explore a topic with specific prompts from others; somewhat able to evaluate knowledge and draw conclusions. Is inactive or gives minimal effort in the learning process; fails to take initiative to explore knowledge beyond what is required or prompted by others. Practice metacognition by analyzing, assessing and reconstructing their ways of thinking Demonstrates clear understanding of one’s own thinking process (metacognition) and gives more than one example of own assessment, analysis and reconstruction/ improvement of own thinking process. Demonstrates and gives at least one example of one’s own assessment, analysis and reconstruction/improvement of own thinking process (metacognition). Somewhat recognizes and acknowledges one’s own thinking process, assumptions, biases and views. Demonstrates limited ability to assess own thinking process in order to analyze or reconstruct/improve thinking. Does not recognize or minimally acknowledges one's own thinking. Fails to identify own assumptions, views, and biases. Not able to assess own thinking process in order to analyze or reconstruct/improve thinking. Exercise openmindedness to new ideas or ways of thinking Synthesizes and integrates alternate points of view into their problem solving; expresses comfort with uncertainty; demonstrates an ability to debate pros and cons of alternate arguments. Recognizes the value of multiple points of view and explores diverse ideas, but does not synthesize or incorporate alternate points of view into problem solving process; willing to accept that not all information is known and able to accept uncertainty. Acknowledges the existence of alternate points of view and the difference from own ideas, but sees them in a dualistic manner (right or wrong); attributes truth to people of authority and attempts to please others through the expression of own ideas. Only able to state own perspective; doesn't recognize the existence of other points of view. Developing *NOTE: In developing these criteria, we emphasized writing and speaking rather than reading. Beginning 4/12/13 Eight Elements of Thought Rubric Purpose: What is the purpose in what I am trying to achieve or make happen? Key Questions, Problem or Issue: What question am I trying to answer or asking students to grapple with? Information: What information is needed to contend with this question, issue or problem? Advanced Central purpose is identified, clearly stated, realistic and achievable. Key questions/problem/issue identified and clearly stated. Recognizes and explores complexities (multiple perspectives/possible solutions). Information gathered is sufficient to address the key question/problem/ issue. Information is carefully evaluated and relevant. Concepts: What are the central concepts at the heart of my program that are part of disciplinary thinking? Assumptions: What am I taking for granted? What are the assumptions shaping my thinking? Key concepts are identified and explained. Identifies and uses a theoretical framework in the discipline to guide reasoning. Clearly identifies assumptions and biases used in making judgments. Adequately justifies assumptions made. Interpretations, Inferences: What inferences or judgments are at play? What are my conclusions? Provides reasonable and substantive justification of how conclusions were reached. Considers multiple possible interpretations/solutions. Points of View: What are the points of view I need to consider when thinking through this problem? Evaluates and qualitatively compares alternative points of view in generating potential solutions. Implications, Consequences: What are implications of this thinking? What are the consequences of the resulting behavior? Clearly articulates both positive and negative implications and possible consequences of potential solutions and/or actions. *Please use this as a template and modify to suit your needs. Intermediate Some elements of purpose are identified and stated, but lacks detail, clarity, realism and/or ability to be fully achieved. Key questions/problem/issue either partially identified and/or complexities not fully explored. Has some pieces, but not all information needed to address the key question/problem/issue. Some information may not be accurate or relevant. Key concepts partially identified and explained, but some elements are missing. Limited use of a theoretical framework. Partially identifies assumptions and biases used to make judgments. Does not adequately justify assumptions made. Offers explanation of how conclusions were reached, but not a reasonable and/or substantive justification. Considers some possible alternative interpretations/ solutions. Considers some alternative points of view in generating possible solutions. Inadequate evaluation and comparison of solutions from different viewpoints. Partially identifies positive and negative implications and consequences of potential solutions and/or actions. Beginner Central purpose is vague, unrealistic and/or not achievable. Limited or mistaken identification of key questions/problem/issue, and complexities not considered (black and white thinking). Uses limited information. Information is not always relevant or accurate. Key concepts not well identified or explained. Theoretical framework not considered. Limited attempt to identify and justify biases and assumptions made. Offers little explanation of how conclusions were reached. Only considers one interpretation of information. Limited consideration of alternative points of view in considering possible solutions. Tends towards dichotomous thinking (only one possible solution, right/wrong). Minimal identification of positive and negative implications and consequences of potential solutions and/or actions.