Lecture #10 Further regulation of the lac operon.
advertisement

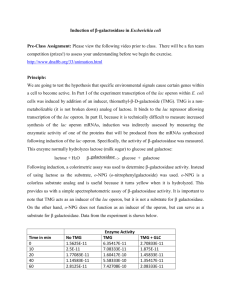
BIOLOGY 207 - Dr. McDermid Lecture #10 Further regulation of the lac operon. Readings for lectures #4 and #5: Griffiths et al, 7th Edition: Ch. 11 pp 335-344 Ch 7 pp210-219 (skim only, beginning and end) Problems for lectures #4 and #5: Griffiths et al, 7th Edition: Ch. 11 Tier 1: #1,2,3,4,8 Tier 2: #9,14,15 Concepts: How is the lac operon regulated? (continued) 1. The Oc mutations in the lac operon define a cis-acting locus 2. The lac operon is also under positive control and is affected by the level of glucose. trans-acting locus cis-acting locus - a genetic region affecting the activity of genes on that same DNA molecule Operator mutants OC mutants Figure 11-8, Table 11-1 Jacob and Monod proposed the "operator element" in the lac operon. How were these mutants obtained? This led to the recovery of OC - operator constitutive mutants. O C mutants - constitutively expressed - no inducer - Lecture #5 Page 1 - with inducer - Genetic mapping positioned the OC mutants to between I locus and Z locus. O C is dominant in the cis position cis dominance - the ability of locus to influence the expression of one or more adjacent loci on the same chromosome, as occurs in lac operator mutants of E.coli Summary of Negative control Lecture #5 Page 2 Repressor protein - Inducer - Positive control Catabolite Repression of the lac Operon: E.coli has the adaptive response that it will utilize glucose before lactose Unknown Catabolic breakdown product of glucose acts to prevent expression of the lac operon even if lactose is present. Glucose levels affect this system Figure 11-11 1- High glucose level 2- Low glucose level Requires cAMP to form a complex with a protein called CAP (crp gene) Mechanism CAP + cAMP form a complex ‡ activate the expression of the lac operon when bound to the CAP binding site Lecture #5 Page 3 Mutations in crp gene lead to a non-functional CAP protein ‡ no lac expression in either the presence or absence of the inducer. Summarized in Figure 11-12 3 situations 1) + glucose - lactose ‡ 2) + glucose + lactose ‡ 3) - glucose + lactose ‡ - CAP-cAMP system is positive control Result: Lac transcription occurs only when needed and useful Comparison of Positive and Negative Control Figure 11-13 ______________________________________________________________________________________________ Lecture notes: Copyright © 2002 Heather McDermid and the Department of Biological Sciences, University of Alberta Images are Copyright©2000 by W.H. Freeman & Co. in Griffiths et al, Introduction to Genetic Analysis Lecture #5 Page 4