Lecture#6 - Further regulation of the lac operon
advertisement

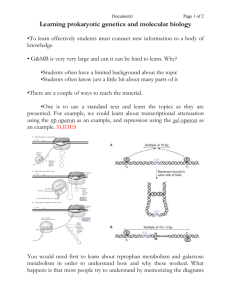
2/17/16 BIOLOGY 207 - Dr. Locke Lecture#6 - Further regulation of the lac operon Required readings and problems: Reading: Open Genetics, Chapter 12 Problems: Chapter 12 Optional Griffiths (2008) 9th Ed. Readings: pp 364-367 Problems: 9th Ed. Ch. 6: 1-7, 25, 28, 50 Campbell (2008) 8th Ed. Readings: Concept 18.1 Concepts: How is the lac operon regulated? (continued) 1. Negative regulation of the lac operon is described using genetics involving the Ffactor (a genetic tool). 2. The lac I mutations define a trans-acting locus. 3. The Oc mutations in the lac operon define a cis-acting locus. 4. The lac operon has both positive and negative regulation. Animations: http://bcs.whfreeman.com/iga9e/default.asp Biol207 Dr. Locke section Lecture#6 Fall'11 page 1 2/17/16 The next step in lac operon genetics needs a brief explanation of "heterozygous diploid strains" F-factor / Fertility factor (pp 195-6, Griffiths 9th) F factor is an E. coli episome - capable of being either either a free plasmid or integrated into bacterial chromosome + If F factor is present, then the strain is an F strain (bacterial sex) The F factor can contain some E. coli genes, therefore making the cell a partial diploid. (merozygote) - can be transferred from one cell to another mutant - lac host with F factor containing a lac + - + = lac / F lac + Advantage: We can: - -> examine lac mutants in partial diploid strains with other lac mutations -> analyze of the mechanisms of regulation using a diploid (partial) state. Biol207 Dr. Locke section Lecture#6 Fall'11 page 2 2/17/16 “Complementation tests” are possible Determine if mutations are cis or trans acting. cis = trans = trans-acting locus A gene able to affect the activity of other genes on a different DNA molecule usually through a diffusible product (e.g. polypeptide/protein) Example: the I locus affecting lac expression in E.coli. Biol207 Dr. Locke section Lecture#6 Fall'11 page 3 2/17/16 I+ is dominant over I- (acts in trans position) Fig strain: I+Z-Y+/F I-Z+Y- Z inducible; Y is inducible I+ is a wild type repressor, which binds to both lac gene operators and makes them inducible I- is a mutation that affects the DNA binding region and therefore there is no repressor binding and thus transcription occurs even without an inducer. IS is dominant to both I+ and I- in trans Fig Strain S + + I Z Y is un-inducible. IS mutant gene product can't bind inducer (mutation in the inducer binding region) so that the repressor remains bound to operator even in the presence of inducer. Repressor protein: Biol207 Dr. Locke section Lecture#6 Fall'11 page 4 2/17/16 I gene repressor product –> two functional domains - Mutate each independently I+ Normal I- mutation DNA Inducer IS mutation DNA DNA Inducer Inducer Summary of I mutant classes: - Dominant in trans therefore it is a diffusible product - the I gene encodes a repressor with two independent domains. Biol207 Dr. Locke section Lecture#6 Fall'11 page 5 2/17/16 Operator mutants - OC mutants - Fig cis-acting locus - a genetic region affecting the activity of genes on that same DNA molecule - Such a locus usually does not code for a protein but instead acts as a binding site for trans-acting proteins. Jacob and Monod proposed the "operator element" in the lac operon. - If mutated this operator element should be dominant in cis, in that it only affects the genes on the same chromosome (directly adjacent to it). - It will not be dominant in trans. How were these mutants obtained? J & M selected for mutants that constitutively expressed lac in cells with two I+ genes. (2 I+ genes prevents the recovery of I- constitutive mutants). This led to the recovery of OC - operator constitutive mutants. Genetic mapping - positioned the OC mutants to between I locus and Z locus. Biol207 Dr. Locke section Lecture#6 Fall'11 page 6 2/17/16 OC is dominant in the cis position Fig - no diffusible product. cis dominant - the ability of locus to influence the expression of one or more adjacent loci on the same chromosome, as occurs in lac operator mutants of E.coli Level of constitutive expression of Operator mutations: OC mutants may not be maximally expressed, but are still constitutively expressed - no inducer - 10-20% of max - with inducer - 100% of max Note: extent of mutation affects the level of expression Fig Biol207 Dr. Locke section Lecture#6 Fall'11 page 7 2/17/16 Summary of "negative" control aspect of the Lac operon Negative control: Repressor protein acts to prevent transcription Inducer binds to repressor to alter conformation so it no longer binds to the operator sequence and transcription can take place. Prokaryotic gene expression summary: Fig Activation - inducer promotes transcription Repression – inducer lifts inhibition of transcription Biol207 Dr. Locke section Lecture#6 Fall'11 page 8