Practice B
advertisement

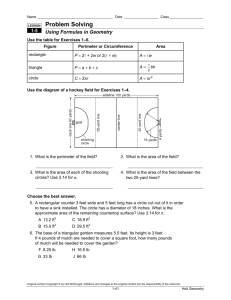
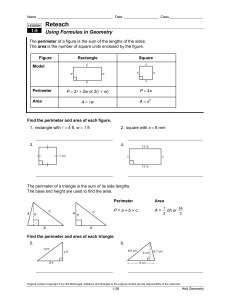
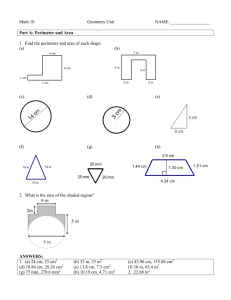
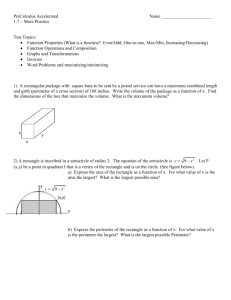
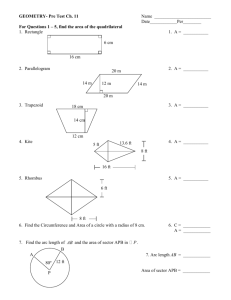
Name ________________________________________ Date __________________ Class__________________ LESSON 1-5 Practice B Using Formulas in Geometry Use the figures for Exercises 1–3. 1. Find the perimeter of triangle A. _______________ 2. Find the area of triangle A. _______________ 3. Triangle A is identical to triangle B. Find the height h of triangle B. _______________ Find the perimeter and area of each shape. 5. rectangle with length (x + 3) and width 7 4. square with a side 2.4 m in length _________________________________________ ________________________________________ 6. Although a circle does not have sides, it does have a perimeter. What is the term for the perimeter of a circle? _______________ Find the circumference and area of each circle. 7. 8. ________________________ 10. The area of a square is 9. _________________________ ________________________ 1 2 in . Find the perimeter. _______________ 4 11. The area of a triangle is 152 m2, and the height is 16 m. Find the base. _______________ 12. The circumference of a circle is 25π mm. Find the radius. _______________ Use the figure for Exercises 13 and 14. Lucas has a 39-foot-long rope. He uses all the rope to outline this T-shape in his backyard. All the angles in the figure are right angles. 13. Find x. _______________ 14. Find the area enclosed by the rope. _______________ Original content Copyright © by Holt McDougal. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. 1-36 Holt Geometry 4. The measures of the vertical angles are equal. 5. Sample answer: ∠ABM, ∠MBK, and ∠KBC 5. If m∠X + m∠Y = 90° and m∠Z + m∠Y = 90°, then m∠X and m∠Z are both equal to 90° − m∠Y. So m∠X = m∠Z. Two angles whose measures are equal are congruent. 6. C 7. G 8. A Reading Strategies 1. complementary 6. Possible answer: ∠ADB and ∠ADC 2. vertical 3. supplementary 7. 4. linear or supplementary 5. adjacent 6. complementary LESSON 1-5 8. 60° 9. 45° Practice A 10. 72° Reteach 1. adjacent and form a linear pair 1. side lengths 2. P = 2A + 2w 3. area 4. A = 1 bh 2 2. only adjacent 3. not adjacent 5. 30 yd 6. 54 yd2 4. only adjacent 5. not adjacent 7. 24 cm 8. 24 cm2 6. adjacent and form a linear pair 9. diameter 7. Possible answers: ∠1 and ∠6, ∠2 and ∠5 11. twice 8. Possible answers: ∠1 and ∠2; ∠1 and ∠5; ∠5 and ∠6; ∠6 and ∠2 12. 9. ∠3 10. center 10. complementary 11. neither 12. 34° 13. 124° 14. 68° 15. 158° 16. m∠LMN = 56°; m∠UVW = 34° 13. A = πr 2 Challenge 15. C = 2πr or C = πd 1. 52°14′24″ 2. 5°12′ 3. 27°37′30″ 4. 64°48′ 14. around Practice B 2. 6 ft2 1. 12 ft 5. Sample answer: ∠KLM and ∠MLN 2 ft 5 6. Sample answer: ∠KLH and ∠MLN 3. 2.4 ft or 2 7. 180 − (3x + 2)° or (178 − 3x)° 4. P = 9.6 m; A = 5.76 m2 8. Sample answer: ∠HCK and ∠RCQ 5. P = 2x + 20; A = 7x + 21 6. circumference Problem Solving 7. C ≈ 44 mi; A ≈ 154 mi2 1. Sample answer: ∠ALB and ∠BLC 8. C ≈ 9.42 cm; A ≈ 7.065 cm2 2. Sample answer: ∠AML and ∠YML 9. C ≈ 2π(x + 1); A ≈ π(x2 + 2x + 1) 3. 45°; they are vertical angles. 10. 2 in. 4. 45°; the angles are supplementary. 11. 19 m Original content Copyright © by Holt McDougal. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. A5 Holt Geometry 12. 12.5 mm 14. 42 ft 13. 7.5 ft Reading Strategies 2 1. Answers will vary. Students should indicate that the perimeter of the square is the sum of the lengths of the sides. Practice C 1. 4 units 2. 2 units 2. Answers will vary. Students should point out that the perimeter of any object is the sum of the lengths of all the sides. 3. Area is measured in square units, and perimeter is measured in linear units. 3. Area = length × width or Area = length of one side × 4 4. A = 121 ft2; A = 11 ft; w = 11 ft 5. For a given perimeter, a rectangle with sides of equal length (a square) encloses the maximum area. 6. about 154 ft2 4. Area = length × width; Area = 2 × 2; Area = 4 square units 7. about 33 ft2 LESSON 1-6 8. If a rectangle and a circle have the same perimeter, then the circle has the greater area. 9. 197.5 in2 Practice A 10. a = 8 Reteach 1. 10 ft; 4 ft2 2 2. 32 mm; 64 mm 1. x-axis; y-axis 2. coordinates ⎛ 1 ⎞ 3. ⎜ 1 , 0 ⎟ ⎝ 2 ⎠ 4. (0, −1) ⎛ 1 ⎞ 5. ⎜ 1 , − 1⎟ ⎝ 2 ⎠ 6. 7. (−2, 4) 8. (−1, −3) 9. 3 miles 10. 4 miles 3. 28 cm; 49 cm2 4. (24 + 2x) in.; 12x in2 5. (18 + y) ft; 4y ft2 6. 24.2 cm; 27 cm2 7. 69.1 in.; 380.1 in2 8. 47.1 mm; 176.7 mm2 11. 1 mile 9. 56.5 in.; 254.5 in2 Practice B 10. 9.4 cm; 7.1 cm2 11. 81.7 m; 530.9 m2 2 12. 103.7 mm; 855.3 mm Challenge 1. (3, −3) ⎛ x y −3⎞ 2. ⎜ , 2 ⎟⎠ ⎝2 3. (−4, −2) 4. 1. P = 11 cm; A = 8.25 cm2 5. 2. The perimeter will double. The area will be 4 times greater. 7. AB and BC 4. 249.6 m2 5. 11.2 cm2 6. 1.7 in2 7. 45.1 mm2 8. 6.4 units 10. 13.4 ft 11. 101.8 in. Practice C 1. Problem Solving 1. 320 yd 2. 6000 yd2 3. about 401.92 yd2 4. 3000 yd2 5. A 6. 4 2 units 26 units 9. 11.4 units 3. The area will be 9 times greater. k2A 26 units ( x1 − x2 ) ( 2 + ( y1 − y 2 ) = 2 ( x2 − x1 ) ) ( ) + ( y − 2y y 2 + ( y 2 − y1 ) since x12 − 2 x1x2 + x22 + y12 − 2y1y 2 + y 22 = 6. G ( x22 − 2 x1x2 + x12 2 2 1 2 + y12 ) 2 ) Original content Copyright © by Holt McDougal. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. A6 Holt Geometry